Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
An APC, such as a macrophage, engulfs and digests a foreign bacterium. An antigen from the bacterium is presented on the cell surface in conjunction with an MHC II molecule Lymphocytes of the adaptive immune response interact with antigen-embedded MHC II molecules to mature into functional immune cells.Antigen processing and presentation is the process by which protein antigen is ingested by an antigen-presenting cell (APC), partially digested into peptide fragments and then displayed on the surface of the APC associated with an antigen-presenting molecule such as MHC class I or MHC class II, for recognition by …The contribution of dendritic cell (DC) antigen cross-presentation to the activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes for immune defense against tumors, viruses, and intracellular pathogens has been recognized widely.

What happens during antigen presentation?
Antigen processing and presentation is the process by which protein antigen is ingested by an antigen-presenting cell (APC), partially digested into peptide fragments and then displayed on the surface of the APC associated with an antigen-presenting molecule such as MHC class I or MHC class II, for recognition by …
What do antigen-presenting macrophages activate?
The contribution of dendritic cell (DC) antigen cross-presentation to the activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes for immune defense against tumors, viruses, and intracellular pathogens has been recognized widely.
Antigen-Presenting Cells (Macrophages, Dendritic Cells and B-Cells)
Images related to the topicAntigen-Presenting Cells (Macrophages, Dendritic Cells and B-Cells)

What is the main goal of antigen presentation?
Antigen presentation serves to ensure adaptive immune responses are initiated to invading microorganisms. Therefore, in an effort to survive in the host, pathogens target antigen presentation pathways and disable their function.
What does antigen-presenting cells mean?
Definition. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are a heterogeneous group of immune cells that mediate the cellular immune response by processing and presenting antigens for recognition by certain lymphocytes such as T cells. Classical APCs include dendritic cells, macrophages, Langerhans cells and B cells.
How are antigen-presenting cells activated?
T cells must be activated before they can divide and perform their function. This is achieved by interacting with a professional APC which presents an antigen recognized by their T cell receptor. The APC involved in activating T cells is usually a dendritic cell.
What is the function of antigen-presenting cells quizlet?
Cells such as B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells that can present exogenous antigens to naive or memory T cells, activating them.
What is the role of antigen-presenting cells in immunity?
Antigen-Presenting Cells in the Eye and Ocular Surface
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are critical for the initiation of adaptive immune responses and for maintenance of peripheral tolerance. APCs are strategically positioned as immune sentinels ready to respond to invading pathogens in peripheral tissues.
See some more details on the topic What will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage? here:
Antigen Cross-Presentation by Macrophages – Frontiers
The contribution of dendritic cell (DC) antigen cross-presentation to the activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes for immune defense against tumors, …
Antigen-presenting cell – Wikipedia
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; …
What is the role of the macrophage during antibody formation?
One of the most important functions performed by macrophages during the induction of an immune response may be the presentation of antigen to antibody-forming cell precursors in a molecular form appropriate for cell activation.
ANTIGEN PROCESSING AND PRESENTATION | Immunology
Images related to the topicANTIGEN PROCESSING AND PRESENTATION | Immunology

How are antigens processed and presented to T cells?
The usual process of antigen presentation through the MHC I molecule is based on an interaction between the T-cell receptor and a peptide bound to the MHC class I molecule. There is also an interaction between the CD8+ molecule on the surface of the T cell and non-peptide binding regions on the MHC class I molecule.
How are macrophages produced?
Most macrophages are derived from bone marrow precursor cells that develop into monocytes. These are formed in the bone marrow from stem cells of the granulocytic–monocytic lineage that are exposed to cytokines such as the granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-3 (IL-3).
Why is a macrophage referred to as an antigen-presenting cell?
Explain why that is an appropriate term. A macrophage is a cell of the innate immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, and then presents fragments on its surface as a signal. Such signals are picked up by other cells of the adaptive immune system, hence antigen-presenting cell.
What types of immunity are stimulated by antigen presentation?
…
- IgG- responsible for resistance against virus, bacteria, toxins.
- IgE- attaches to individual molecule to exposed surfaces of basophils/mast cells.
- IgD- binds antigens in extracellular fluid, play role in sensitization of B cells.
Which of the following are antigen presenting cells quizlet?
Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells that engulf antigens and then present fragments of them to their own surfaces, where T cells can recognize them.
How do APCs work to activate the adaptive response?
An APC, such as a macrophage, engulfs and digests a foreign bacterium. An antigen from the bacterium is presented on the cell surface in conjunction with an MHC II molecule Lymphocytes of the adaptive immune response interact with antigen-embedded MHC II molecules to mature into functional immune cells.
Antigen Presenting Cells – Few basic differences
Images related to the topicAntigen Presenting Cells – Few basic differences
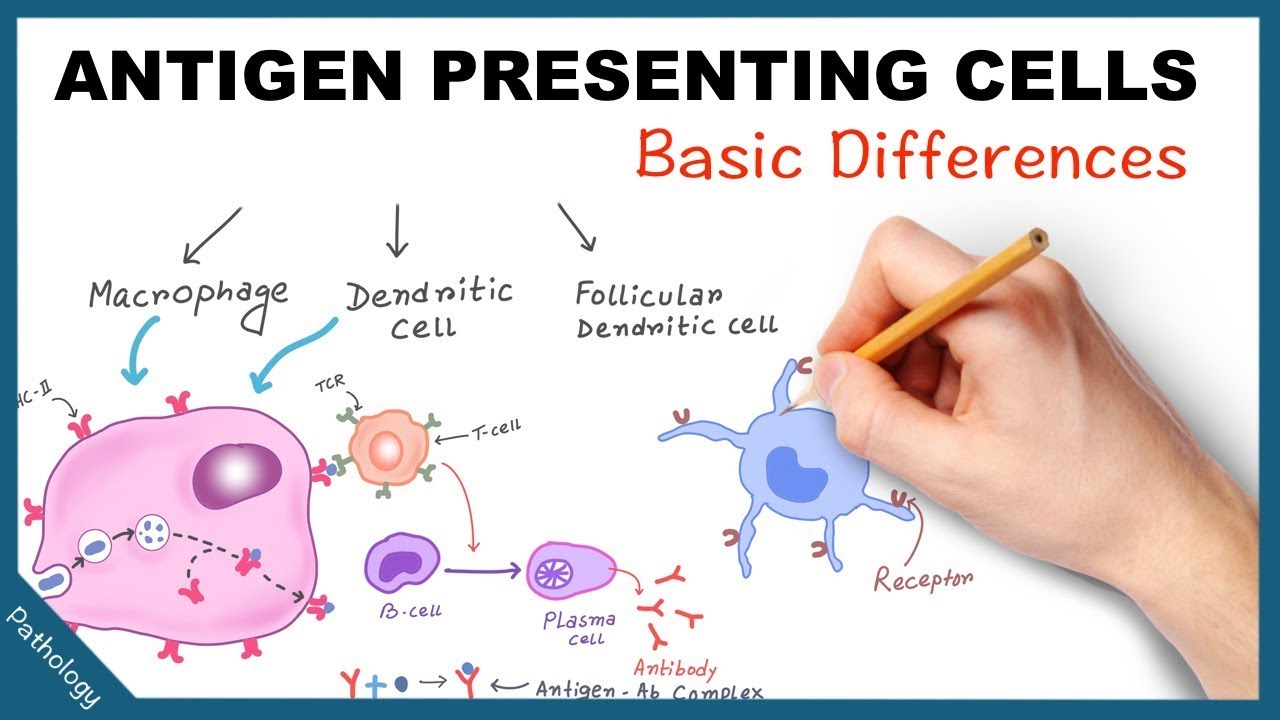
What is the interaction between macrophages and T lymphocytes during the presentation of antigen?
Macrophages interact with T cells in order to bring about T cell activation in target organs, and are themselves activated by inflammatory messenger molecules (cytokines) produced by the T cells. Macrophages produce toxic chemicals, such as nitric oxide, that can kill surrounding cells.
Which of the following are the main antigen-presenting cells?
Dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells are the principal antigen-presenting cells for T cells, whereas follicular dendritic cells are the main antigen-presenting cells for B cells. The immune system contains three types of antigen-presenting cells, i.e., macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells.
Related searches to What will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage?
- antigen presentation
- antigen-presenting cells are
- are neutrophils antigen-presenting cells
- antigen presenting cells are
- why is antigen presentation important in fighting infection
- what will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage
- are neutrophils antigen presenting cells
- do macrophages present antigens to b cells
- why is antigen-presentation important in fighting infection?
- what is meant by antigen presentation and how do antigen presenting cells present antigens
- macrophage antigen presentation assay
- antigen cross presentation
Information related to the topic What will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage?
Here are the search results of the thread What will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What will occur after presentation of antigen by a macrophage?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.