Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is active and potential acidity?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Active acidity may be directly determined using a pH meter, such as an electron probe. The second pool, exchangeable acidity, refers to the amount of acid cations, aluminum and hydrogen, occupied on the CEC. When the CEC of a soil is high but has a low base saturation, the soil becomes more resistant to pH changes.Active acidity is the quantity of hydrogen ions that are present in the soil water solution. The active pool of hydrogen ions is in equilibrium with the exchangeable hydrogen ions that are held on the soil’s cation exchange complex. This pool most readily affects plant growth.Potential acidity is often referred to as the soil’s buffer capacity or resistance to change in pH. Usually, the higher the clay and organic matter content the greater the soil’s buffer capacity. More lime is needed to change the pH of a soil with a high buffer capacity than a soil with a low buffer capacity.

What is active acidity and potential acidity?
Active acidity is the quantity of hydrogen ions that are present in the soil water solution. The active pool of hydrogen ions is in equilibrium with the exchangeable hydrogen ions that are held on the soil’s cation exchange complex. This pool most readily affects plant growth.
What do you mean by potential acidity?
Potential acidity is often referred to as the soil’s buffer capacity or resistance to change in pH. Usually, the higher the clay and organic matter content the greater the soil’s buffer capacity. More lime is needed to change the pH of a soil with a high buffer capacity than a soil with a low buffer capacity.
Acidification of agricultural soils
Images related to the topicAcidification of agricultural soils

What is the relationship between active reserve residual and total acidity?
The total acidity is summation of active, exchange and residual acidity. It can be written as, Total acidity = Active acidity + Exchange acidity + Residual acidity. Therefore, total soil acidity depends on the active, exchange and residual acidity of the soil.
What is the difference between active and exchangeable acidity?
Active acidity may be directly determined using a pH meter, such as an electron probe. The second pool, exchangeable acidity, refers to the amount of acid cations, aluminum and hydrogen, occupied on the CEC. When the CEC of a soil is high but has a low base saturation, the soil becomes more resistant to pH changes.
What is buffering in soils?
Buffering capacity is defined as the soil’s capacity to maintain a relatively stable pH despite the presence of acidifying or alkalizing factors [1]. Soil buffering capacity is caused by the protonation of minerals and organic material that occurs in the soil or is intentionally added to the soil [2].
What is pH full form?
The letters pH stand for potential of hydrogen, since pH is effectively a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions (that is, protons) in a substance. The pH scale was devised in 1923 by Danish biochemist Søren Peter Lauritz Sørensen (1868-1969).
What is the full form of pH paper?
pH Full Form – Potential of Hydrogen.
See some more details on the topic What is active and potential acidity? here:
Active soil acidity
Active acidity is the quantity of hydrogen ions that are present in the soil water solution. The active pool of hydrogen ions is in …
Soil pH and acidity | Cropaia
Active acidity is the concentration of free hydrogen ions (H+) in the soil solution. Soil pH is a measure of the active acidity of the soil.
What Is Reserve Acidity in Soil? – Home Guides
Active acidity is the hydrogen ion concentration in soil water or moisture; these hydrogen ions are in solution. Reserve acidity refers to …
Soil Reaction: Pools of Soil Acidity – Plantlet
The active acidity pool is defined by the H+ ion activity on the soil solution. This pool is very negligible compared to the acidity in the exchangeable and …
What is neutral pH?
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. pHs less than 7 are acidic while pHs greater than 7 are alkaline (basic).
What is reserve basicity?
The resistance of a buffer solution to change in pH upon addition of a strong acid is called ‘reserve basicity’ Reserve acidity: The resistance of a buffer solution to change in pH upon addition of a strong base is called ‘reserve basicity’
What is soil acidity and alkalinity?
Soils can be classified according to their pH value: 6.5 to 7.5—neutral. over 7.5—alkaline. less than 6.5—acidic, and soils with pH less than 5.5 are considered strongly acidic.
What is alkaline soil?
Alkaline soil is a type of soil with high amounts of calcium, sodium, and magnesium. All soil falls on the pH scale, which monitors the concentration of hydrogen ions and ranges from zero to fourteen. Soil with a pH level below seven is acidic soil, while soil pH levels above seven indicate alkaline soil.
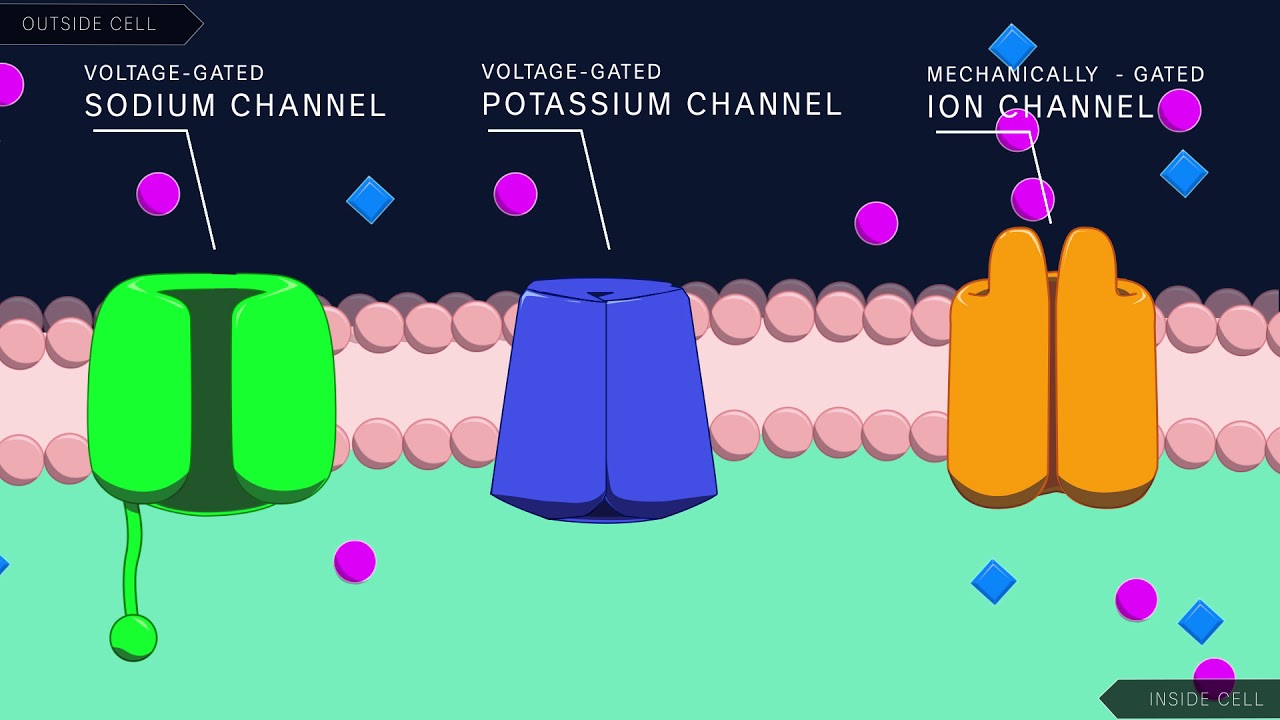
Action Potential in the Neuron
Images related to the topicAction Potential in the Neuron
What are the types of acidity in water?
Acidity can be caused by weak organic acids, such as acetic and tannic acids, and strong mineral acids including sulfuric and hydrochloric acids; however, the most common source of acidity in unpolluted water is carbon dioxide in the form of carbonic acid.
What is the relationship of pH with active Fe?
Solubility of Fe decreases by approximately 1000-fold for each unit increase of soil pH in the range of 4–9 compared to approximately 100-fold decreases in activity of Mn, Cu, and Zn (Lindsay, 1979).
How is soil reserve acidity measured?
If the pH is 6.2 or lower, a buffer pH is run to measure the reserve acidity. The result of the buffer pH shows the amount of lime required to neutralize a major portion of the reserve acidity.
What is base saturation in soil?
Base saturation (BS) represents the percentage of CEC occupied by bases (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, and Na+). The %BS increases with increasing soil pH (Figure 5). The availability of Ca2+, Mg2+, and K+ increases with increasing %BS. For example, an 80% BS soil provides cations to plants more easily than 40% BS soil.
Why is lime application done in acid soil?
Soil acidity is ameliorated by applying lime or other acid‐neutralizing materials. ‘Liming’ also reduces N2O emissions, but this is more than offset by CO 2 emissions from the lime as it neutralizes acidity.
What are the different sources of soil acidity?
- Rainfall and leaching.
- Acidic parent material.
- Organic matter decay.
- Harvest of high yielding crops.
- Nitrification of ammonium.
What is the difference between pH and buffer pH?
pH is a fundamental scale that we use in chemistry to measure the acidity r basicity of a solution. Buffers are chemical solutions that can resist the changes in pH. Therefore, the difference between pH and buffer is that the pH is a logarithmic scale whereas a buffer is an aqueous solution.
What is pH buffer capacity?
Buffer capacity (β) is defined as the moles of an acid or base necessary to change the pH of a solution by 1, divided by the pH change and the volume of buffer in liters; it is a unitless number.
What do you mean by buffer?
Definition of buffer (Entry 2 of 4) 1 : any of various devices or pieces of material for reducing shock or damage due to contact. 2 : a means or device used as a cushion against the shock of fluctuations in business or financial activity. 3 : something that serves as a protective barrier: such as. a : buffer state.
What is the pH of blood?
The pH scale ranges from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline). Blood is usually between 7.35 to 7.45.
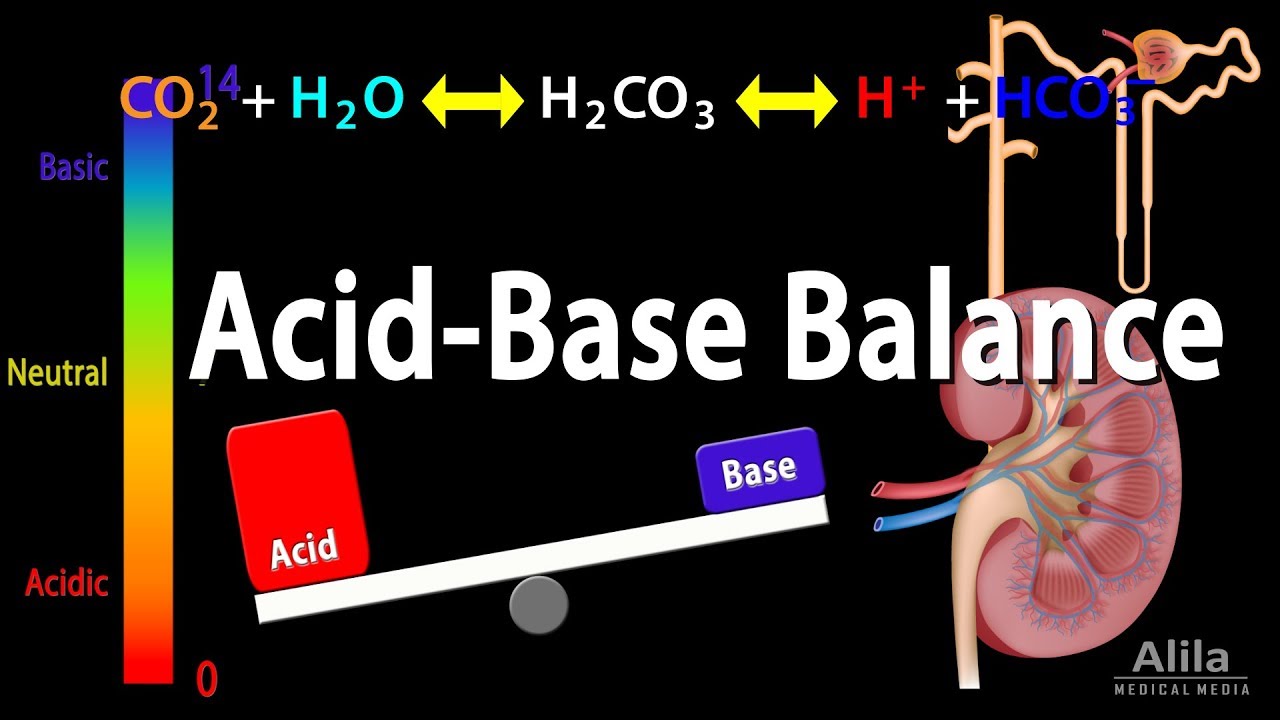
Acid Base Balance, Animation.
Images related to the topicAcid Base Balance, Animation.
What is human blood pH?
In the absence of pathological states, the pH of the human body ranges between 7.35 to 7.45, with the average at 7.40.
What is the pH of urine?
Normal Results
The normal values range from pH 4.6 to 8.0. The examples above are common measurements for results of these tests. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples.
Related searches to What is active and potential acidity?
- what is active and potential acidity in food
- what is buffering capacity of soil
- what is active and potential acidity in soil
- causes of soil acidity
- active acidity of soil
- what is potential acidity
- what are the two types of soil acidity
- what is active acidity
- what is exchangeable acidity
- what is active and potential acidity in water
- what is active and potential acidity in the body
- potential acidity of soil
Information related to the topic What is active and potential acidity?
Here are the search results of the thread What is active and potential acidity? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is active and potential acidity?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.