Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is folding in geography class 9?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Folding: A fold is a bend in the rock strata resulting from compression of an area in the Earth’s crust. Folding occurs when the lithospheric plate pushes up against another plate. … Fold mountains such as the Himalayas have been formed due to folding.Folding is a concept that embraces all geologic processes by which surfaces in rocks become curved during deformation. Since folds are permanent deformation structures with no or little loss of cohesion of the folded layer, folding refers to the essentially slow, ductile behaviour of relatively soft and/or hot rocks.1 : to lay one part over another part of fold a letter. 2 : to reduce the length or bulk of by doubling over fold a tent. 3 : to clasp together : entwine fold the hands. 4 : to clasp or enwrap closely : embrace.

What is folding in geography?
Folding is a concept that embraces all geologic processes by which surfaces in rocks become curved during deformation. Since folds are permanent deformation structures with no or little loss of cohesion of the folded layer, folding refers to the essentially slow, ductile behaviour of relatively soft and/or hot rocks.
What do you mean by folding?
1 : to lay one part over another part of fold a letter. 2 : to reduce the length or bulk of by doubling over fold a tent. 3 : to clasp together : entwine fold the hands. 4 : to clasp or enwrap closely : embrace.
Folding | Types of Folding | Characteristics of Folding | Formation of Mountains
Images related to the topicFolding | Types of Folding | Characteristics of Folding | Formation of Mountains

What is folding class 9 SST?
(i) Folding: A bend in the rock strata resulting from. compression of an area of the earth’s crust.
What is folding in plate tectonics?
Folding- Folding occurs when tectonic processes put stress on a rock, and the rock bends, instead of breaking. This can create a variety of landforms as the surfaces of the folded rocks are eroded. Anticlines are folds shaped like an arch, and synclines are shaped like the letter ‘U. ‘
What is folding and faulting?
Folds are bends in the rocks that are due to compressional forces. Faults are due to tensional forces along which displacements of rocks take pace. Folding occurs when compressional force is applied to rocks that are ductile or flexible.
What is folding of mountains?
Fold mountains are created where two or more of Earth’s tectonic plates are pushed together. At these colliding, compressing boundaries, rocks and debris are warped and folded into rocky outcrops, hills, mountains, and entire mountain ranges. Fold mountains are created through a process called orogeny.
What is folding in earthquake?
Folding is the bend in the rock in response to the compressional forces. This creates ripples on the surface from which high and low points are created. High points are called anticlines and low points are called synclines. Fold mountains are a result of folding.
See some more details on the topic What is folding in geography class 9? here:
define the following a folding b faulting | 9cmrehe88
Folding: A fold is a bend in the rock strata resulting from compression of an area in the Earth’s crust. Folding occurs when the …
Difference between Folding and Faulting in Tabular Format
Folding and faulting are two terms in geology used to describe the changes the surface of the earth goes through. In structural geology, a fold is a stack …
What is folding and faulting in geography? – AnswersToAll
Folding: A fold is a bend in the rock strata resulting from compression of an area in the Earth’s crust. Folding occurs when …
Differentiate between Folding and faulting – Geography
Folds are bends in the rocks that are due to compressional forces. Faults are formed due to tensional forces along which displacement of rock takes place.
What is folds and its types?
Types of Folds. Anticline: linear, strata normally dip away from axial center, oldest strata in center. Syncline: linear, strata normally dip toward axial center, youngest strata in center. Antiform: linear, strata dip away from axial center, age unknown, or inverted.
What are the example of folding?
Examples include vertical plunging folds and recumbent folds. Orogenic belts usually have regional anticlines and synclines. When the limbs of a major anticline are further folded into second-order and third-order anticlines (composite anticlines), it is called an anticlinorium.
What is folding in social?
In folding, the land between the two tectonic plates, acting towards each other, rises up. Fold mountains such as the Himalayas have been formed due to folding. Faulting: At times, when the crustal rocks are subjected to horizontal compressional pressure, they do not get folded.
What is folding and faulting Upsc?
1. Folding occurs when the Earth’s rock layers become folded. Faulting occurs when the Earth’s crust gets cracked forming a fault. 2.
What is folding class 7?
Explanation: Folding is a result of the force of compression when two lithospheric plates collide during a convergent plate movement. This causes the lifting and folding of the rock layers on the Earth’s crust leading to the formation of fold mountains.
TMart Science Folding and Faulting
Images related to the topicTMart Science Folding and Faulting
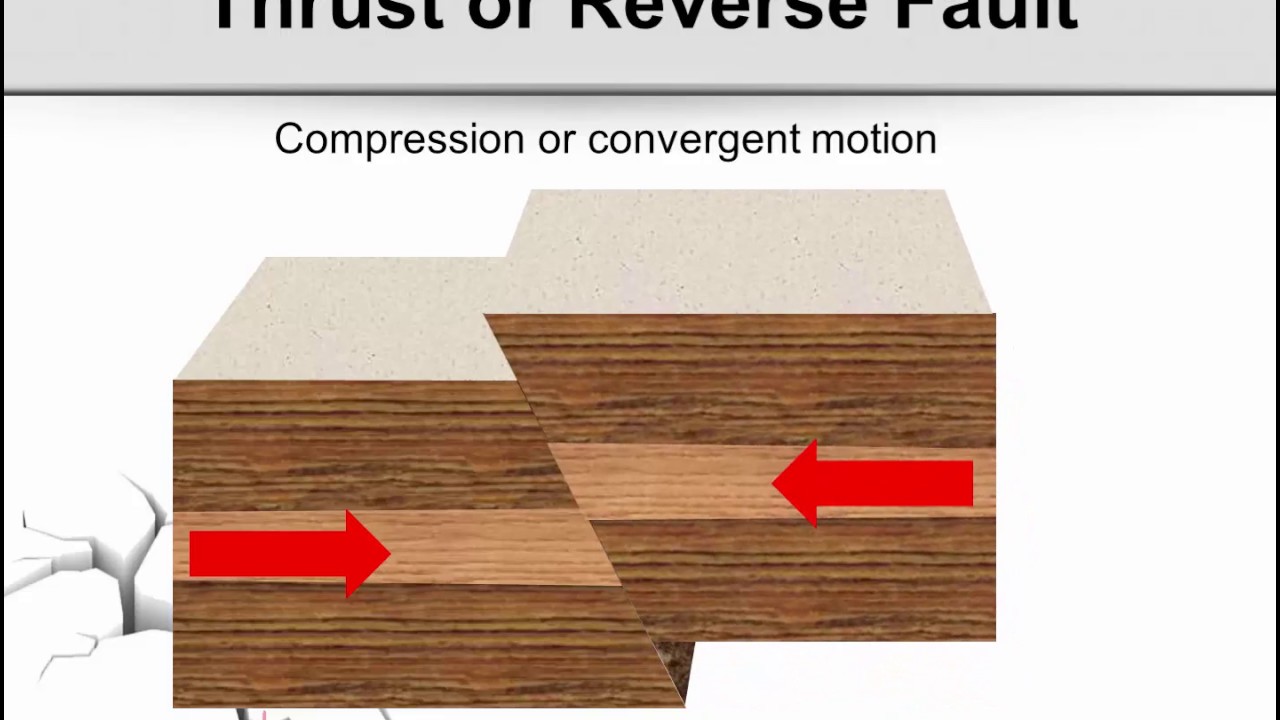
What are causes of folding?
Folding may be either due to tectonic causes or due to non-tectonic causes. By tectonic causes is understood folding taking place as a response of the rocks to various forces originating from within the body of the Earth.
How does folding in rocks occur?
Folds in the rock are formed about the stress field in which the rocks are located and the rheology, or method of response to stress, of the rock at the time at which the stress is applied. The rheology of the layers being folded determines characteristic features of the folds that are measured in the field.
What is faulting in geography class 9?
When the crustal rocks are subjected to horizontal compressional pressure, they develop fractures or cracks along the line of weakness. These lines of fracture are known as faults. In faulting, blocks of rocks may move up or down.
What is folding and faulting Brainly?
Brainly User. Answer: The difference between folding and faulting is that folding is the pressure of converging plates causing the crust to fold and buckle, resulting in the creation of mountains and hills and faulting is where cracks in the earth’s rock are created because of different movement of tectonic plates.
What is faulting in geography?
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake – or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers.
What is the difference between folds and faults Brainly?
Folds are formed when heat and pressure is applied to the rock. The higher the temperature, the more pliable rocks become. Folds are more likely to occur when the deformation caused by the compression is applied slowly. … Faults are defined as the displacement of rock that were once connected along a fault line.
What are fold mountains Class 9?
Fold mountains are formed when two or more of Earth’s tectonic plates are pushed together. At this point of collision, the compressing boundaries, rocks and debris are warped and folded into rocky outcrops, hills, mountains, and entire mountain ranges.
What are fold mountains 6?
(1) Fold mountains: When the land gets uplifted because of the compressional forces acting on it, a fold mountain is formned. The Himalayas (India) and the Rockies (USA) are examples of fold mountains.
Why are the fold mountains called so?
Fold mountains are called so because of the result of large- scale earth movements caused by stresses in the earth’s crust. Such stresses may be caused by weight of the overlying rocks movements in the mantle the expansion or contraction of some part of the earth etc.
How does folding and faulting cause earthquakes?
folding and faulting creates a abnormal tension inside the earth’s crust which leads to unequal levelling of the mantle and hence it forms pressure on the surface of earth. If such tension is exerted under the land of any reservoir, it leads to collapsing of it.
How fold mountains are formed
Images related to the topicHow fold mountains are formed

What is the difference between faults and fold?
1. Figure 10.6: Rocks that were originally deposited in horizontal layers can subsequently deform by tectonic forces into folds and faults. Folds constitute the twists and bends in rocks. Faults are planes of detachment resulting when rocks on either side of the displacement slip past one another.
What are the three types of folds?
There are three basic types of folds (1) anticlines, (2) synclines and (3) monoclines.
Related searches to What is folding in geography class 9?
- what is sst geography
- what is folding in geography class 9
- what is folding and faulting in geography
- types of folding and faulting
- what is folds in geography
- what is strait in geography class 9
- importance of folding in geography
- what does folding mean in geography
- class 9 geography chapter name
- types of folds and faults
- fold vs fault
- types of folding in geography
- what is faulting in geography class 9
- define folding in geology
- types of folds
Information related to the topic What is folding in geography class 9?
Here are the search results of the thread What is folding in geography class 9? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is folding in geography class 9?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.