Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is estrogen receptor dimerization?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Abstract. Estrogen receptor (ER) dimerization is prerequisite for its activation of target gene transcription. Because the two forms of ER, ERα and ERβ, exhibit opposing functions in cell proliferation, the ability of ligands to induce ERα/β heterodimers vs.Receptor dimerization is essential for stimulation of the intrinsic catalytic activity and for the autophosphorylation of growth factor receptors. Moreover, receptor PTKs are able to undergo both homo- and heterodimerization.Once activated by estrogen, the ER is able to translocate into the nucleus and bind to DNA to regulate the activity of different genes (i.e. it is a DNA-binding transcription factor). However, it also has additional functions independent of DNA binding.

What is a receptor dimerization?
Receptor dimerization is essential for stimulation of the intrinsic catalytic activity and for the autophosphorylation of growth factor receptors. Moreover, receptor PTKs are able to undergo both homo- and heterodimerization.
What happens when estrogen receptors are activated?
Once activated by estrogen, the ER is able to translocate into the nucleus and bind to DNA to regulate the activity of different genes (i.e. it is a DNA-binding transcription factor). However, it also has additional functions independent of DNA binding.
ESTROGEN RECEPTOR FUNCTION the more complicated version 1
Images related to the topicESTROGEN RECEPTOR FUNCTION the more complicated version 1

What is the role of estrogen receptors?
ER is a transcription factor and a member of the nuclear receptor super family. ER regulates the transcription of hundreds of genes and ultimately leads to cell division, and has an important role in mammary gland development and the cell proliferation growth that occurs during pregnancy.
What happens when Estradiol binds to its receptor?
When estrogen enters the nucleus, it binds to the estrogen receptor, causing it to pair up and form a dimer. This dimer then binds to several dozen specific sites in the DNA, strategically placed next to the genes that need to be activated.
What is meant by dimerization?
: a compound formed by the union of two radicals or two molecules of a simpler compound specifically : a polymer formed from two molecules of a monomer. Other Words from dimer. dimeric \ (ˈ)dī-ˈmer-ik \ adjective. dimerization or British dimerisation \ ˌdī-mə-rə-ˈzā-shən \ noun.
What does dimerization mean in biology?
What is dimerization? It is a process where two molecules of similar chemical composition come together to form a single polymer known as a dimer.
How do you stimulate estrogen receptors?
- Phytoestrogen-Rich Foods. Phytoestrogens, found in plants and plant-based foods, have a similar structure to estradiol, which is the strongest of the estrogen hormones. …
- B Vitamins. …
- Vitamin D. …
- Chasteberry (also known as Vitex Agnus-Castus) …
- Boron. …
- Black Cohosh. …
- Evening Primrose Oil.
See some more details on the topic What is estrogen receptor dimerization? here:
Identification of Estrogen Receptor Dimer Selective Ligands …
Two phytoestrogens, angolensin and cosmosiin, were identified as ER dimer selective ligands. These molecules were validated using in vitro …
Estrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ): A Ligand Activated Tumor …
… a superfamily of nuclear receptors called steroid hormone receptors, which, upon binding ligand, dimerize and translocate to the nucleus …
What does estrogen receptor positive mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (ES-truh-jin reh-SEP-ter PAH-zih-tiv) Describes cells that have a protein that binds to the hormone estrogen. Cancer cells that are estrogen receptor positive may need estrogen to grow.
What diseases are caused by too much estrogen?
For example, elevated estrogen levels are a risk factor for breast cancer and ovarian cancer. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS) , estrogen dominance can also increase your risk of endometrial cancer. High levels of estrogen may put you at higher risk of blood clots and stroke.
What does estrogen receptor negative mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (ES-truh-jin reh-SEP-ter NEH-guh-tiv) Describes cells that do not have a protein that binds to the hormone estrogen. Cancer cells that are estrogen receptor negative do not need estrogen to grow.
How do you reduce estrogen receptors?
- avoiding environmental estrogens, such as parabens in personal care products.
- losing weight (or, more importantly, body fat)
- reducing your alcohol intake.
- adding cruciferous vegetables (like broccoli) to your diet.
Where are estrogen receptors in the body?
Central to these mechanisms is the protein to which estrogens bind, the estrogen receptor (ER). In the “classical” mechanism of estrogen action, estrogens diffuse into the cell and bind to the ER, which is located in the nucleus.
Steroid hormone receptors
Images related to the topicSteroid hormone receptors

Is estrogen hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
The highly hydrophobic nature of estrogens allows them to pass through cellular membranes by passive diffusion43 and also allows its concentration in cellular membranes. Cellular responses to estrogens are mediated by receptors that initiate a complex array of cellular events upon ligand binding.
What type of effect is caused downstream of estrogen binding to its receptor?
The binding of estrogen to the ER results in a series of downstream steps that modulate transcription of genes responsible for cellular function, tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and survival.
What would interfere with the binding of estrogen to the estrogen receptor?
What would interfere with the binding of estrogen to the estrogen receptor? A mutation in a G-protein prevents the alpha-subunit from dissociating from the beta/gamma-subunit.
What happens in dimerization?
Table of contents No headers A dimerization is an addition reaction in which two molecules of the same compound react with each other to give the adduct.
What causes dimerization?
Molecular dimers are often formed by the reaction of two identical compounds e.g.: 2A → A-A. In this example, monomer “A” is said to dimerise to give the dimer “A-A”.
What is dimerization physiology?
noun, plural: dimerizations. (1) The chemical reaction that joins two molecular subunits, resulting in the formation of a single dimer. (2) The process or act of forming a dimer. Supplement.
How do you determine dimerization?
You need to determine with what links the dimer is formed. If using a hydrophobic interaction then it is not a dimer. This is an associate. If using disulfide bonds, then it is a dimer.
How do proteins dimerize?
Although dimerization can involve covalent interactions such as those formed in the disulphide-bonded metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 [14], most GPCRs dimerize via noncovalent interactions between extracellular domains, transmembrane regions and/or C-terminal tails of the proteins [15].
What’s dimer in biology?
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word dimer has roots meaning “two parts”, di- + -mer.
What are the signs of low estrogen?
- Dry skin.
- Tender breasts.
- Weak or brittle bones.
- Trouble concentrating.
- Moodiness and irritability.
- Vaginal dryness or atrophy.
- Hot flashes and night sweats.
- Irregular periods or no periods (amenorrhea).
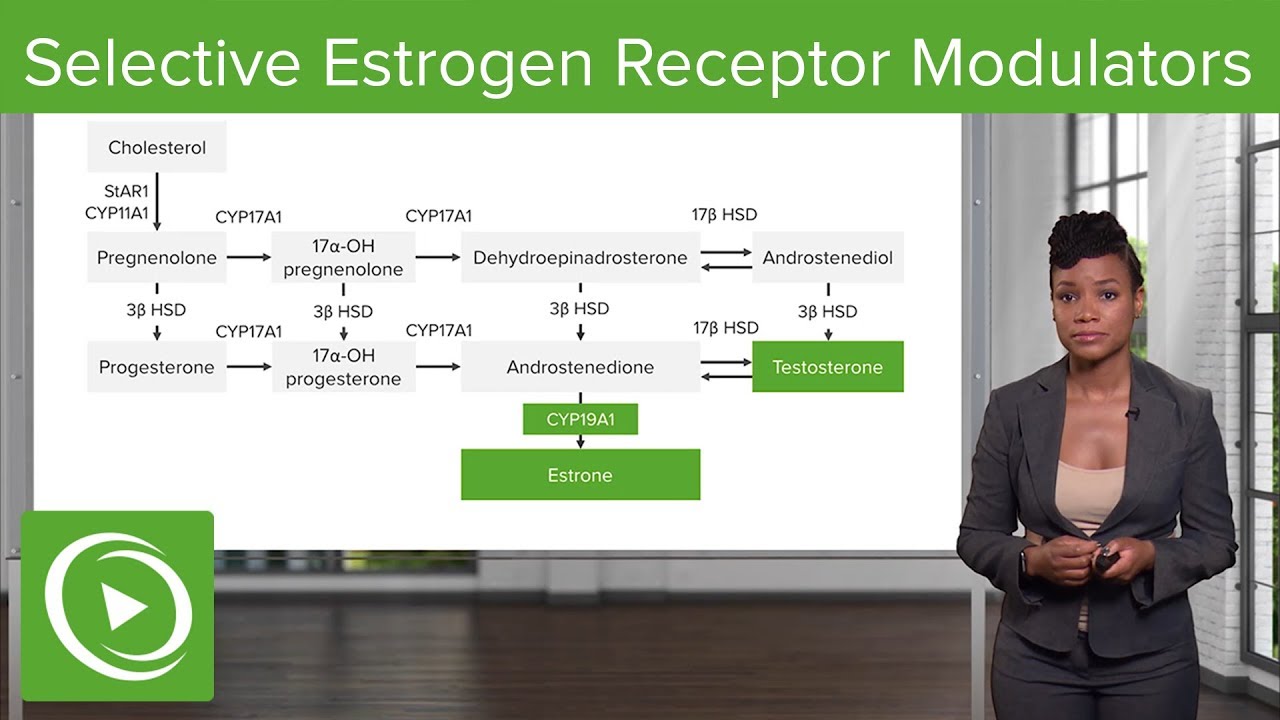
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators – Gynecology | Lecturio
Images related to the topicSelective Estrogen Receptor Modulators – Gynecology | Lecturio
Does vitamin D increase estrogen?
High blood levels of vitamin D linked to reduced estrogen – and potentially lower breast cancer risk. Can taking daily vitamin D supplements decrease sex-hormone levels and thereby potentially reduce the risk of breast cancer in older women?
How do I know if I have estrogen dominance?
Estrogen dominance can affect a woman’s body in many ways, including abnormal menstruation (heavy/painful periods), PMS, headaches, decreased sex drive, bloating, mood swings, fatigue, anxiety & depression, breast tenderness, endometriosis, fibroids, and hormonal weight gain.
Related searches to What is estrogen receptor dimerization?
- what is estrogen receptor dimerization of
- what is estrogen receptor dimerization inhibitor
- what is estrogen receptor dimerization definition
- what is estrogen receptor dimerization inhibition
Information related to the topic What is estrogen receptor dimerization?
Here are the search results of the thread What is estrogen receptor dimerization? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is estrogen receptor dimerization?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.