Are you looking for an answer to the topic “When a monopolist increases the amount of output?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading
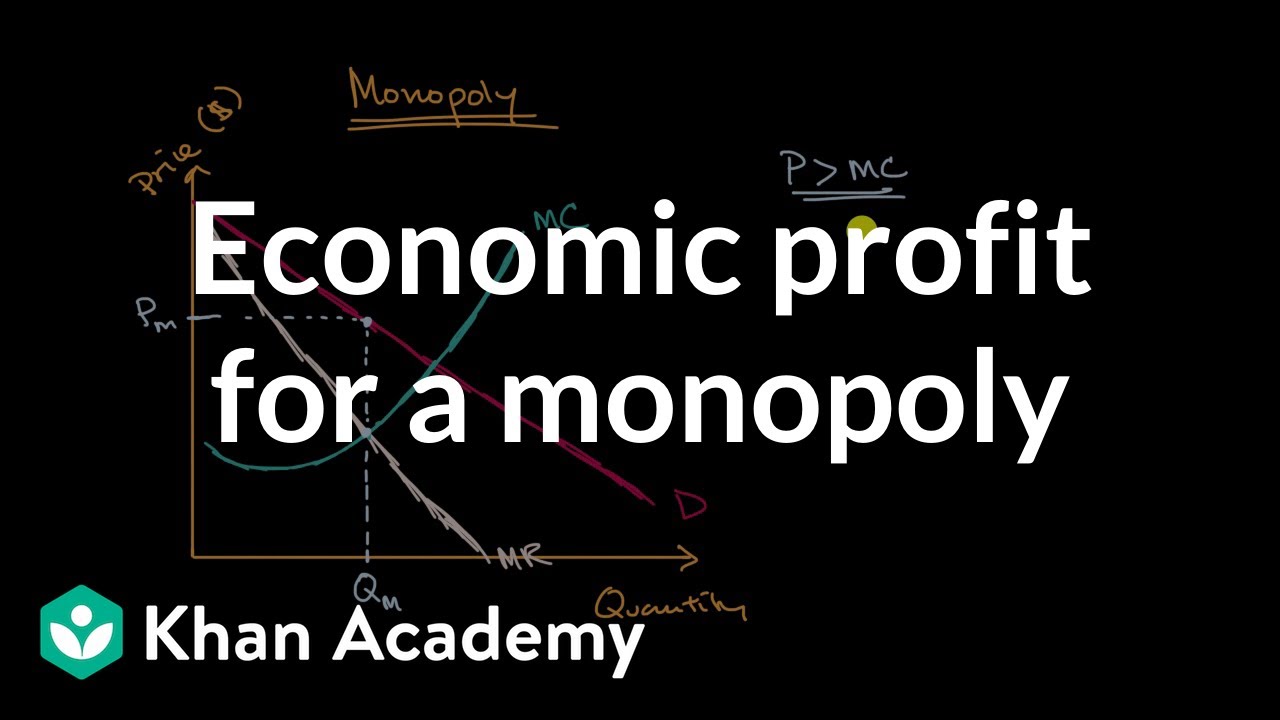
What happens when a monopolist increases output?
The monopolist faces the downward‐sloping market demand curve, so the price that the monopolist can get for each additional unit of output must fall as the monopolist increases its output. Consequently, the monopolist’s marginal revenue will also be falling as the monopolist increases its output.
When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells the price of its output *?
When a monopoly increases the amount it sells, it has two effects on total revenue (P x Q). The output effect—more output is sold, so Q is higher. The price effect—price falls, so P is lower. Profit Maximization •A monopoly maximizes profit by producing the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
Economic profit for a monopoly | Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Images related to the topicEconomic profit for a monopoly | Microeconomics | Khan Academy

When a monopoly increases its output and sales?
When a monopoly increases its output and sales, the output effect works to increase total revenue, and the price effect works to decrease total revenue.
Do monopolies increase output?
Monopoly Pricing: Monopolies create prices that are higher, and output that is lower, than perfectly competitive firms.
What might happen if a monopolist increased output of its product each week?
What might happen if a monopolist increased output of its product each week? A. The price of the good would eventually fall and so would revenue.
When a monopolist increases sales does he increase marginal revenue or decrease it?
When a monopolist increases sales by one unit, it gains some marginal revenue from selling that extra unit, but also loses some marginal revenue because every other unit must now be sold at a lower price.
When a monopolist reduces the amount of output that it sells the price of its output?
Also, if the monopolist reduces the quantity of output it produces and sells, the price of its output increases. Less than the price of its good because a monopoly faces a downward-sloping demand curve. To increase the amount sold, a monopoly firm must lower the price it charges to all customers. 1.
See some more details on the topic When a monopolist increases the amount of output? here:
Solved When a monopolist increases the amount of output that
Question: When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells, what happens to its average revenue and its marginal revenue?
When a monopolist increases the amount of output that
39. When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells,average revenueD) decreases, and marginal revenue decreases.
Chapter 14: SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:
With the higher price, the typical firm increases its output from q1 to q2, … A monopolist chooses the amount of output to produce by finding the quantity …
How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and Price
However, a monopolist can sell a larger quantity and see a decline in total revenue. When a monopolist increases sales by one unit, it gains some marginal …
When a monopolist firm increases the number of units it sells what are the two effects on revenue?
However, a monopolist can sell a larger quantity and see a decline in total revenue. When a monopolist increases sales by one unit, it gains some marginal revenue from selling that extra unit, but also loses some marginal revenue because it must now sell every other unit at a lower price.
When a monopolist decreases the price of its good?
When a monopolist decreases the price of its good, consumers: buy more. When a monopolist maximizes social surplus, it produces at an optimal Q where: AR = MC.
When a monopoly firm sells an additional unit of output Its revenue increases by an amount less than the price?
(ii) When a monopoly firm sells an additional unit of output, its revenue increases by an amount less than the price. (iii) Average revenue is the same as price for both competitive and monopoly firms. A competitive firm’s marginal revenue curve is horizontal; a monopolist’s marginal revenue curve is downward sloping.
How does a monopoly maximize profit?
A monopolistic market has no competition, meaning the monopolist controls the price and quantity demanded. The level of output that maximizes a monopoly’s profit is when the marginal cost equals the marginal revenue.
Which of the following is an effect of a monopoly?
A monopoly causes a reduction in economic efficiency.
MONOPOLY – OUTPUT DECISION
Images related to the topicMONOPOLY – OUTPUT DECISION

How do monopolies affect the price of goods?
In a monopoly, the firm will set a specific price for a good that is available to all consumers. The quantity of the good will be less and the price will be higher (this is what makes the good a commodity). The monopoly pricing creates a deadweight loss because the firm forgoes transactions with the consumers.
What is the monopolist’s profit at the profit-maximizing level of output quizlet?
A monopolist maximizes its profits by producing to the point at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. The monopolist then charges the maximum price for this amount of output, which is the price that consumers are willing to pay for that quantity of output.
Do all monopolies make a profit?
Although Monopolists likely make greater profits than they would in pure competition, they are not guaranteed a profit. They are not immune to changes in tastes, economic g , effects, escalating resource prices, etc. Faced with continuing loses, monopolists will choose to do something else with their resources.
What happens to price as output increases in a purely competitive market?
Under purely competitive conditions, the product price charged by the firm increases as output increases. The purely competitive firm can maximize its economic profit (or minimize its loss) only by adjusting its output.
When output changes the profit-maximizing firm must consider?
To maximize profit, a firm must consider economic cost, as well as revenue. exist only in the short run. Variable costs are costs of production that change when the rate of output is altered. Marginal costs (MC) are the increase in total costs associated with a one-unit increase in production.
What output quantity will the monopolistically competitive firm produce to maximize profits?
In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profit or minimizes losses by producing that quantity where marginal revenue = marginal cost. If average total cost is below the market price, then the firm will earn an economic profit.
How does a monopolist’s quantity of output compare to the quantity of output that maximizes total surplus?
A monopolist produces a quantity of output that’s less than the quantity of output that maximizes total surplus because it produces the quantity at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue rather than the quantity at which marginal cost equals price.
How do monopolists set the output level and price for their products?
Monopolists set the price of their products on the demand curve at the output level where the supply curve intersects the marginal revenue curve.
Why is marginal revenue less than price in a monopoly?
For a monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price. a. Because the monopolist must lower the price on all units in order to sell additional units, marginal revenue is less than price.
How does a monopolist change the price of its product quizlet?
A monopolist can change its product’s price by changing the quantity supplied of the product.
Monopolistic competition and economic profit | Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Images related to the topicMonopolistic competition and economic profit | Microeconomics | Khan Academy

How price and output is determined in short and long run in monopoly competition?
The equilibrium price and output is determined at a point where the short-run marginal cost (SMC) equals marginal revenue (MR). Since costs differ in the short-run, a firm with lower unit costs will be earning only normal profits. In case, it is able to cover just the average variable cost, it incurs losses.
Is a monopoly demand curve elastic or inelastic?
Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue And Costs, Price Determination, Profit Maximization And Loss Minimization. For a seller in a purely competitive market, the demand curve is completely elastic, and, therefore, horizontal in a price-quantity graph.
Related searches to When a monopolist increases the amount of output?
- the supply curve for the monopolist
- how monopolist determine price and output
- at the profit maximizing level of output for a monopolist quizlet
- when a monopolist increases the number of units it sells, there are two effects on revenue the
- when a monopolist increases output total revenue will
- for a monopolist an increase in output sold causes marginal revenue to be negative when
- when a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells average revenue
- for a monopolist, marginal revenue is
- the deadweight loss that arises from a monopoly is a consequence of the fact that the monopoly
- a profit-maximizing monopolist will produce the level of output at which
- a monopolist maximizes profits by
- for a monopolist marginal revenue is
- when a monopolist increases the amount of output
- what is the most profitable level of output for a monopolist
- because a monopolist must lower its price in order to sell another unit of output,
- because a monopolist must lower its price in order to sell another unit of output
- when a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells the price of its output
- when a monopolist increases the number of units it sells there are two effects on revenue the
- what output will the monopolist produce
Information related to the topic When a monopolist increases the amount of output?
Here are the search results of the thread When a monopolist increases the amount of output? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic When a monopolist increases the amount of output?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.