Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which ECG lead looks at the lateral wall view?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
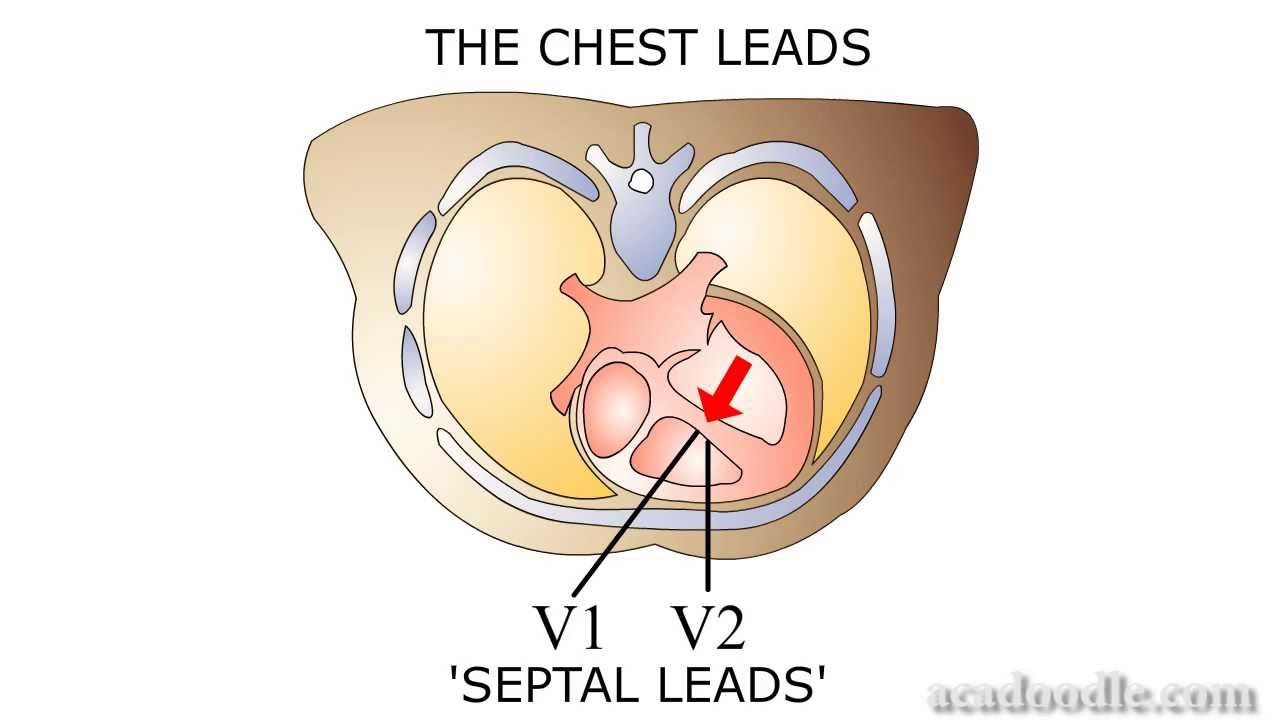
The septum is represented on the ECG by leads V1 and V2, whereas the lateral wall is represented by leads V5, V6, lead I and lead aVL.Leads II, III and aVF are leads that have their positive electrode located at the left foot. They are contiguous leads that all look at the inferior wall of the left ventricle.AVL is on the left wrist or shoulder and looks at the upper left side of the heart. Lead l travels towards AVL creating a second high lateral lead. AVf is on the left ankle or left lower abdomen and looks at the bottom, or inferior wall, of the heart.
| ELECTRODE | PLACEMENT |
|---|---|
| RL | Anywhere above the right ankle and below the torso |
| RA | Anywhere between the right shoulder and the wrist |
| LL | Anywhere above the left ankle and below the torso |
| LA | Anywhere between the left shoulder and the wrist |
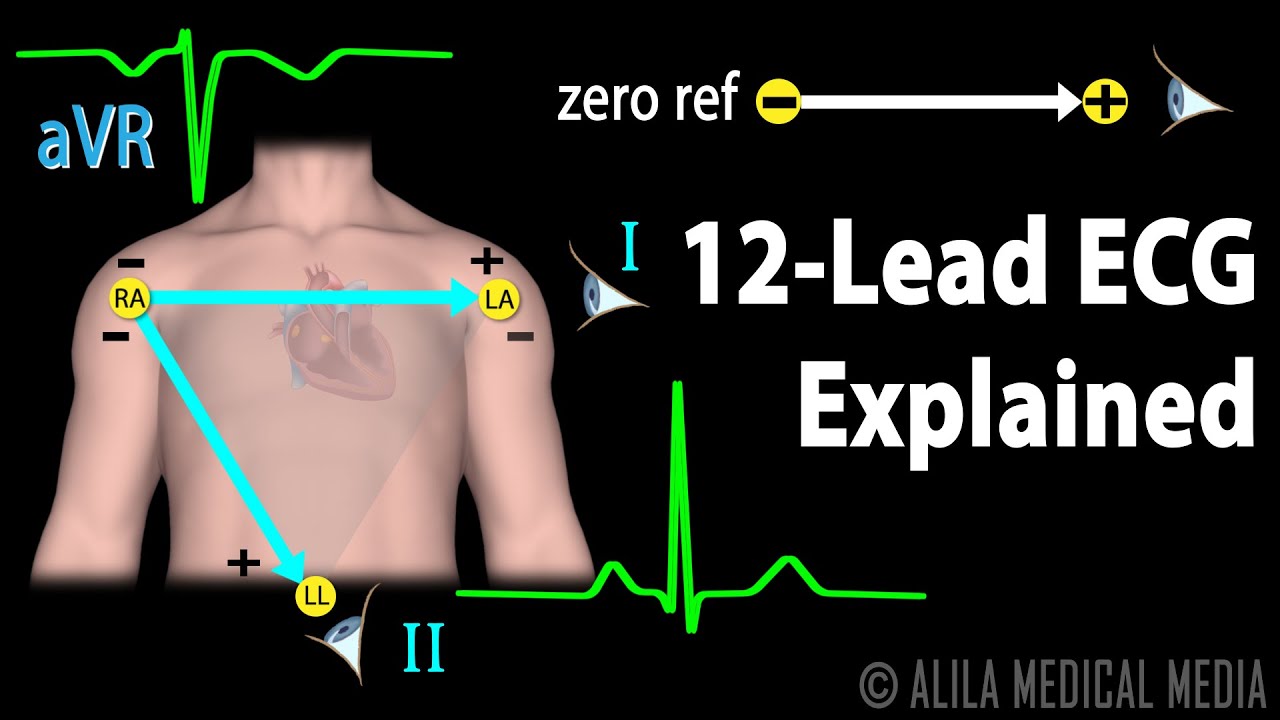
Table of Contents
Which of the following ECG leads looks at an inferior wall view?
Leads II, III and aVF are leads that have their positive electrode located at the left foot. They are contiguous leads that all look at the inferior wall of the left ventricle.
What do the aVR aVL and aVF leads look at?
AVL is on the left wrist or shoulder and looks at the upper left side of the heart. Lead l travels towards AVL creating a second high lateral lead. AVf is on the left ankle or left lower abdomen and looks at the bottom, or inferior wall, of the heart.
12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation
Images related to the topic12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation

Which ECG leads Look where?
| ELECTRODE | PLACEMENT |
|---|---|
| RL | Anywhere above the right ankle and below the torso |
| RA | Anywhere between the right shoulder and the wrist |
| LL | Anywhere above the left ankle and below the torso |
| LA | Anywhere between the left shoulder and the wrist |
Is Lead II lateral?
Bipolar limb leads (frontal plane):
Lead I: RA (-) to LA (+) (Right Left, or lateral) Lead II: RA (-) to LL (+) (Superior Inferior) Lead III: LA (-) to LL (+) (Superior Inferior)
Which wall does lead aVF?
In clinical practice, it is typically expressed as if lead aVF “views the inferior wall of the left ventricle”.
What is a lead 1 ECG?
Introduction. Although 1-lead ECG (EKG) recorders are normally used primarily for basic heart monitoring, checking for various arrhythmias, or simple educational or research purposes, they can also be used for looking at the effects of exercise on the ECG.
What does aVR look at on ECG?
CLINICAL UTILITY OF LEAD aVR
The lead aVR is oriented to ‘look’ at the right upper side of the heart, and can provide specific information about the right ventricle outflow tract and basal part of the septum (10).
See some more details on the topic Which ECG lead looks at the lateral wall view? here:
Walls and Leads
WALL. Inferior. Lateral. Sep. Anterior. Walls and Leads. LAD. V2, V3, V4. Anterior … Interpret ECG rhythm at bottom of 12 lead. ▫ Measure PR, QRS, QT.
Introduction. I—Leads, rate, rhythm, and cardiac axis – NCBI
The six chest leads (V1 to V6) “view” the heart in the horizontal plane. … aVL, V5, and V6 view the lateral surface; and leads V1 and aVR look through the …
EKG Basics # 2
Leads V5 and V6 collectively look at the lateral wall of the left ventricle. In Review : 1. Anterior Chest Leads = V1, V2, V3 and V4 2. Lateral Wall of the …
12 Lead ECG STEMI Recognition
Lateral Wall. Right Anterior Ventricular Artery. Right Marginal Artery. Vascular Anatomy. • Right Coronary Artery. – Right Ventricle. – Inferior wall of LV.
What type of leads are aVR aVL and aVF?
These nine wires are known as “unipolar leads“. The three active peripheral leads are AVr, AVL, and AVf. These 3 leads create a triangle with the heart in the middle, as below.
Why is lead aVR used?
Possible mechanisms of ST segment elevation in lead aVR
Thus, the purpose of lead aVR was to obtain specific information from the right upper side of the heart, such as the outflow tract of the right ventricle and the basal part of the septum.
Where is V6 lead placed?
Placement of Lead V6
V6 therefore is placed in the 5th intercostal space, mid axillary line.
Where is V4 placed?
The position for V4 is in the 5th intercostal space , in line with the middle of the clavicle (mid-clavicular).
Where do you place a 5 lead ECG?
The recommended 5-wire ECG lead placement is as follows. Place RA (white) electrode under the right clavicle, mid-clavicular line within the rib cage frame. Place LA (black) electrode under the left clavicle, mid-clavicular line within the rib cage frame.
ECG Interpretation – ECG Lead Perspectives
Images related to the topicECG Interpretation – ECG Lead Perspectives
Where is lead 3?
Lead III has the positive electrode on the left leg and the negative electrode on the left arm. These three bipolar limb leads roughly form an equilateral triangle (with the heart at the center) that is called Einthoven’s triangle in honor of Willem Einthoven who developed the electrocardiogram in the early 1900s.
What is V4 V5 V6 in ECG?
The electrical activity on an ECG (EKG). The areas represented on the ECG are summarized below: V1, V2 = RV. V3, V4 = septum. V5, V6 = L side of the heart.
What is a 3 lead ECG used for?
3-lead ECG
3-lead ECGs are used most often for recording a 24-hour reading. A 24-hour reading is a frequently used tool for the diagnosis of heart problems and is reimbursed as a long-term reading.
What leads look at the anterior wall?
The arrangement of the leads produces the following anatomical relationships: leads II, III, and aVF view the inferior surface of the heart; leads V1 to V4 view the anterior surface; leads I, aVL, V5, and V6 view the lateral surface; and leads V1 and aVR look through the right atrium directly into the cavity of the …
What view of the heart do leads II III and aVF represent?
If ST-elevation was noted in leads II, III and aVF, what would it suggest? Question 7 Explanation: Leads II, III and aVF all view the heart in the inferior plane. ST-elevation in only these leads would be suggestive of an inferior myocardial infarction.
Where is lead V8 placed?
V8 is placed at the tip of the left scapula, in the same horizontal plane.
What are the three types of ECG leads?
- Limb Leads (Bipolar)
- Augmented Limb Leads (Unipolar)
- Chest Leads (Unipolar)
Why is lead II the most common?
Lead II is the most common, most popular, and generally the best view because the placement of the positive electrode in Lead II views the wavefront of the impulse from the inferior aspect of the heart, as it travels from the right shoulder (RA) towards the left leg (LL).
What is a 12 lead ECG used for?
The 12-lead EKG provides more information on the diagnosis of your cardiac arrhythmia than an outpatient Holter or Event monitor, as it represents information recorded from a larger surface area surrounding the heart.
Is aVR lateral lead?
Specifically, lead aVR obtains information from the right upper side of the heart. It also gives reciprocal information on the left lateral side of the heart, which is already covered by leads aVL, I, II, V5, and V6. This is the main reason lead aVR has become forgotten.
What are reciprocal changes?
Images related to the topicWhat are reciprocal changes?

What are the augmented leads?
The three augmented leads are designated aVR, aVL, and aVF. An impulse directed toward a limb lead records a positive or upright deflection in that lead.
Why is aVR The Forgotten lead?
Lead aVR is often considered as a neglected lead or forgotten lead owing to its reciprocal location to the lateral leads. However, it has diagnostic and prognostic importance in cases of acute coronary syndromes.
Related searches to Which ECG lead looks at the lateral wall view?
- which leads look at the lateral wall of the left ventricle
- which leads view the septal wall
- ecg lateral wall view
- which leads look at the anterior wall of the left ventricle
- which ecg lead looks at the septal wall view
- which leads look at the inferior wall of the left ventricle
- which ecg lead looks at the inferior wall view
- leads ii iii and avf view which coronary artery and which branch
- leads ii, iii, and avf view which coronary artery and which branch?
Information related to the topic Which ECG lead looks at the lateral wall view?
Here are the search results of the thread Which ECG lead looks at the lateral wall view? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which ECG lead looks at the lateral wall view?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
