Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is folding and faulting 7?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Folds are bends in the rocks that are due to compressional forces. Faults are due to tensional forces along which displacements of rocks take pace. Folding occurs when compressional force is applied to rocks that are ductile or flexible.1. Folding occurs when the Earth’s rock layers become folded. Faulting occurs when the Earth’s crust gets cracked forming a fault. 2. It happens when two lithospheric plates collide with each other.(i) Folding: A bend in the rock strata resulting from. compression of an area of the earth’s crust. Faulting: Rocks are moved or displaced or linear cracks may appear. (ii) Folding: It results from convergent plate boundaries. Faulting: It results from divergent plate boundaries.
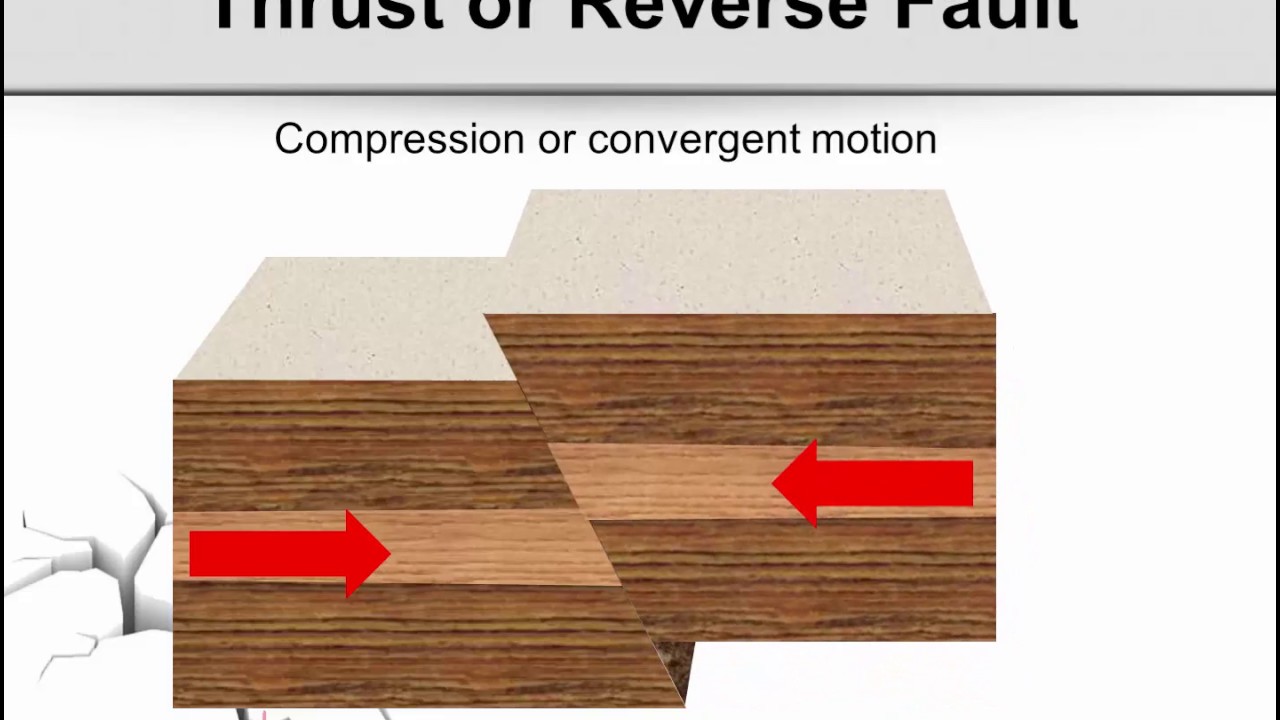
What is a folding and faulting?
1. Folding occurs when the Earth’s rock layers become folded. Faulting occurs when the Earth’s crust gets cracked forming a fault. 2. It happens when two lithospheric plates collide with each other.
What is folding and faulting Class 9?
(i) Folding: A bend in the rock strata resulting from. compression of an area of the earth’s crust. Faulting: Rocks are moved or displaced or linear cracks may appear. (ii) Folding: It results from convergent plate boundaries. Faulting: It results from divergent plate boundaries.
TMart Science Folding and Faulting
Images related to the topicTMart Science Folding and Faulting

What is faulting in geography class 6?
When the crustal rocks are subjected to horizontal compressional pressure, they develop fractures or cracks along the line of weakness. These lines of fracture are known as faults. In faulting, blocks of rocks may move up or down.
What is folding in geography?
Folding is a concept that embraces all geologic processes by which surfaces in rocks become curved during deformation. Since folds are permanent deformation structures with no or little loss of cohesion of the folded layer, folding refers to the essentially slow, ductile behaviour of relatively soft and/or hot rocks.
What is faulting in geography?
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake – or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers.
What do you mean fault?
Definition of fault
1a : weakness, failing especially : a moral weakness less serious than a vice He loves her despite her many faults. b : a physical or intellectual imperfection or impairment : defect a theory with some serious faults.
What is folding in geography class 6?
When two tectonic plates of the earth’s crust collide, they fold over each other and form mountains known as fold mountains. The Himalayas and the Alps, with their with rugged relief and high peaks, are the youngest fold mountains of the world.
See some more details on the topic What is folding and faulting 7? here:
Difference between folding and faulting – Flash Education
1. Folding occurs when the Earth’s rock layers become folded. Faulting occurs when the Earth’s crust gets cracked forming a fault. ; 2. It happens when two …
What is the difference between folding and faulting explain …
Folding occurs when the Earth’s rock layers become folded. Faulting occurs when the Earth’s crust gets cracked forming …
Differentiate between Folding and faulting – Geography
Folding, Faulting ; Folds are bends in the rocks that are due to compressional forces. Faults are formed due to tensional forces along which displacement of rock …
CHAPTER 10 (Folds, Faults and Rock Deformation)
1. Figure 10.6: Rocks that were originally deposited in horizontal layers can subsequently deform by tectonic forces into folds and faults. Folds constitute the …
What do you mean by folding?
1 : to lay one part over another part of fold a letter. 2 : to reduce the length or bulk of by doubling over fold a tent. 3 : to clasp together : entwine fold the hands. 4 : to clasp or enwrap closely : embrace.
What is difference between folds and faults?
Folds constitute the twists and bends in rocks. Faults are planes of detachment resulting when rocks on either side of the displacement slip past one another.
What is the difference between folds and faults Brainly?
Folds are formed when heat and pressure is applied to the rock. The higher the temperature, the more pliable rocks become. Folds are more likely to occur when the deformation caused by the compression is applied slowly. … Faults are defined as the displacement of rock that were once connected along a fault line.
What causes earthquakes?
Earthquakes are the result of sudden movement along faults within the Earth. The movement releases stored-up ‘elastic strain’ energy in the form of seismic waves, which propagate through the Earth and cause the ground surface to shake.
FOLDING FAULTING // detailed explanation of folding and faulting
Images related to the topicFOLDING FAULTING // detailed explanation of folding and faulting

What is folding in geography class 9th?
Folding: A fold is a bend in the rock strata resulting from compression of an area in the Earth’s crust. Folding occurs when the lithospheric plate pushes up against another plate. In folding, the land between the two tectonic plates, acting towards each other, rises up.
How are folds and faults formed?
When the Earth’s crust is pushed together via compression forces, it can experience geological processes called folding and faulting. Folding occurs when the Earth’s crust bends away from a flat surface. A bend upward results in an anticline and a bend downward results in a syncline.
How are faults formed?
A fault is formed in the Earth’s crust as a brittle response to stress. Generally, the movement of the tectonic plates provides the stress, and rocks at the surface break in response to this. Faults have no particular length scale.
What are tectonic plates 7?
The crust of the earth is completely made of rocks and hence it is called the lithosphere. The lithosphere is broken into several rocky plates which are called tectonic plates. They form the continents and the beds of the oceans. They are called continental and oceanic plates respectively.
What are faults types?
There are four types of faulting — normal, reverse, strike-slip, and oblique. A normal fault is one in which the rocks above the fault plane, or hanging wall, move down relative to the rocks below the fault plane, or footwall.
What is an example of faulting?
The San Andreas Fault is the world’s most famous; it splits California between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate and moved 20 feet (6 m) in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. These types of faults are common where land and ocean plates meet.
What is a fault earthquake?
Earthquakes occur on faults. A fault is a thin zone of crushed rock separating blocks of the earth’s crust. When an earthquake occurs on one of these faults, the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other. Faults can be centimeters to thousands of kilometers long.
What is sentence fault?
This is when the sentence lacks some essential element, usually the subject or verb. The most common sentence fragment occurs when the subject is a phrase which includes a verb, but there’s actually no main verb in the sentence.
What FORT means?
Definition of fort
1 : a strong or fortified place especially : a fortified place occupied only by troops and surrounded with such works as a ditch, rampart, and parapet : fortification. 2 : a permanent army post —often used in place names.
What is folding faulting and volcanic activity?
Folding –> The phenomenon where two tectonic plates of the earth converge is called folding. This causes a part of the earth to rise up. Faulting –> The tension and compression associated with the plate tectonics that causes rocks to break apart is called faulting.
Faulting
Images related to the topicFaulting
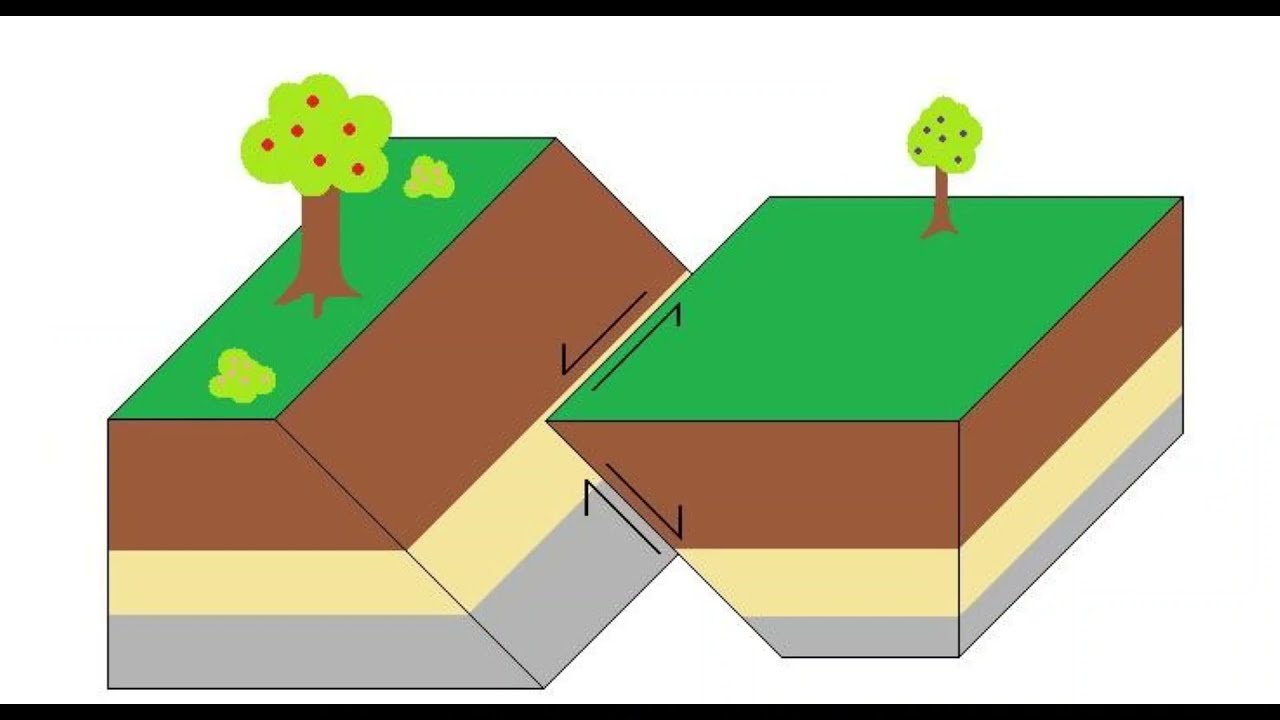
What is fold mountain 6th?
Fold mountains are created where two or more of Earth’s tectonic plates are pushed together. At these colliding, compressing boundaries, rocks and debris are warped and folded into rocky outcrops, hills, mountains, and entire mountain ranges. Fold mountains are often associated with continental crust.
What are folds and its types?
Types of Folds. Anticline: linear, strata normally dip away from axial center, oldest strata in center. Syncline: linear, strata normally dip toward axial center, youngest strata in center. Antiform: linear, strata dip away from axial center, age unknown, or inverted.
Related searches to What is folding and faulting 7?
- folding and faulting pdf
- what is folding in geography
- folding and faulting diagram
- what is faulting in geography
- types of folding and faulting
- differentiate folding and faulting
- what is folding and faulting 7 little words
- similarities of folding and faulting
- folding and faulting in geography
- when do folding and faulting occur
Information related to the topic What is folding and faulting 7?
Here are the search results of the thread What is folding and faulting 7? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is folding and faulting 7?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.