Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Lead III records electrical difference between the left leg and the left arm electrodes.Lead I records the difference in electrical potentials between the left arm and right arm. Lead II records it between the left leg and right arm.Another popular monitoring lead is the MCL1 lead (or modified V1). To connect this lead, the negative electrode is placed near the left shoulder, usually under the outer third of the left clavicle, and the positive electrode is placed to the right of the sternum in the fourth intercostal space.

Which lead shows the voltage difference between the right arm and left arm Lead I Lead II Lead III?
Lead I records the difference in electrical potentials between the left arm and right arm. Lead II records it between the left leg and right arm.
Which lead monitors an electrode at the 4th intercostal space on the left side of the sternum?
Another popular monitoring lead is the MCL1 lead (or modified V1). To connect this lead, the negative electrode is placed near the left shoulder, usually under the outer third of the left clavicle, and the positive electrode is placed to the right of the sternum in the fourth intercostal space.
Unit-1 ECG
Images related to the topicUnit-1 ECG

Which of these items are placed on the patients limbs and chest in an ECG to detect impulses?
Electrodes (small, plastic patches that stick to the skin) are placed at certain spots on the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are connected to an ECG machine by lead wires. The electrical activity of the heart is then measured, interpreted, and printed out. No electricity is sent into the body.
What does a 3 lead ECG show?
3-lead ECGs are used most often for recording a 24-hour reading. A 24-hour reading is a frequently used tool for the diagnosis of heart problems and is reimbursed as a long-term reading.
What is Lead II in ECG?
ECG Leads I, II and III (Willem Einthoven’s original leads)
Lead II compares the left leg with the right arm, with the leg electrode being the exploring electrode. Therefore, lead II observes the heart from an angle of 60°.
Why is lead II used in ECG?
By setting the ECG monitor to Lead II, we are essentially viewing the impulse as it travels from the right atria toward the left ventricle; hence, Lead II is the “best seat in the house” for viewing the wavefront.
Which lead is created between the left arm and left leg?
Lead III is the potential difference between the left arm and leg; there is a positive ECG deflection when the impulse direction is toward the leg.
See some more details on the topic Which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg? here:
ECG Leads | Clinical Gate
The LA electrode detects the electrical voltages of the heart that are transmitted to the left arm. The RA electrode detects the voltages …
Conquering the ECG – Cardiology Explained – NCBI Bookshelf
Three bipolar leads and three unipolar leads are obtained from three electrodes attached to the left arm, the right arm, and the left leg, respectively. (An …
Electrocardiographic Lead – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
where aVR stands for the augmented voltage for the right arm. In an ideal field where the heart sits at the center of an equilateral triangle, the average of …
The ECG leads: electrodes, limb leads, chest (precordial …
Lead II compares the left leg with the right arm, with the leg electrode being the exploring electrode. Therefore, lead II observes the heart from an angle of …
What are the different ECG leads?
Parts of an ECG
The six limb leads are called lead I, II, III, aVL, aVR and aVF. The letter “a” stands for “augmented,” as these leads are calculated as a combination of leads I, II and III. The six precordial leads are called leads V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 and V6.
Where is V5 lead placed?
| ELECTRODE | PLACEMENT |
|---|---|
| V2 | 4th Intercostal space to the left of the sternum |
| V3 | Midway between V2 and V4 |
| V4 | 5th Intercostal space at the midclavicular line |
| V5 | Anterior axillary line at the same level as V4 |
Which leads are limb leads?
Limb leads are made up of 4 leads placed on the extremities: left and right wrist; left and right ankle. The lead connected to the right ankle is a neutral lead, like you would find in an electric plug. It is there to complete an electrical circuit and plays no role in the ECG itself.
Where do you place ECG leads?
| Electrode | Placement Area |
|---|---|
| V1 | Fourth intercostal space to the right of the sternum. |
| V2 | Fourth intercostal space to the left of the sternum. |
| V3 | Directly between leads V2 and V4. |
| V4 | Fifth intercostal space at midclavicular line. |
How do you use ECG leads?
- Prepare the skin. …
- Find and mark the placements for the electrodes:
- First, identify V1 and V2. …
- Next, find and mark V3 – V6. …
- Apply electrodes to the chest at V1 – V6. …
- Connect wires from V1 to V6 to the recording device. …
- Apply limb leads.
12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation
Images related to the topic12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation
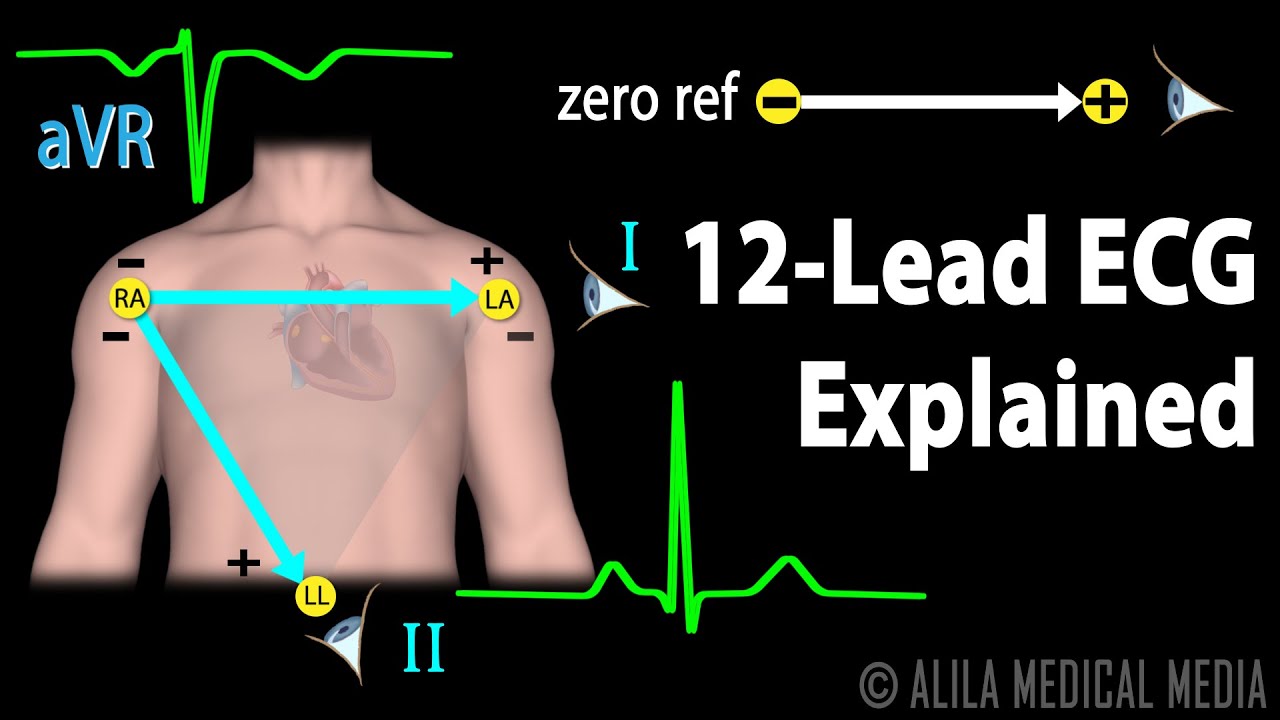
What is a lead 1 ECG?
Introduction. Although 1-lead ECG (EKG) recorders are normally used primarily for basic heart monitoring, checking for various arrhythmias, or simple educational or research purposes, they can also be used for looking at the effects of exercise on the ECG.
Where is V6 lead placed?
Placement of Lead V6
V6 therefore is placed in the 5th intercostal space, mid axillary line.
What is a 5 lead ECG used for?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive method of monitoring the electrophysiology of the heart. Electrodes are placed on the patient’s torso, and the electrical activity of the heart is measured from several leads (voltage difference between electrodes).
Which lead is aVF?
AVf is on the left ankle or left lower abdomen and looks at the bottom, or inferior wall, of the heart. Lead lll travels from AVL towards AVf to become a 3rd inferior lead.
What does V1 V2 V3 mean in ECG?
The areas represented on the ECG are summarized below: V1, V2 = RV. V3, V4 = septum. V5, V6 = L side of the heart. Lead I = L side of the heart.
What does the V1 lead measure?
The precordial, or chest leads, (V1,V2,V3,V4,V5 and V6) ‘observe’ the depolarization wave in the frontal plane. Example: V1 is close to the right ventricle and the right atrium. Signals in these areas of the heart have the largest signal in this lead. V6 is the closest to the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
Why is lead II the best?
The most commonly used lead is lead II – a bipolar lead with electrodes on the right arm and left leg. This is the most useful lead for detecting cardiac arrhythmias as it lies close to the cardiac axis (the overall direction of electrical movement) and allows the best view of P and R waves.
Why is lead aVR used?
Possible mechanisms of ST segment elevation in lead aVR
Thus, the purpose of lead aVR was to obtain specific information from the right upper side of the heart, such as the outflow tract of the right ventricle and the basal part of the septum.
Why is lead II positive?
A maximal positive deflection is recorded in lead II when the depolarization wave travels parallel to the axis between the right arm and left leg. Similarly, a maximal positive deflection is obtained in lead III when the depolarization wave travels parallel to the axis between the left arm and left leg.
Which type of leads are aVR aVL and aVF?
These nine wires are known as “unipolar leads“. The three active peripheral leads are AVr, AVL, and AVf. These 3 leads create a triangle with the heart in the middle, as below.
ECG | Electrocardiogram | In English | Physiology | MBBS | Medicine | EKG | Part 1 @Doctors Corner
Images related to the topicECG | Electrocardiogram | In English | Physiology | MBBS | Medicine | EKG | Part 1 @Doctors Corner

What is aVR aVL aVF in ECG?
Keywords: aVR, unipolar limb lead, aVR sign. The conventional ECG has 12 leads. Each lead records electrical activity of the heart from different perspective. Therefore, it correlates to different anatomical areas of the heart. aVR, aVL, and aVF are augmented unipolar leads in the frontal plane, after their inventor Dr …
What are the augmented leads?
The three augmented leads are designated aVR, aVL, and aVF. An impulse directed toward a limb lead records a positive or upright deflection in that lead.
Related searches to Which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg?
- which lead monitors an electrode at the 5th intercostal space on the left mid-clavicular line?
- which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg quizlet
- which part of an ecg machine moves against the tracing paper to record the waves of the ecg cycle
- how many leads are in a standard ecg
- how did augmented leads get their name?
- which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg? quizlet
- which lead monitors an electrode at the 5th intercostal space on the left mid clavicular line
- how many leads are in a standard ecg?
- which lead monitors an electrode midway between the v2 and v4 positions
- which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg
- which lead monitors an electrode midway between the v2 and v4 positions?
- how did augmented leads get their name
- which of the following is not true of ecgs?
- which of these tissues is known as the bodys natural pacemaker
- which of the following is not true of ecgs
Information related to the topic Which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg?
Here are the search results of the thread Which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which lead shows the voltage difference between the left arm and left leg?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.