Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is the effusion formula?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
You can write the formula for Graham’s law of diffusion or effusion of gases as: rate 1 / rate 2 = √ (mass 2 / mass 1) , where: rate 1 and rate 2 – Rates of effusion or diffusion of Gas 1 and 2, respectively, measured moles per unit time.Effusion : Example Question #7
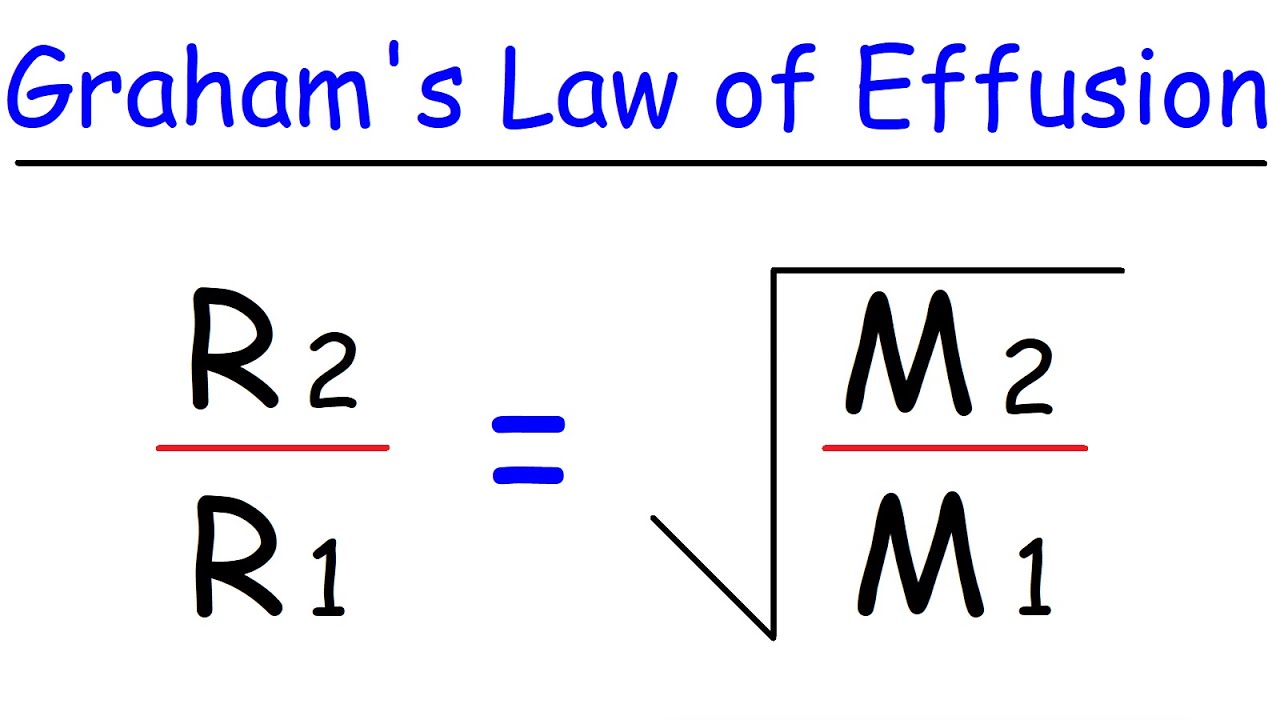
The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular weight of the gas. \displaystyle \frac{\text{Rate}_1}{\text{Rate}_2}=\sqrt{\frac{M_2}{M_1}} The lighter a gas is, the faster it will effuse; the heavier a gas is, the slower it will effuse.Effusion is defined as a loss of material across a boundary. A common example of effusion is the loss of gas inside of a balloon over time. The rate at which gases will effuse from a balloon is affected by a number of factors.

Table of Contents
What is effusion rate?
Effusion : Example Question #7
The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular weight of the gas. \displaystyle \frac{\text{Rate}_1}{\text{Rate}_2}=\sqrt{\frac{M_2}{M_1}} The lighter a gas is, the faster it will effuse; the heavier a gas is, the slower it will effuse.
What is effusion example?
Effusion is defined as a loss of material across a boundary. A common example of effusion is the loss of gas inside of a balloon over time. The rate at which gases will effuse from a balloon is affected by a number of factors.
Graham’s Law of Effusion Practice Problems, Examples, and Formula
Images related to the topicGraham’s Law of Effusion Practice Problems, Examples, and Formula

What is the law of effusion?
Graham’s law of effusion (also called Graham’s law of diffusion) was formulated by Scottish physical chemist Thomas Graham in 1848. Graham found experimentally that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of its particles.
What is effusion in chemistry?
Effusion occurs when a gas passes through an opening that is smaller than the mean free path of the particles, that is, the average distance traveled between collisions. Effectively, this means that only one particle passes through at a time.
What is the formula for diffusion?
Diffusion coefficient is the proportionality factor D in Fick’s law (see Diffusion) by which the mass of a substance dM diffusing in time dt through the surface dF normal to the diffusion direction is proportional to the concentration gradient grad c of this substance: dM = −D grad c dF dt.
What is the formula of rms velocity?
v rms = v 2 – = 3 k B T m . The rms speed is not the average or the most likely speed of molecules, as we will see in Distribution of Molecular Speeds, but it provides an easily calculated estimate of the molecules’ speed that is related to their kinetic energy.
What is the effusion rate of oxygen?
From Graham’s law, we can use the molar mass of each gas: rate of effusion of hydrogenrate of effusion of oxygen=√32g mol−1 √2g mol−1 =√16√1=41 rate of effusion of hydrogen rate of effusion of oxygen = 32 g mol − 1 2 g mol − 1 = 16 1 = 4 1 Hydrogen effuses four times as rapidly as oxygen.
See some more details on the topic What is the effusion formula? here:
Effusion and Diffusion of Gases | General College Chemistry I
From Graham’s law, we can use the molar mass of each gas: rate of effusion of hydrogenrate of effusion of oxygen=√32g mol−1 √2g mol−1 =√16√1=41 rate of …
2.9: Graham’s Laws of Diffusion and Effusion – Chemistry …
The rate of effusion of a gaseous substance is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Graham’s law is an empirical …
Effusion – Wikipedia
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes from a container through a hole of diameter considerably …
AP Chemistry : Effusion – Varsity Tutors
The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular weight of the gas.
What is the formula for partial pressure?
As has been mentioned in the lesson, partial pressure can be calculated as follows: P(gas 1) = x(gas 1) * P(Total); where x(gas 1) = no of moles(gas 1)/ no of moles(total).
What is Graham’s Law equation for diffusion?
Graham’s law states that the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. See this law in equation form below. r ∝ 1/(M)½ or. r(M)½ = constant.
What is Graham Law of effusion?
Graham’s law states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely propertional to the square root of the density of the gas.
What is ideal gas equation derive it?
The ideal gas equation is formulated as: PV = nRT. In this equation, P refers to the pressure of the ideal gas, V is the volume of the ideal gas, n is the total amount of ideal gas that is measured in terms of moles, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature.
Graham’s Law of Effusion
Images related to the topicGraham’s Law of Effusion
What is the kinetic gas equation?
Solution : Kinetic gas equation `PV=1/3mn u_(rms)^2` <br> where <br> P=pressure of the gas <br> V=Volume of the gas <br> m= mass of one molecule of the gas <br> n= number of molecules of the gas <br> `u_(rms)`=RMS speed of the gas molecules.
Which of the following gases is the heaviest O2 ch4 co2 cl2 O2 ch4 co2 cl2?
Answer: The heaviest gas is chlorine gas .
What is the effusion rate of N2?
This ratio of effusion rates follows the pattern that the gas with the lesser molar mass or density has a greater rate of effusion. Adjusting to the appropriate significant figures, we find that the rate is 1.07. This tells us that N2 is 1.07 times as fast as O2. It is faster, but not by much.
What is diffusion and effusion?
Diffusion refers to the ability of the gases to mix without needing a bulkier motion. On the other hand, effusion refers to the ability of the gases for travelling or escaping through a tiny hole having a smaller aperture and from a place having a higher concentration to a lower concentration.
What is Fick’s first law?
Fick’s First Law states that flux is proportional to the CONCENTRATION GRADIENT, and the proportionality constant D is the DIFFUSION COEFFICIENT.
How do you calculate RMS?
Divide the sum of the squares by the number of numbers. 83 divided by 3 is 27.67. Take the square root of the sum divided by the number of numbers. The square root of 27.67 is 5.26, so for the series 5, -3 and -7, the RMS is 5.26.
What is RMS velocity of gas?
Gases consist of atoms or molecules that move at different speeds in random directions. The root mean square velocity (RMS velocity) is a way to find a single velocity value for the particles. The average velocity of gas particles is found using the root mean square velocity formula: μrms = (3RT/M)½
What is RMS speed in physics?
Solution : RMS speed is defined as the square root of the mean of the square of speeds of all molecules.
What is the rate of diffusion?
The greater the difference in concentration, the quicker the rate of diffusion. The higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy the particles will have, so they will move and mix more quickly. The greater the surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion.
Graham’s Law of Effusion (Diffusion) + Example
Images related to the topicGraham’s Law of Effusion (Diffusion) + Example

What is the rate of effusion of so2 compared to no2?
The rate of effusion of SO2 is 0.85 times the rate of effusion of NO2, which is logical because SO2 is more massive than NO2, and moves more slowly, on average.
What is the effusion rate of helium?
Helium (M = 4.00 g/mol) effuses much more rapidly than ethylene oxide (M = 44.0 g/mol).
Related searches to What is the effusion formula?
- effusion rate calculator
- rate of diffusion formula
- graham’s law of effusion formula
- rate of effusion formula with temperature
- grahams law of effusion formula
- effusion chemistry
- rate of effusion units
- effusion chemistry example
- what is the effusion formula in chemistry
- what is the effusion formula of a gas
- what is effusion
Information related to the topic What is the effusion formula?
Here are the search results of the thread What is the effusion formula? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is the effusion formula?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
