Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is ERCP used to diagnose?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
What is ERCP? Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or ERCP, is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. It combines X-ray and the use of an endoscope—a long, flexible, lighted tube.Doctors use ERCP to diagnose and treat problems that affect the: Bile ducts, including cancer, stones and strictures. Gallbladder, including gallstones and cholecystitis (inflamed gallbladder). Pancreas, including pancreatitis (inflamed, swollen pancreas), pancreatic cancer and pancreatic cysts and pseudocysts.They are relatively similar to each other as both involve the use of an endoscope. The main difference between the two is that endoscopic ultrasound utilizes high-frequency sound waves to generate a virtual image and ERCP procedure uses a video camera.

What can ERCP detect?
Doctors use ERCP to diagnose and treat problems that affect the: Bile ducts, including cancer, stones and strictures. Gallbladder, including gallstones and cholecystitis (inflamed gallbladder). Pancreas, including pancreatitis (inflamed, swollen pancreas), pancreatic cancer and pancreatic cysts and pseudocysts.
Is an endoscopy the same as ERCP?
They are relatively similar to each other as both involve the use of an endoscope. The main difference between the two is that endoscopic ultrasound utilizes high-frequency sound waves to generate a virtual image and ERCP procedure uses a video camera.
ERCP : What to Expect | IU Health
Images related to the topicERCP : What to Expect | IU Health

Is ERCP considered surgery?
Scott Sundick, MD, is board-certified in general surgery and vascular surgery. Since 2012, he has practiced with The Cardiovascular Care Group in New Jersey. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an invasive procedure used for the diagnosis and treatment of obstruction in the biliary system.
How serious is an ERCP?
An ERCP is considered a low-risk procedure; however, complications can occur. These can include pancreatitis, infections, bowel perforation, and bleeding.
When is ERCP indicated?
ERCP indications include obstructive jaundice, biliary or pancreatic ductal system disease treatment or tissue sampling, suspicion for pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis of unknown cause, manometry for sphincter of Oddi, nasobiliary drainage, biliary stenting for strictures and leakage, drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts, …
What will happen if the bile duct is blocked?
If something is blocking the bile duct, bile can back up into the liver. This can cause jaundice, a condition in which the skin and white of the eyes become yellow. The bile duct might become infected and require emergency surgery if the stone or blockage is not removed.
Is a stone in the bile duct serious?
While some gallstones pass or resolve on their own, bile duct stones are trapped in the bile duct. These stones can cause immediate health issues, including pancreatitis — a potentially life threatening inflammation of the pancreas.
See some more details on the topic What is ERCP used to diagnose? here:
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Doctors use ERCP to treat problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts. Doctors also use ERCP to diagnose problems of the bile and pancreatic ducts if they expect …
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
ERCP combines X-rays and an endoscopic procedure to help doctors diagnose and treat gallstones and other bile duct problems.
Digestive Diseases and ERCP Testing – WebMD
ERCP (short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is a procedure used to diagnose diseases of the gallbladder, biliary system, …
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP …
An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is used to diagnose and treat problems in the pancreas. Learn more about ERCP in kids.
What is the most common complication of ERCP?
Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) is the most frequent complication, occurring in about 3 to 5 percent of people undergoing ERCP. When it occurs, it is usually mild, causing abdominal pain and nausea, which resolve after a few days in the hospital.
Is an ERCP painful?
Most ERCPs are done without any problems. Some people have a mild sore throat for a day or so afterwards. You may feel tired or sleepy for several hours, caused by the sedative.
Why would I need an ERCP?
You may need ERCP to find the cause of unexplained abdominal pain or yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice). It may be used to get more information if you have pancreatitis or cancer of the liver, pancreas, or bile ducts. Other things that may be found with ERCP include: Blockages or stones in the bile ducts.
What are the symptoms of common bile duct stones?
- Severe abdominal pain (can occur irregularly and last for hours at a time)
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Fever.
- Jaundice.
Is it necessary to remove gallbladder after ERCP?
Based on the results of this study, cholecystectomy is recommended for patients who remain symptomatic after ERCP, while this can be forgone in asymptomatic patients.
When are MRCP and ERCP used for diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis?
Images related to the topicWhen are MRCP and ERCP used for diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis?

What happens after ERCP procedure?
Possible ERCP complications:
The most common problem after ERCP is a condition called “pancreatitis.” This happens when the duct to the pancreas is irritated by the X-ray dye or small plastic tube used in ERCP. This can cause abdominal pain that gets worse instead of better after the procedure.
How long can a stent stay in bile duct?
The mean duration of the patency of the stent is about 12 months. The biliary stenting is performed either with plastic or metal stents, studies recommending their replacement after 3-6 months. Patients with long stayed forgotten biliary stents are inevitably treated with surgical intervention.
Can ERCP cause pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis remains the most common complication of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). It is reported to occur in 2–10% of unselected patient samples and up to 40% of high-risk patients.
When is ERCP indicated in pancreatitis?
ERCP should be performed after complete recovery from acute pancreatitis, usually 4 to 6 wk after presentation. If microlithiasis is detected, patients should be considered for cholecystectomy or biliary sphincterotomy depending on surgical risk.
When should you not use ERCP?
In recent clinical trials and guidelines, ERCP is not recommended in most patients with ABP for whom there is a lack of evidence of biliary obstruction or cholangitis, regardless of predicted severity [2,4,5].
Is pancreatitis a contraindication to ERCP?
Routine ERCP before laparoscopic cholecystectomy is contraindicated if there are no objective signs of biliary obstruction or stone (moderate-quality evidence) In patients with acute biliary pancreatitis, ERCP should be reserved for those with concomitant cholangitis or biliary obstruction (high-quality evidence)
What is the most common cause of biliary obstruction?
Extrahepatic obstruction to the flow of bile may occur within the ducts or secondary to external compression. Overall, gallstones are the most common cause of biliary obstruction. Other causes of blockage within the ducts include malignancy, infection, and biliary cirrhosis.
What does a blocked bile duct feel like?
People with bile duct obstruction also often experience: itching. abdominal pain, usually in the upper right side. fever or night sweats.
Will a CT scan show blocked bile ducts?
CT scans can show the organs near the bile duct (especially the liver), as well as lymph nodes and distant organs where cancer might have spread to. A type of CT known as CT angiography can be used to look at the blood vessels around the bile ducts.
What would happen if a gallstone get stuck in the bile duct?
When a gallstone is stuck in the bile duct, the bile can become infected. The bacteria from the infection can spread rapidly, and may move into the liver. If this happens, it can become a life-threatening infection. Other possible complications include biliary cirrhosis and pancreatitis.
Understanding ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
Images related to the topicUnderstanding ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
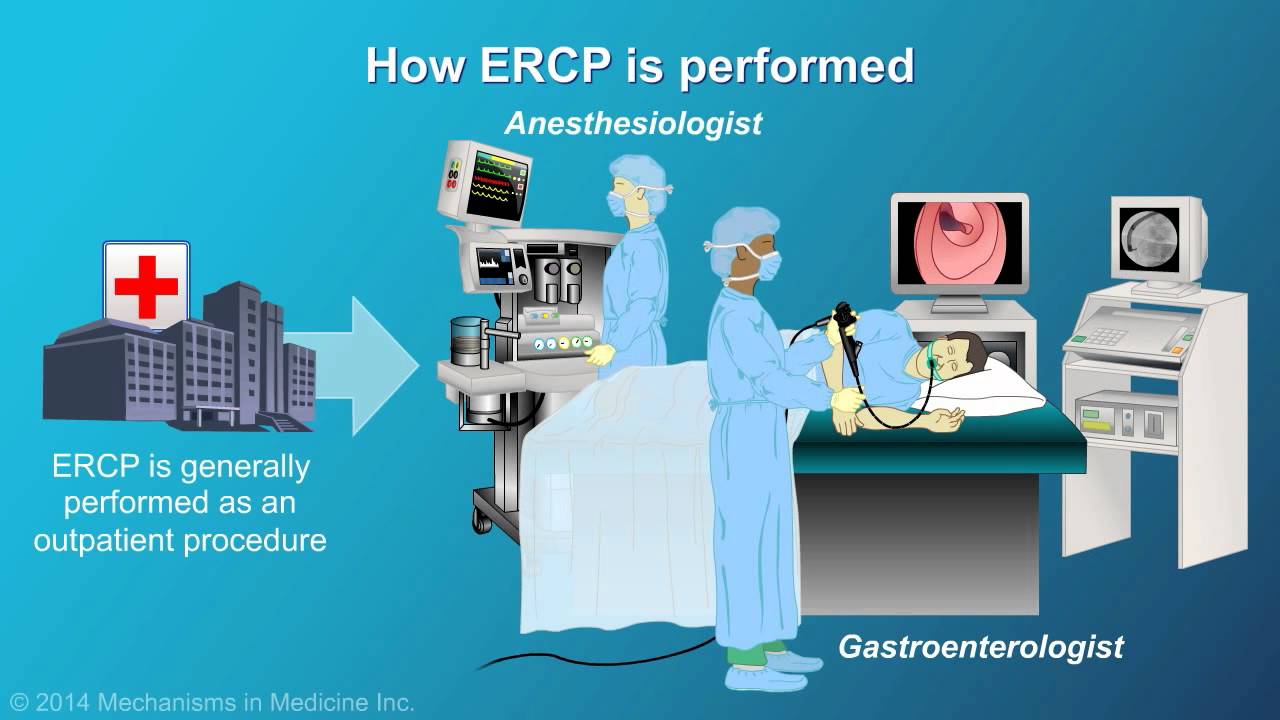
Should I remove my gallbladder if I have stones?
If your gallstones aren’t causing symptoms, there’s usually no need for you to have surgery. You’ll only need it if a stone goes into, or blocks, one of your bile ducts. This causes what doctors call a “gallbladder attack.” It’s an intense, knife-like pain in your belly that can last several hours.
Can you have a stone in the bile duct without a gallbladder?
About 1 in 7 people with gallstones will develop stones in the common bile duct. This is the small tube that carries bile from the gallbladder to the intestine. Risk factors include a history of gallstones. However, choledocholithiasis can occur in people who have had their gallbladder removed.
Related searches to What is ERCP used to diagnose?
- ercp test cost
- what is ercp used to diagnose
- what does ercp check for
- ercp stent
- what can an ercp find
- what can ercp diagnose
- what does an ercp test show
- ercp procedure steps
- ercp procedure video
- ercp procedure to remove gallstones
- ercp vs mrcp
- ercp pancreatitis
- how do you perform an ercp
- ercp procedure complications
- ercp procedure recovery time
Information related to the topic What is ERCP used to diagnose?
Here are the search results of the thread What is ERCP used to diagnose? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is ERCP used to diagnose?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.