Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is aggregate demand shock?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
A demand shock is a sudden and temporary increase or decrease in the demand for a good or a bundle of goods. Usually, the phrase “demand shock” is used in the context of aggregate demand, which describes the cumulative demand for an entire economy.In economics, a demand shock is a sudden event that increases or decreases demand for goods or services temporarily. A positive demand shock increases aggregate demand (AD) and a negative demand shock decreases aggregate demand. Prices of goods and services are affected in both cases.Economic shocks are random, unpredictable events that have a widespread impact on the economy and are caused by things outside the scope of economic models. Economic shocks can be classified by the economic sector that they originate from or by whether they primarily influence either supply or demand.
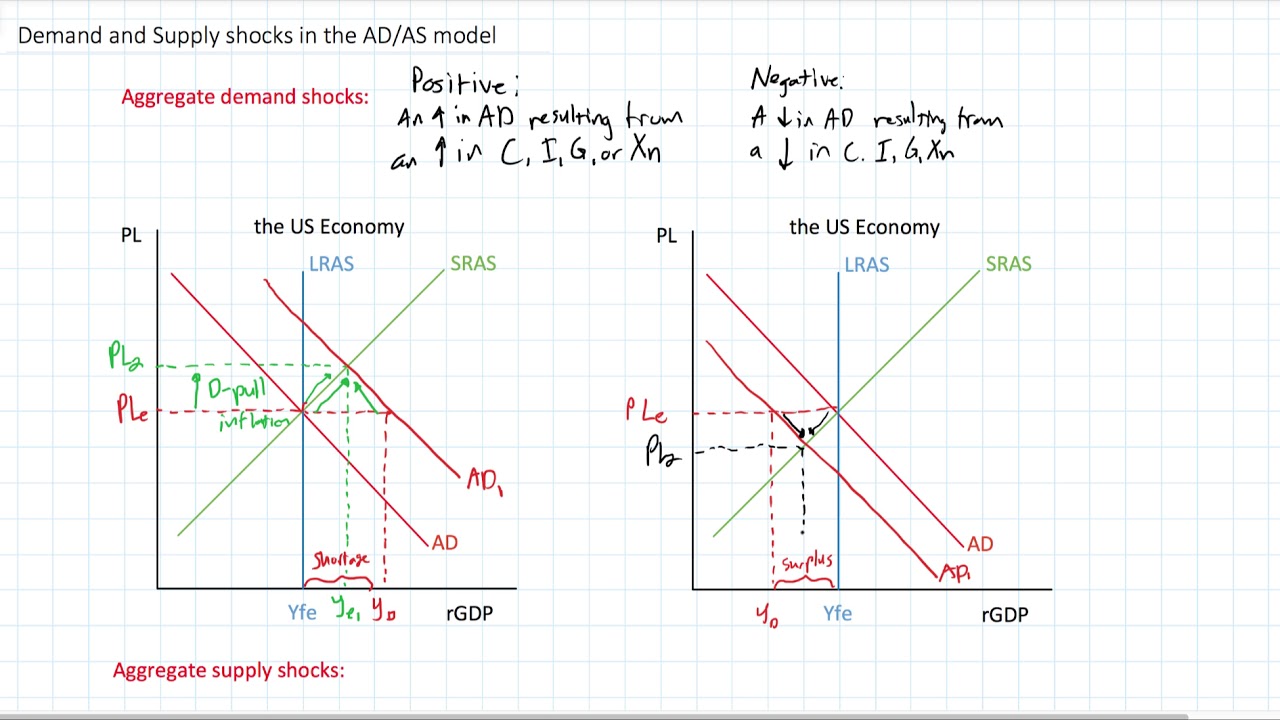
Table of Contents
What is aggregate demand shock explain the factors responsible for demand shock?
In economics, a demand shock is a sudden event that increases or decreases demand for goods or services temporarily. A positive demand shock increases aggregate demand (AD) and a negative demand shock decreases aggregate demand. Prices of goods and services are affected in both cases.
What is a shock in an economy?
Economic shocks are random, unpredictable events that have a widespread impact on the economy and are caused by things outside the scope of economic models. Economic shocks can be classified by the economic sector that they originate from or by whether they primarily influence either supply or demand.
Demand and Supply Shocks in the AD-AS Model
Images related to the topicDemand and Supply Shocks in the AD-AS Model

What causes an aggregate supply shock?
The most common explanation is that an unexpected event causes a dramatic change in future output. According to contemporary economic theory, a supply shock creates a material shift in the aggregate supply curve and forces prices to scramble towards a new equilibrium level.
How does aggregate demand shock affect GDP and the price level?
Aggregate supply shock cause the price level and real GDP to change in opposite directions. With an increase in supply, the price level falls and output rises. With a decrease in supply, the price level rises and output falls.
Which of the following is an example of a demand shock?
Demand shock is a surprise event that can lead to a temporary increase or decrease in demand for goods or services. An example of a negative demand shock would be a global pandemic. An example of a positive demand shock would be government stimulus checks and relaxed monetary policy in response to the pandemic.
Which of the following would qualify as an aggregate demand shock?
Which of the following would qualify as an aggregate demand shock? An unexpected surge in consumer confidence, resulting in increased purchases of new automobiles.
What is an inflation shock?
An inflationary shock happens when prices of commodities increase suddenly (e.g., after a decrease of government subsidies) while not all salaries are adjusted immediately throughout society (this results in a temporary loss of purchasing power for many consumers); or that production costs begin to exceed corporate …
See some more details on the topic What is aggregate demand shock? here:
Demand shock – Wikipedia
A positive demand shock increases aggregate demand (AD) and a negative demand shock decreases aggregate demand. Prices of goods and services are affected in …
Shifts in Aggregate Demand | Macroeconomics with Prof. Dolar
Demand shocks are events that shift the aggregate demand curve. We defined the AD curve as showing the amount of total planned expenditure on domestic goods …
Lesson summary: Changes in the AD-AS model in the short run
Why a shock? Because the change come as a complete surprise! An unexpected change in the economy will shift either the aggregate demand (AD) or short-run …
A history of aggregate demand and supply shocks for the …
We highlight two episodes of particular interest: an aggregate supply shock in the late 1920s, which we attribute to changes in the bargaining …
What is a trade shock?
Trade shocks are defined here as net gains or losses from trade caused by changes in international prices and in the volume of goods and services that are traded internationally. It relates to shifts in global markets typically outside of the influence of individual countries.
What is an example of a supply shock?
Examples of adverse supply shocks are increases in oil prices, higher union pressures, and a drought that destroys crops. Basically, anything that drastically and immediately increases the cost of output is considered an adverse supply shock.
Aggregate Demand Shocks
Images related to the topicAggregate Demand Shocks

How does supply shock affect inflation?
An adverse supply-side shock is an event that causes an unexpected increase in costs or disruption to production. This will cause the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left, leading to higher inflation and lower output.
What happens when aggregate demand increases?
In the most general sense (and assuming ceteris paribus conditions), an increase in aggregate demand corresponds with an increase in the price level; conversely, a decrease in aggregate demand corresponds with a lower price level.
What happens to the price level when aggregate demand AD declines?
What happens to the price level when aggregate demand (AD) declines? Multiple choice question. The price level remains the same.
What happens when aggregate demand decreases?
When government spending decreases, regardless of tax policy, aggregate demand decrease, thus shifting to the left. The fourth term that will lead to a shift in the aggregate demand curve is NX(e). This term means that net exports, defined as exports less imports, is a function of the real exchange rate.
Why is an aggregate supply shock more difficult to combat than an aggregate demand shock?
It is easier for the Fed to deal with demand shocks than with supply shocks because the Fed can reduce or even eliminate the impact of demand shocks on output by controlling the money supply.
How has Covid affected aggregate demand?
We attribute two thirds of the decline in 2020:Q1 GDP to a negative shock to aggregate demand. In contrast, regarding the staggeringly large decline in GDP in 2020:Q2, we estimate two thirds of this shock was due to a reduction in aggregate supply.
Which of the following is an example of a negative aggregate demand shock?
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply shocks only occur in the short run. An example of a negative aggregate supply shock would be if multiple businesses were to fail in the economy.
Which of the following will cause a positive demand shock?
Which of the following causes a positive demand shock? AG price level increases, real GDP decreases.
Aggregate Demand- Macro Topic 3.1
Images related to the topicAggregate Demand- Macro Topic 3.1

What is a stochastic shock?
“Stochastic shocks: shocks originating from outside the community, which affect all people in the same locality, such as natural disasters or economic crises“.
What is a growth shock?
We find that a growth shock is inequality-increasing, and an inequality shock is growth-reducing. We also find, however, that the sizes of the effects of these shocks are very small, accounting for under 2 per cent of the variance for both countries.
Related searches to What is aggregate demand shock?
- what is a positive demand shock
- what causes demand shocks
- demand shock examples
- what is aggregate demand price
- what is aggregate demand pdf
- what are shock loads
- positive aggregate demand shock graph
- what is demand load in electrical
- what is demand side shock
- supply shock vs demand shock
- what is aggregate demand shock
- supply shock
- what is a negative demand shock
- what is shock load
- positive demand shock examples
- what is a negative aggregate demand shock
- what is a demand load
- negative demand shock examples
- what is aggregate demand class 12
Information related to the topic What is aggregate demand shock?
Here are the search results of the thread What is aggregate demand shock? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is aggregate demand shock?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
