Are you looking for an answer to the topic “When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion the argument is valid?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism, if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion, the argument is valid. In a Venn diagram, a shaded area indicates an empty class. The first step in diagramming a categorical statement is drawing two overlapping circles.If a categorical syllogism is valid, its diagram should reflect what the conclusion asserts. In a categorical syllogism, the middle term appears in each premise but not the conclusion. In a categorical syllogism, the major term appears as the predicate term in the conclusion and also in one of the premises.If one of the premises is a universal proposition, diagram it first. (If both premises are universal, it does not matter which one you diagram first.) This is because you want to eliminate any place where an x, which represents a particular proposition, cannot go.
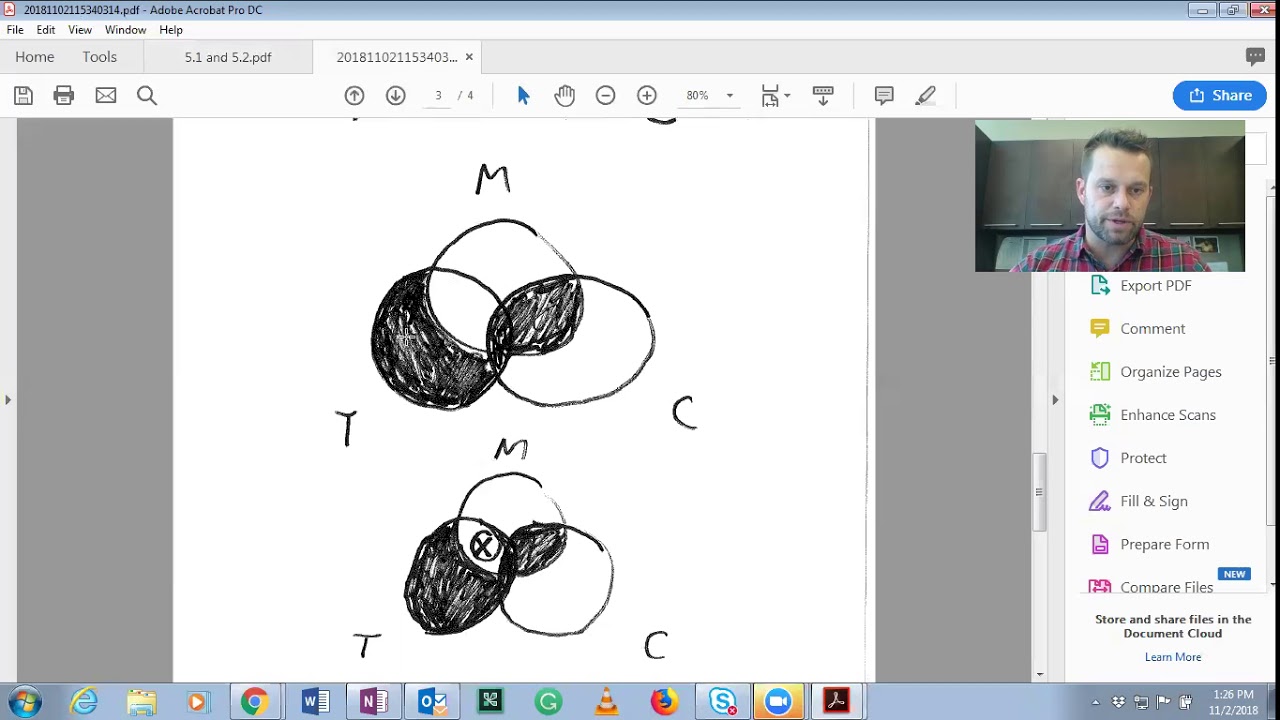
How do you tell if a categorical syllogism is valid its diagram should reflect what the conclusion asserts?
If a categorical syllogism is valid, its diagram should reflect what the conclusion asserts. In a categorical syllogism, the middle term appears in each premise but not the conclusion. In a categorical syllogism, the major term appears as the predicate term in the conclusion and also in one of the premises.
When diagramming a categorical syllogism with a universal premise and a particular premise Why is it important to diagram the universal premise first?
If one of the premises is a universal proposition, diagram it first. (If both premises are universal, it does not matter which one you diagram first.) This is because you want to eliminate any place where an x, which represents a particular proposition, cannot go.
Determining Validity of Categorical Syllogisms Using Venn Diagrams
Images related to the topicDetermining Validity of Categorical Syllogisms Using Venn Diagrams

Is an argument consisting of exactly three categorical propositions two premises and a conclusion?
The Structure of Syllogism
A categorical syllogism is an argument consisting of exactly three categorical propositions (two premises and a conclusion) in which there appear a total of exactly three categorical terms, each of which is used exactly twice.
What is the main purpose of translating categorical statements into standard form what steps are involved in such translations?
Translations and Standard Form
Categorical statements must be translated into standard form before you can work with them. Translating involves identifying terms and ensuring that they designate classes and determining the quantifiers.
When using a Venn diagram to test a categorical syllogism for validity we should draw?
In using Venn diagrams to determine the validity of a categorical syllogism, we draw three overlapping circles to represent the minor, middle and major terms. The three circles are divided into seven areas. A categorical syllogism is valid if its two premises together imply the conclusion.
How do you determine the validity of categorical syllogism?
- The argument must have exactly three terms.
- Every term must be used exactly twice.
- A term may be used only once in any premise.
- The middle term of a syllogism must be used in an unqualified or universal sense.
How many circles does a Venn diagram that tests a categorical syllogism have?
Three-circle diagrams, in which each circle intersects the other two, are used to represent categorical syllogisms, a form of deductive argument consisting of two categorical premises and a categorical conclusion.
See some more details on the topic When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion the argument is valid? here:
Chapter 7 Flashcards | Chegg.com
If a categorical syllogism is valid, its diagram should reflect the conclusion asserts. Tue. The first step in checking validity with Venn diagrams is to …
When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism – Course …
When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism, if the Venn diagram reflectsthe assertion in the conclusion, the argument is valid.a. Trueb. False.
Testing Syllogisms for Validity
Using Venn Diagrams. A syllogism, like any other type of argument is valid just in case it is not possible for the premises to be true and the conclusion …
PHI 103 Final Cat Logic Flashcards – Cram.com
in categorical statments, “some” means “at least one”. true ; when checking the validity of a categorical syllogism, if the venn diagram reflects the assertion …
What are the rules of categorical syllogism?
1) The middle term must be distributed in at least one premise. 2) If a term is distributed in the conclusion, then it must be distributed in a premise. 3) A categorical syllogism cannot have two negative premises. 4) A negative premise must have a negative conclusion.
How can we determine if the statements just like presented are valid or not?
Valid: an argument is valid if and only if it is necessary that if all of the premises are true, then the conclusion is true; if all the premises are true, then the conclusion must be true; it is impossible that all the premises are true and the conclusion is false. Invalid: an argument that is not valid.
Can any standard for categorical syllogism be valid that contains exactly three terms each of which is distributed in both of its occurrences?
No, such a syllogism cannot be valid. If each of the three terms were distributed in both of its occurrences, all three of its propositions would have to be E propositions, and the mood of the syllogism would thus be EEE, which violates Rule 4, which forbids two negative premises.
Which one of the following is true with respect to the first figure of categorical syllogism?
Hence, the middle term is the subject of the major premise and the predicate of the minor premise, with respect to the first figure of a categorical syllogism.
Venn Diagrams and Testing Validity
Images related to the topicVenn Diagrams and Testing Validity
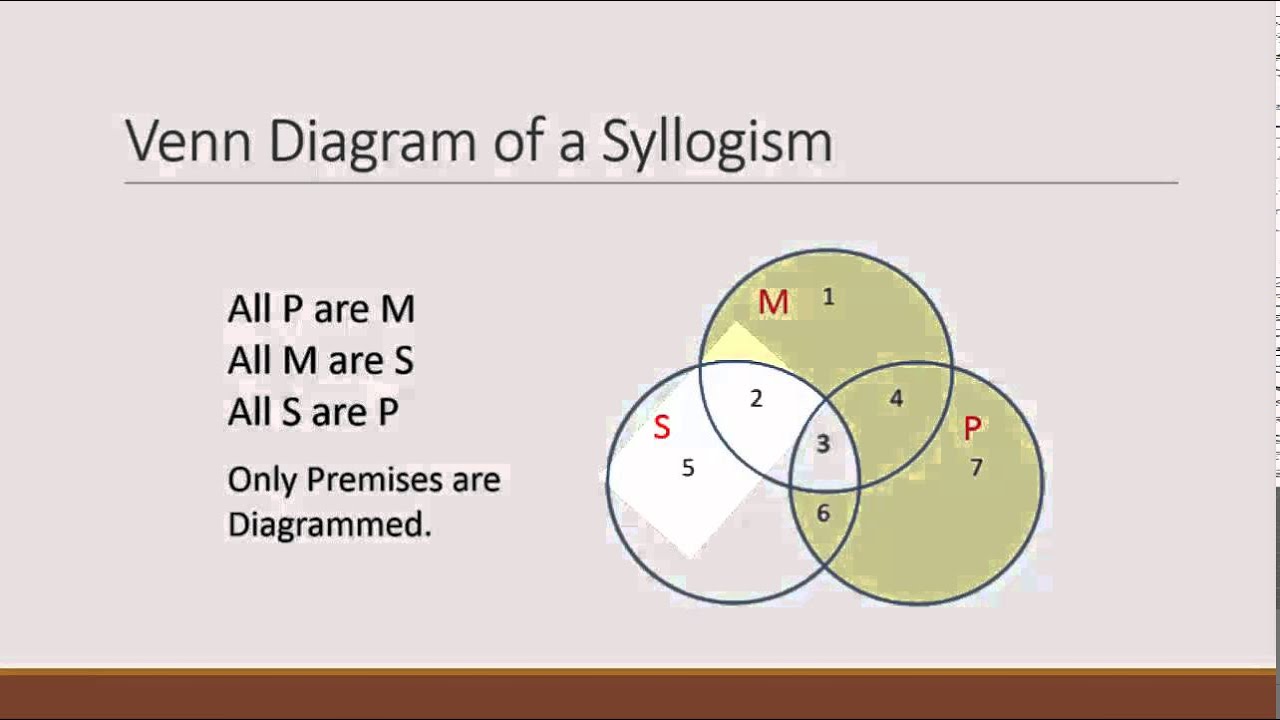
What are the characteristics of categorical syllogism?
- There must exactly three terms in a syllogism where all terms are used in the same respect & context. …
- The subject term and the predicate term ought to be a noun or a noun clause. …
- The middle term must be distributed at least once in the premises or the argument is invalid.
What is a Venn diagram representation of categorical statements?
A Venn diagram for one categorical statement consists of two interlocking circles placed in a box. The box, including the circles, represents the universe of discourse. The circle on the left represents the subject class; the circle on the right represents the predicate class.
How do you translate a categorical proposition to standard form?
- Rule 1: The subject and predicate terms must be the names of classes.
- Rule 2: Categorical propositions should have a form of the verb “to be” as the copula in the present tense.[1] …
- Rule 3: The quality and quantity indicators are set up from the meaning of the sentences.
How do you test for validity in a Venn diagram?
To sum up: To test a syllogism for validity, Venn diagram the premises. Inspect the diagram. If the diagram already represents the conclusion, then the argument is valid. If a representation of the conclusion is absent, the argument is invalid.
When you test a syllogism with a Venn diagram how do you diagram the conclusion?
- make the usual two circles. …
- Add a third overlapping circle on top. …
- Enter the information from the premises into the diagram.
- Then read it and see whether the conclusion can be read back out of it.
How do you determine the validity of evidence as basis for your conclusion?
- Look at the author’s credentials. For scholarly articles, this is usually pretty simple. …
- Review the article’s contents.
- Examine the evidence.
- Determine bias.
What makes a syllogism valid?
A syllogism is valid (or logical) when its conclusion follows from its premises. A syllogism is true when it makes accurate claims – that is, when the information it contains is consistent with the facts. To be sound, a syllogism must be both valid and true.
What are the information to consider in justifying whether an argument is valid or not?
In short, a deductive argument must be evaluated in two ways. First, one must ask if the premises provide support for the conclusion by examing the form of the argument. If they do, then the argument is valid. Then, one must ask whether the premises are true or false in actuality.
What are the rules of a Venn diagram?
A Venn diagram is a diagram that shows all possible logical relations between a finite collection of sets. The general addition rule is a way of finding the probability of a union of 2 events. It is P(A U B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A n B) Let A and B be subsets of Ω.
Testing the Validity of Syllogistic Forms Through Venn Diagram Technique II Venn Diagram
Images related to the topicTesting the Validity of Syllogistic Forms Through Venn Diagram Technique II Venn Diagram

What is the use of Venn diagram in testing?
Venn diagram validity tests provide a graphic tool for using this approach to testing for validity. A categorical syllogism is valid if, but only if, a diagram of its premises produces a diagram that expresses the propositional content of its conclusion.
What conditions must be considered in making a Venn diagram?
- A Venn diagram uses circles that overlap or don’t overlap to show the commonalities and differences among things or groups of things.
- Things that have commonalities are shown as overlapping circles while things that are distinct stand alone.
Related searches to When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion the argument is valid?
- in an a statement the words only and only if precede the
- a particular negative statement is designated by the letter
- in a categorical syllogism, the middle term appears in each premise but not the conclusion.
- in an a-statement the words only and only if precede the
- the pattern of all standard-form categorical statements is
- a syllogism is a deductive argument made up of
- the pattern of all standard form categorical statements is
- the easiest way to check the validity of a categorical syllogism is to
- the statement something is a breakfast only if its a meal is equivalent to an
- in a categorical syllogism the middle term appears in each premise but not the conclusion
- the basic unit of concern in categorical logic is the
- the easiest way to check the validity of a categorical syllogism is to…
Information related to the topic When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion the argument is valid?
Here are the search results of the thread When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion the argument is valid? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic When checking the validity of a categorical syllogism if the Venn diagram reflects the assertion in the conclusion the argument is valid?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.