Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading

What causes repolarization of the heart?
Repolarization (phase 3 of the action potential) occurs because of an increase in potassium permeability. At the SA node, potassium permeability can be further enhanced by vagal stimulation. This has the effect of hyperpolarizing the cell and reducing the rate of firing.
What ion movement causes repolarization?
Repolarization typically results from the movement of positively charged K+ ions out of the cell. The repolarization phase of an action potential initially results in hyperpolarization, attainment of a membrane potential, termed the afterhyperpolarization, that is more negative than the resting potential.
Cardiac Action Potential, Animation.
Images related to the topicCardiac Action Potential, Animation.

Which electrolytes are involved in cardiac action potentials?
The electrolytes potassium, magnesium, sodium and calcium play a crucial role in the function of the myocardium, the muscular tissue of the heart.
What electrolyte causes depolarization by movement into the cell?
The depolarization is brought about by the entry of sodium and calcium ions that results from the opening of membrane channels.
What causes repolarization phase of action potential?
as the voltage-gated K+ channels open, K+ rushes out of the cell, causing the membrane potential to become more negative on the inside, thus repolarizing the cell.
How does depolarization and repolarization occur in the heart?
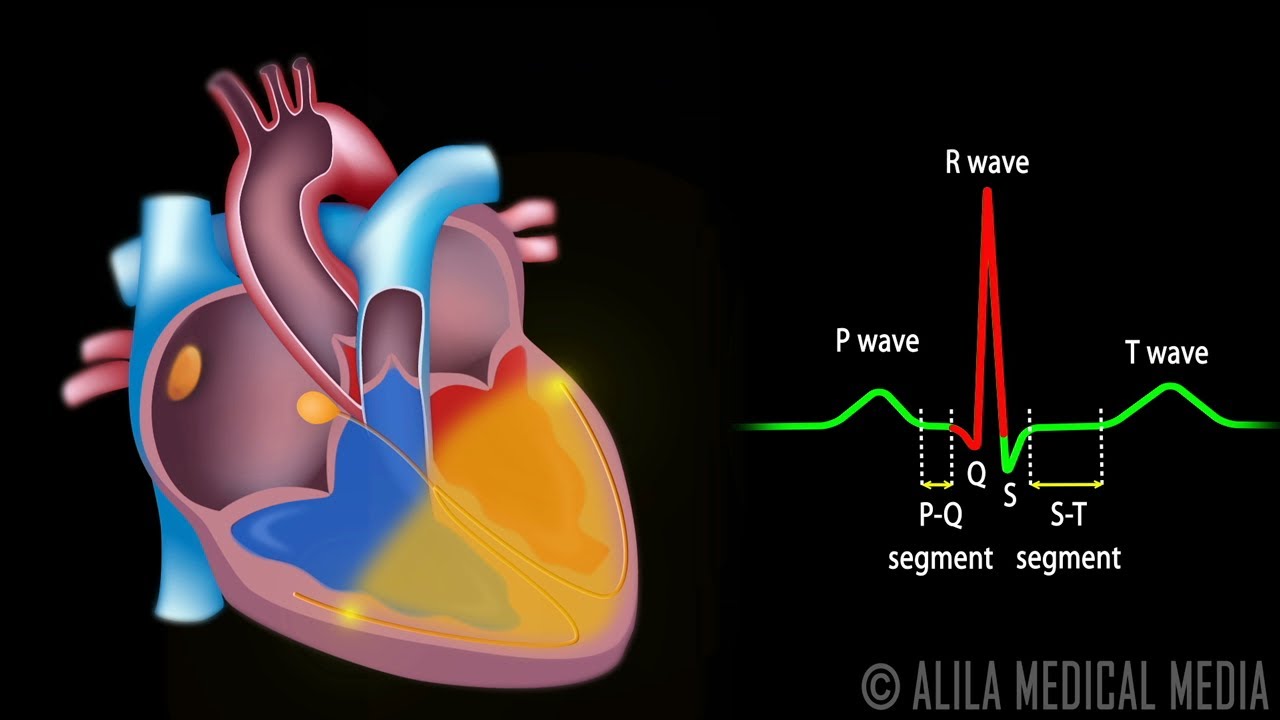
Each deflection (wave) of the ECG represents either depolarization or repolarization of the specific parts of the heart. Because depolarization occurs before mechanical contraction, the waves of depolarization can be associated with contraction and relaxation of the atria and the ventricles.
What causes repolarization quizlet?
Why does repolarization occur? Potassium ions continue to diffuse out of the cell after the inactivation gates of the voltage-gated sodium channels begin to close.
See some more details on the topic Which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization? here:
Physiology, Cardiac Repolarization Dispersion and Reserve
Cardiac action potentials and their associated repolarizations are vital in stimulating and maintaining the heart’s regular contractions, which …
Cardiac Cycle – Anatomy and Physiology – BC Open Textbooks
The cardiac cycle begins with atrial systole and progresses to ventricular … Ventricular relaxation, or diastole, follows repolarization of the ventricles …
action potential, automaticity and vectors – ECG & ECHO
During de- and repolarization ions (Na+ [sodium], K+ [potassium] and Ca2+ [calcium]) flows back and forth across the cell membrane.
Cardiac muscle physiology | BJA Education | Oxford Academic
Phase 2—plateau phase in which the movement of calcium ions out of the cell, maintains depolarization. Phase 3—repolarization, sodium, and …
Does potassium enter the cell during repolarization?
Repolarization returns the membrane potential to the −70 mV value that indicates the resting potential, but it actually overshoots that value. Potassium ions reach equilibrium when the membrane voltage is below −70 mV, so a period of hyperpolarization occurs while the K+ channels are open.
What happens to sodium and potassium ions during depolarization?
To summarize, sodium ions (Na+) enter the nerve membrane during depolarization and potassium ions (K+) leave the nerve membrane during repolarization.
Why is magnesium an important electrolyte of the action potential?
Magnesium and Action Potential
Studies show that the ion has depressive action on the heart: an induced increase in the concentration of magnesium ions causes a reduction in sinus rate.
Which of the following electrolytes is essential in the contraction of the cardiac muscle?
Muscle Function
The electrolyte calcium is needed for muscle contraction ( 7 ).
Why potassium is important in cardiac function?
Potassium plays a role in every heartbeat. A hundred thousand times a day, it helps trigger your heart to squeeze blood through your body. It also helps your muscles to move, your nerves to work, and your kidneys to filter blood.
Cardiac Conduction System and Understanding ECG, Animation.
Images related to the topicCardiac Conduction System and Understanding ECG, Animation.
What ions cause depolarization?
The inward flow of sodium ions increases the concentration of positively charged cations in the cell and causes depolarization, where the potential of the cell is higher than the cell’s resting potential. The sodium channels close at the peak of the action potential, while potassium continues to leave the cell.
Which is most responsible for depolarization of a neuron?
What ion is responsible for the depolarization of the neuron during an action potential? The influx of sodium ions causes the rapid depolarization during the action potential.
What is depolarization and repolarization?
The main difference between the two is: depolarization is described as the loss of resting membrane potential as a result of the alteration of the polarization of cell membrane. repolarization is described as the restoration of the resting membrane potential after every depolarization event.
Which of the following drug prolongs the repolarization phase of the action potential?
Ivabradine prolongs phase 3 of cardiac repolarization and blocks the hERG1 (KCNH2) current over a concentration-range overlapping with that required to block HCN4. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
What happens to potassium during depolarization?
Potassium ions (K+) begin to move down the electrochemical gradient (in favor of the concentration gradient and the newly established electrical gradient). As potassium moves out of the cell the potential within the cell decreases and approaches its resting potential once more.
Which ion channel is responsible for the rising phase of the action potential and why?
The rising phase is caused by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. These ion channels are activated once the cell’s membrane potential reaches threshold and open immediately. The electrochemical gradients drive sodium into the cell causing the depolarization.
What is atrial repolarization?
Atrial repolarization waves can simulate myocardial ischemia by causing ST segment elevation or depression depending upon the site of origin of the atrial impulse. Awareness and identification of pseudoinfarct patterns on ECGs is important to avoid unnecessary diagnostic interventions and treatment.
Where is the atrial repolarization wave?
As the human Ta wave of atrial repolarization occurs during the PR segment and QRS complex, it is not observed and recorded widely in sinus rhythm subjects by the standard 12-lead ECG (1).
Is P wave a repolarization?
The P wave represents the depolarization of the left and right atrium and also corresponds to atrial contraction. Strictly speaking, the atria contract a split second after the P wave begins. Because it is so small, atrial repolarization is usually not visible on ECG.
What ions are pumped out of the cell during repolarization?
-During repolarization, the ions that are pumped out of the cell, are – b. Potassium and calcium.
Conduction system of the heart – Sinoatrial node, AV Node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers Animation
Images related to the topicConduction system of the heart – Sinoatrial node, AV Node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers Animation
Why is it important for potassium ions K +) to move out of the axon Once an action potential has been fired?
The correct answer is *b. So that the neuron will have the ability to generate another action potential . See full answer below.
What happens in the membrane during repolarization quizlet?
During repolarization the sodium gates close and potassium gates open allowing potassium to rush out of the axon. This returns a negative charge to the inside of the axon re-establishing the negative potential.
Related searches to Which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization?
- cardiac depolarization
- what happens during repolarization of the heart
- what causes repolarization of the heart
- repolarization of an autorhythmic cell is due to the opening of which channels
- depolarization and repolarization heart
- ventricular repolarization
- cardiac action potential
- cardiac action potential phases 0 4
- cardiac action potential phases 0-4
- resting membrane potential of cardiac muscle
- which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization
Information related to the topic Which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization?
Here are the search results of the thread Which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which electrolyte is responsible for the majority of atrial repolarization?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.