Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is faulting in geography class 6?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Faulting happens when the Earth’s crust completely breaks and slides past each other. Rocks along a fault tend to move in opposite directions. As the overlying rock strata press them, the friction locks them together. Faulting results in the formation of block mountains and river valleys like the Narmada, Tapi.A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake – or may occur slowly, in the form of creep.Faults are cracks in the earth’s crust along which there is movement. These can be massive (the boundaries between the tectonic plates themselves) or very small. If tension builds up along a fault and then is suddenly released, the result is an earthquake.
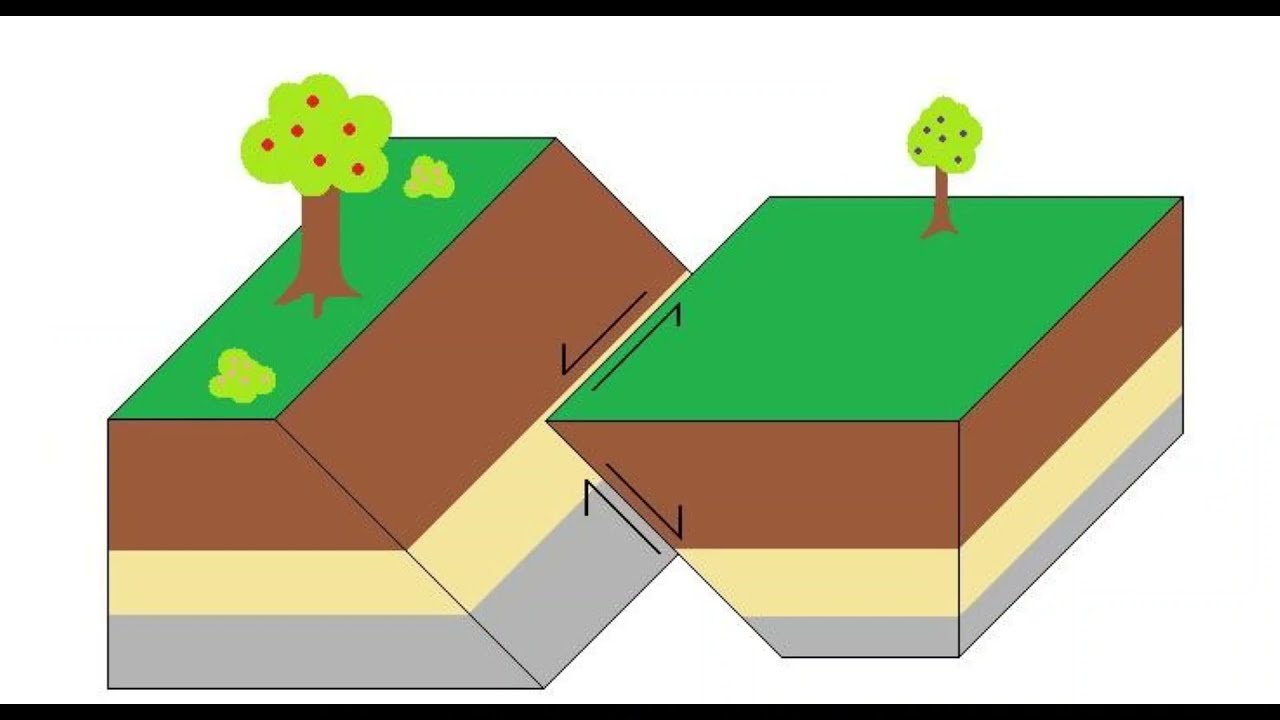
What is a faulting in geography?
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake – or may occur slowly, in the form of creep.
What is faulting of the earth?
Faults are cracks in the earth’s crust along which there is movement. These can be massive (the boundaries between the tectonic plates themselves) or very small. If tension builds up along a fault and then is suddenly released, the result is an earthquake.
Faulting
Images related to the topicFaulting

What is folding and faulting in geography?
Folds are bends in the rocks that are due to compressional forces. Faults are due to tensional forces along which displacements of rocks take pace. Folding occurs when compressional force is applied to rocks that are ductile or flexible.
What is faulting mean in science?
Scientific definitions for fault
fault. [ fôlt ] A fracture in a rock formation along which there has been movement of the blocks of rock on either side of the plane of fracture. Faults are caused by plate-tectonic forces.
What is an example of faulting?
The San Andreas Fault is the world’s most famous; it splits California between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate and moved 20 feet (6 m) in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. These types of faults are common where land and ocean plates meet.
How fault is formed?
A fault is formed in the Earth’s crust as a brittle response to stress. Generally, the movement of the tectonic plates provides the stress, and rocks at the surface break in response to this. Faults have no particular length scale.
What is fault sentence?
Fault sentence example. Don’t dare to say it was her fault . It’s all your fault , you know. I am afraid I find fault with the poem as much as I enjoy it.
See some more details on the topic What is faulting in geography class 6? here:
Faulting & Fault in Geography – Definition, Types, Features …
The movement of the part of the Earth’s crust along the line or fault is known as faulting. Block mountains are formed because of faulting.
What is a fault and what are the different types? – USGS.gov
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other.
Difference between Folding and Faulting in Tabular Format
A fault is formed in the Earth’s crust as a brittle response to stress. Generally, the movement of the tectonic plates provides the stress, and rocks at the …
fault | Definition & Types – Encyclopedia Britannica
fault, in geology, a planar or gently curved fracture in the rocks of Earth’s crust, where compressional or tensional forces cause relative displacement of …
What is fault and its types?
Fault is a fracture or crack where two rock blocks slide past one to another. If this movement may occur rapidly, it can be causes earthquike or slowly, in the form of creep. Types of faults include strike-slip faults, normal faults, reverse faults, thrust faults, and oblique-slip faults.
What is the difference between a fault and earthquake?
As nouns the difference between fault and earthquake
is that fault is a defect; something that detracts from perfection while earthquake is a shaking of the ground, caused by volcanic activity or movement around geologic faults.
What is folding and faulting Brainly?
Brainly User. Answer: The difference between folding and faulting is that folding is the pressure of converging plates causing the crust to fold and buckle, resulting in the creation of mountains and hills and faulting is where cracks in the earth’s rock are created because of different movement of tectonic plates.
What is folding in geography?
Folding is a concept that embraces all geologic processes by which surfaces in rocks become curved during deformation. Since folds are permanent deformation structures with no or little loss of cohesion of the folded layer, folding refers to the essentially slow, ductile behaviour of relatively soft and/or hot rocks.
What is folding class 7?
Explanation: Folding is a result of the force of compression when two lithospheric plates collide during a convergent plate movement. This causes the lifting and folding of the rock layers on the Earth’s crust leading to the formation of fold mountains.
Faults Faulting | Definition Types of Faults in Geology | Formation of Faults
Images related to the topicFaults Faulting | Definition Types of Faults in Geology | Formation of Faults

What is the difference between folding and faulting?
1. Folding occurs when the Earth’s rock layers become folded. Faulting occurs when the Earth’s crust gets cracked forming a fault.
Does faulting cause earthquakes?
Earthquakes are the result of sudden movement along faults within the Earth. The movement releases stored-up ‘elastic strain’ energy in the form of seismic waves, which propagate through the Earth and cause the ground surface to shake.
What happens in the process of faulting?
Faulting happens when the Earth’s crust completely breaks and slides past each other. Whether the Earth’s crust experiences a fold or fault will depend on the material it is made out of in that area.
What is an example of a fault in geography?
Well-known terrestrial examples include the San Andreas Fault, which, during the San Francisco earthquake of 1906, had a maximum movement of 6 metres (20 feet), and the Anatolian Fault, which, during the İzmit earthquake of 1999, moved more than 2.5 metres (8.1 feet).
What is a fault earthquake?
Earthquakes occur on faults. A fault is a thin zone of crushed rock separating blocks of the earth’s crust. When an earthquake occurs on one of these faults, the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other. Faults can be centimeters to thousands of kilometers long.
What are the 3 faults?
There are three main types of fault which can cause earthquakes: normal, reverse (thrust) and strike-slip.
How faults and folds are formed?
Figure 10.6: Rocks that were originally deposited in horizontal layers can subsequently deform by tectonic forces into folds and faults. Folds constitute the twists and bends in rocks. Faults are planes of detachment resulting when rocks on either side of the displacement slip past one another.
Do faults create mountains?
Fault-block mountains are formed by the movement of large crustal blocks along faults formed when tensional forces pull apart the crust (Figure 3). Tension is often the result of uplifting part of the crust; it can also be produced by opposite-flowing convection cells in the mantle (see Figure 1).
Which landforms is formed due to faulting?
A Rift-valley is formed due to faulting.
The cracks in the surface of the earth are found where faulting takes place. A fault is a planar fracture (crack) in a volume of the earth’s crust, across which there has been significant displacement of a block of crust.
How do you use at fault?
Responsible for a mistake, trouble, or failure; deserving blame. For example, At least three cars were involved in the accident, so it was hard to determine which driver was at fault, or He kept missing the target and wondered if the sight on his new rifle was at fault.
Types of Faults in Geology
Images related to the topicTypes of Faults in Geology

How can I use make in a sentence?
[M] [T] I’m going to make a cake for Mary’s birthday. [M] [T] He tried to make his wife happy, but couldn’t. [M] [T] I asked her to make four copies of the letter. [M] [T] I checked to make sure that he was still alive.
How do you use talk in a sentence?
[M] [T] I can talk about anything with my best friend. [M] [T] She was determined never to talk to him again. [M] [T] Tom doesn’t really talk about his problems much. [M] [T] I’ll talk to him at the earliest possible moment.
Related searches to What is faulting in geography class 6?
- what is geography class 6
- what is faulting in geography class 6 rapids
- fault plane
- types of faults
- fault earthquake
- what is faulting in geography
- what is fault in science
- what is reverse fault
- normal fault
- strike-slip fault
- what is faulting in geography class 6 and 7
- what is grid in geography class 6
- what is faulting in geography class 6 quizlet
- what is faulting in geography class 9
- what is faulting in geography class 6 felony
- what is the meaning of faulting in geography
- what is faulting in geography class 6
- strike slip fault
Information related to the topic What is faulting in geography class 6?
Here are the search results of the thread What is faulting in geography class 6? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is faulting in geography class 6?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.