Are you looking for an answer to the topic “When a neuron is at its resting membrane potential What are the states of Na+ and K +?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading
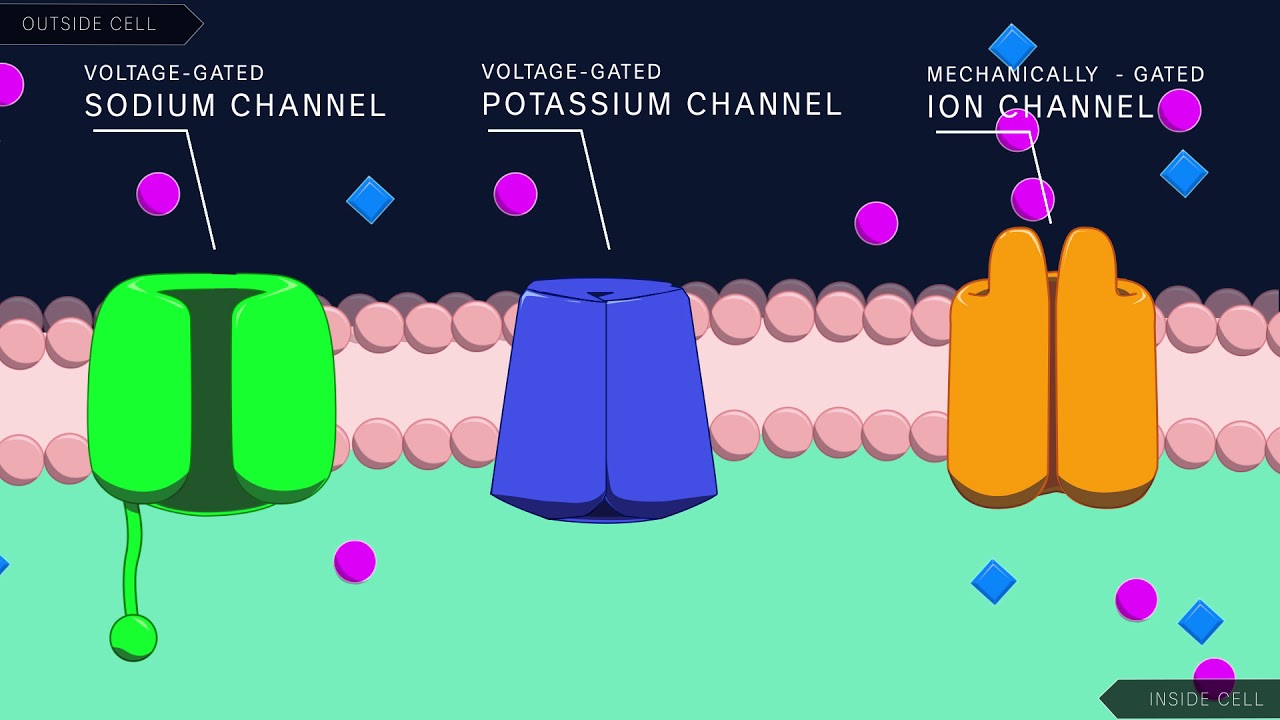
What is happening to Na and K during resting state?
At normal resting membrane potential, sodium is forced outwards and potassium is carry into the cells (see Fig. 2.4). This requires the sodium-potassium exchange pump, which uses ATP in order to operate. Three intracellular sodium ions will be exchanged for every two extracellular potassium ions.
What is the state of a neuron when it is at its resting potential?
A neuron at rest is negatively charged: the inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside (−70 mV, note that this number varies by neuron type and by species).
Action Potential in the Neuron
Images related to the topicAction Potential in the Neuron

What happens to Na+ movements at the resting potential?
The Na+ ions have moved down their concentration gradient until their further movement is opposed by a countervailing electrical potential difference across the membrane. There are extra positive charges on the inside of the cell in the form of Na+ ions, and these Na+ ions line up along the membrane.
What happens to Na and K during action potential?
The inward flow of sodium ions increases the concentration of positively charged cations in the cell and causes depolarization, where the potential of the cell is higher than the cell’s resting potential. The sodium channels close at the peak of the action potential, while potassium continues to leave the cell.
What happens at resting potential?
resting potential, the imbalance of electrical charge that exists between the interior of electrically excitable neurons (nerve cells) and their surroundings.
What will happen to the resting membrane potential if the extracellular K concentration is increased?
extracellular K concentration is increased. Your answer: The resting membrane potential will become less negative.
What state is the neuron in when it is resting quizlet?
When a neuron is at its resting potential, the inside of the cell has a negative charge relative to the outside. 2. A stimulus begins to change the distribution of charge across the membrane.
See some more details on the topic When a neuron is at its resting membrane potential What are the states of Na+ and K +? here:
Neuroscience For Kids – action potential
The resting membrane potential of a neuron is about -70 mV (mV=millivolt) – this means that the inside of the neuron is 70 mV less than the outside. At rest, …
Physiology, Resting Potential – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
The membrane is permeable to K+ at rest because many channels are open. In a normal cell, Na+ permeability is about 5% of the K+ permeability or even less, …
Resting Potential – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The basis for the RMP is the unequal distribution of ions, in particular K+ and Na+, on either side of the plasma membrane, with a K+ concentration of ~140 mmol …
Chapter 1: Resting Potentials & Action Potentials – Department …
Consequently, the positive K+ ions leaving the inner surface of the membrane leave behind some negatively charged ions. That negative charge attracts the …
Why is the resting membrane potential negative?
What generates the resting membrane potential is the K+ that leaks from the inside of the cell to the outside via leak K+ channels and generates a negative charge in the inside of the membrane vs the outside. At rest, the membrane is impermeable to Na+, as all of the Na+ channels are closed.
Are sodium ions positive or negative?
An ion is a charged particle, such as Na+, the sodium ion. It has a positive charge, because it is missing one electron.
Which of the following is true about the concentration gradient of Na+ in a neuron at rest?
Which of the following is TRUE about the concentration gradient of Na+ in a neuron at rest? It favors its movement into the cell at the resting membrane potential.
What happens in the membrane during repolarization?
The repolarization phase usually returns the membrane potential back to the resting membrane potential. The efflux of potassium (K+) ions results in the falling phase of an action potential. The ions pass through the selectivity filter of the K+ channel pore.
What is resting potential and action potential?
Action potential. 1. It is the potential difference across the nerve fibre when there is no conduction of nerve impulse. It is the potential difference across nerve fibre when there is conduction of nerve impulse.
Resting membrane potential – definition, examples
Images related to the topicResting membrane potential – definition, examples
What is depolarization and repolarization?
The main difference between the two is: depolarization is described as the loss of resting membrane potential as a result of the alteration of the polarization of cell membrane. repolarization is described as the restoration of the resting membrane potential after every depolarization event.
What happens during depolarization and repolarization?
Depolarization is caused by a rapid rise in membrane potential opening of sodium channels in the cellular membrane, resulting in a large influx of sodium ions. Membrane Repolarization results from rapid sodium channel inactivation as well as a large efflux of potassium ions resulting from activated potassium channels.
What is depolarization of a neuron?
Depolarization is a positive change from the resting potential achieved by increased permeability to an ion with a Nernst potential above the RBP.
Why does NA enter the cell during the action potential?
Because sodium is a positively charged ion, it will change the relative voltage immediately inside the cell relative to immediately outside. The resting potential is the state of the membrane at a voltage of −70 mV, so the sodium cation entering the cell will cause it to become less negative.
What is true of a neuron with a resting potential?
Resting potential is dependent on the specific potential inside a neuron in the case of a neuron staying at rest. This is a condition that occurs when there is no impulse in the system.
What is resting membrane potential value?
Across the cell membrane of each neurone there exists a small difference in electrical charge, known as the membrane potential. In electrically inactive neurones, this is known as the resting membrane potential. Its typical value lies between -50 and -75 mV.
What happens to the resting membrane potential when the extracellular Na+ concentration is decreased?
As the concentration of sodium in the extracellular solution is reduced, the action potentials become smaller.
How does a change in Na or K conductance affect the resting membrane potential?
When the conductance to sodium goes back to its original value, the membrane potential will return to the resting potential. If the neuron is at resting potential (-70mV) and the conductance to potassium increases, the membrane potential will be hyperpolarized (it will move toward -90mV).
What would happen to the resting membrane potential of a neuron if Na+ ion permeability increased at rest quizlet?
Explain why a change in extracellular Na+ did not alter the membrane potential in the resting neuron. A change in extracellular Na+ results in little change to resting membrane potential because the plasma membrane of a neuron is only slightly permeable to Na+ because it contains relatively few Na+ leakage channels.
What is the state of the electrical charge when a neuron is at resting potential quizlet?
The difference in electrical charge between two locations. The neuron inside the membrane has a slightly negative electrical potential w/ respect to the outside. What is resting potential? The result of negatively charged proteins inside the cell.
Membrane Potential, Equilibrium Potential and Resting Potential, Animation
Images related to the topicMembrane Potential, Equilibrium Potential and Resting Potential, Animation
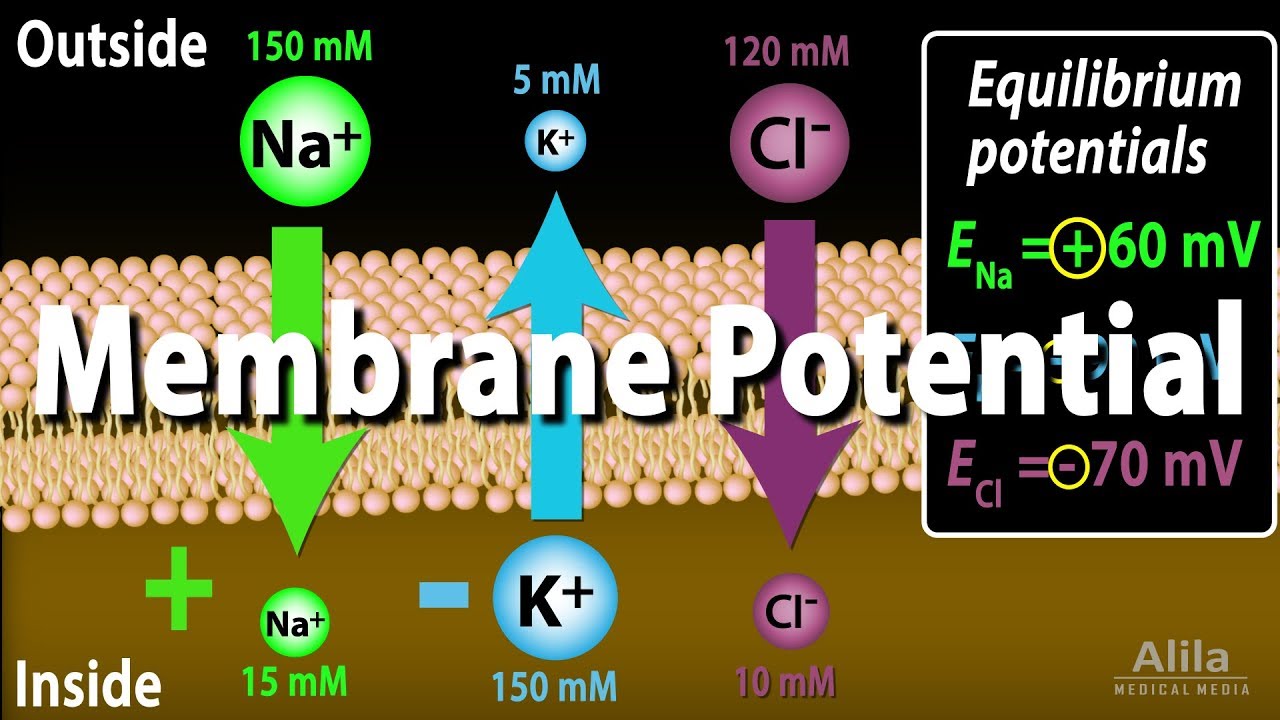
Which of the following best describes a neuron at resting state?
what statement best describes the resting state of a neuron? neurons are polarized with more sodium ions outside the cell and more potassium ions inside the cell. Neurons either conduct action potentials along the length of their axons, or they remain at rest.
What is a resting neuron quizlet?
In a resting neuron, would the concentration of sodium ions be higher inside or outside the cell. Na+ is higher outside the cell at resting potential. In a resting neuron the plasma membrane separates ions on the inside of the cell from those on the outside.
Related searches to When a neuron is at its resting membrane potential What are the states of Na+ and K +?
- hyperpolarization
- what is the resting membrane potential
- what is the resting membrane potential of a neuron
- action potential
- action potential graph
- equilibrium potential of potassium
- the resting membrane potential is established primarily due to
- resting membrane potential pdf
- depolarization
Information related to the topic When a neuron is at its resting membrane potential What are the states of Na+ and K +?
Here are the search results of the thread When a neuron is at its resting membrane potential What are the states of Na+ and K +? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic When a neuron is at its resting membrane potential What are the states of Na+ and K +?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.