Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which is the reproductive mechanism of terms mosses and fungi?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Spore formation is the process by which fungus, moss, and fern gets reproduced.Mosses, ferns, and fungi all reproduce with spores. Spores are an important adaptation that allowed the ancestors of these organisms to reproduce on land. A spore is a single reproductive cell that is pro- tected by a hard, watertight covering. The covering prevents the cell from drying out.Most fungi reproduce by forming spores that can survive extreme conditions such as cold and lack of water. Both sexual meiotic and asexual mitotic spores may be produced, depending on the species and conditions. Most fungi life cycles consist of both a diploid and a haploid stage.

Which is the reproductive mechanism of fern mosses and fungi?
Mosses, ferns, and fungi all reproduce with spores. Spores are an important adaptation that allowed the ancestors of these organisms to reproduce on land. A spore is a single reproductive cell that is pro- tected by a hard, watertight covering. The covering prevents the cell from drying out.
What is the reproductive mechanism of fungi?
Most fungi reproduce by forming spores that can survive extreme conditions such as cold and lack of water. Both sexual meiotic and asexual mitotic spores may be produced, depending on the species and conditions. Most fungi life cycles consist of both a diploid and a haploid stage.
Asexual Reproduction-Fission-Budding-Fragmentation-Spores
Images related to the topicAsexual Reproduction-Fission-Budding-Fragmentation-Spores

Which is the reproductive mechanism of ferns mosses and fungi Brainly?
Answer: Spores is the reproduction in fungus fern and mosses .
What type of reproduction is mosses?
Mosses have two forms of reproduction: sexual reproduction and asexual/ vegetative reproduction. This is true for all bryophytes. Practically all flowering plants are diploid, but for mosses, this is different. Mosses alternate between diploid generations (as sporophytes) and haploid generations (as gametophytes).
How do mosses and ferns reproduce?
To reproduce sexually, mosses and ferns produce sperm and eggs. The motile sperm must be able to swim through water to reach and fertilize the eggs, which is why most mosses and ferns live in damp habitats. Even in the absence of rainfall, moisture-laden fog or morning dew produce enough water to accomplish this task.
How do mosses reproduce by fragmentation?
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where a part of the moss can grow to form a new moss. This is used by mosses to help ensure their survival. Not all plants can reproduce from any part of their body, but moss is a great example of a plant with this unique ability.
Which form of reproduction in fungi can allow the fungi?
The most common mode of asexual reproduction is by the development of asexual spores, formed only by one parent (through mitosis) and genetically identical to that parent. Spores make it possible for fungi to extend their spread and colonize new habitats.
See some more details on the topic Which is the reproductive mechanism of terms mosses and fungi? here:
Name the mode of reproduction in fungus ferns and mosses
Mosses, ferns, and fungi all reproduce with spores. Spores are an important adaptation that allowed the ancestors of these organisms to …
What Are Spores? – Definition & Types – Study.com
Spores are single-cell reproductive cells that help asexual organisms, such as nonflowering plants, bacteria, fungi, and algae, …
Fungi | Organismal Biology
In both sexual and asexual reproduction as shown above, fungi produce many … fungi and photosynthetic organisms on land involved moss-like plants and …
Do fungi reproduce by binary fission?
Explanation: Binary fission occurs in prokaryotes and is a form of asexual reproduction. Fungi are considered haploid eukaryotes and undergo reproduction through processes like asexual spore release, vegetative reproduction, and sexual spore release.
Which kind of reproductive structure is found within the fungi quizlet?
Each Ascomycota has a reproductive structure called an ascus.
Which is the reproductive mechanism of ferns mosses and fungi A Flower b Sori C spores D roots?
In ferns, spores are contained within cases called sporangia that are located on the underside of leaves. Among liverworts, mosses, lycopods, ferns, and seed plants, few-to many-celled specially organized buds, or gemmae, also serve as agents of asexual reproduction.
Where does spores come from?
Spores are produced by bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants. Bacterial spores serve largely as a resting, or dormant, stage in the bacterial life cycle, helping to preserve the bacterium through periods of unfavourable conditions.
Lichen-Algae and Fungi working together
Images related to the topicLichen-Algae and Fungi working together

How do sperms or flowering plants reproduce?
Reproduction in flowering plants begins with pollination, the transfer of pollen from anther to stigma on the same flower or to the stigma of another flower on the same plant (self-pollination) or from the anther on one plant to the stigma of another plant (cross-pollination).
How does fertilization occur in mosses?
In all bryophytes fertilization is dependent on water—usually a film of water or the splashing of raindrops—for the transfer of sperm to the egg. Chemical stimuli direct the motile flagellate sperm to the archegonium. The fertilized egg (zygote) grows out of the gametophyte, which is also the source of its nourishment.
Are reproductive cells of ferns and mosses?
Ferns use both sexual and asexual reproduction methods. In sexual reproduction, a haploid spore grows into a haploid gametophyte. If there is enough moisture, the gametophyte is fertilized and grows into a diploid sporophyte. The sporophyte produces spores, completing the life cycle.
Is moss a natural vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative reproduction involves vegetative or non-sexual plant structures, whereas sexual propagation is accomplished through gamete production and subsequent fertilization. In non-vascular plants such as mosses and liverworts, vegetative reproductive structures include gemmae and spores.
What do you call the reproductive organ of mosses?
archegonium, the female reproductive organ in ferns and mosses. An archegonium also occurs in some gymnosperms, e.g., cycads and conifers. A flask-shaped structure, it consists of a neck, with one or more layers of cells, and a swollen base—the venter—which contains the egg.
When mosses and ferns reproduce what do they produce in the first cycle?
Spores. Spores are small reproductive structures that are released from the sporangium.
What do you call the male reproductive organ of mosses?
Mosses are the most common, diverse, and advanced group of bryophytes, a division of green, seedless plants that dates back to the Permian period (286 to 245 million years ago). In bryophytes, the antheridium is the male sex organ, which produces sperm.
What is simple about moss reproduction?
Moss Reproduction Cycle
Sexual, which involves a male and female to produce offspring, and asexual, which requires only one plant to reproduce. The sexual reproduction phase includes gametophytes, this is also the dominant life stage in the overall cycle.
Which fungi reproduce by budding?
Yeasts are fungi. The mode of reproduction adapted by them is asexual reproduction, to be precise, budding. This is usually seen in some yeasts and filamentous fungi.
Never Eat The ‘Clean’ Part Of Moldy Bread
Images related to the topicNever Eat The ‘Clean’ Part Of Moldy Bread
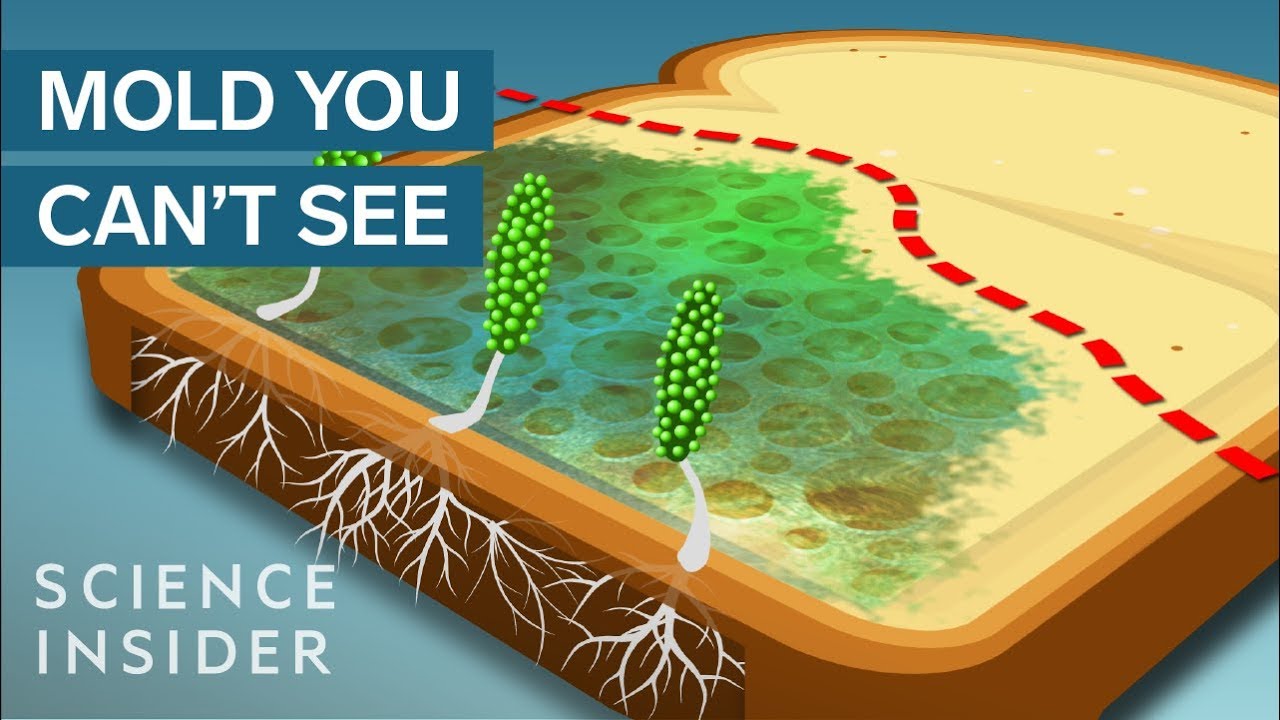
Which form of reproduction in fungi can allow the fungi Brainly?
Fungi reproduce asexually by fragmentation, budding, or producing spores. Fragments of hyphae can grow new colonies. Mycelial fragmentation occurs when a fungal mycelium separates into pieces with each component growing into a separate mycelium.
Which is the most common method of reproduction in majority of fungi and bacteria?
So, the correct option is ‘Binary fission‘.
Related searches to Which is the reproductive mechanism of terms mosses and fungi?
- reproduction common among insects and rotifers
- fungi life cycle
- asexual reproduction in fungi
- reproduction common among social insects and rotifers
- an entire animal grows from a cut piece of a parent animal
- Fungi life cycle
- the type of flower which has both the male and the female reproductive parts
- how do angiosperm plants reproduce
- Asexual reproduction in fungi
- reproduction exhibited by ferns mosses and fungi is called
Information related to the topic Which is the reproductive mechanism of terms mosses and fungi?
Here are the search results of the thread Which is the reproductive mechanism of terms mosses and fungi? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which is the reproductive mechanism of terms mosses and fungi?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.