Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which is younger the fault or the intrusion?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
The
states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts. The fault labeled ‘E’ cuts through all three sedimentary rock layers (A, B, and C) and also cuts through the intrusion (D). So the fault must be the youngest formation that is seen.Intrusion A is younger than fault 10 because the Intrusion A is in one piece and did not moved unlike the layers in fault 10.The fault cuts through all three sedimentary rock layers (A, B, and C) and also the intrusion (D). So the fault must be the youngest feature. The intrusion (D) cuts through the three sedimentary rock layers, so it must be younger than those layers.

Is intrusion a younger or older than fault 10 Why?
Intrusion A is younger than fault 10 because the Intrusion A is in one piece and did not moved unlike the layers in fault 10.
Does intrusion happen before fault?
The fault cuts through all three sedimentary rock layers (A, B, and C) and also the intrusion (D). So the fault must be the youngest feature. The intrusion (D) cuts through the three sedimentary rock layers, so it must be younger than those layers.
Intrusion basic and faulting
Images related to the topicIntrusion basic and faulting

Are intrusions younger?
There, the magma cools and hardens into a mass of igneous rock called an intrusion. An intrusion is always younger than the rock layers around and beneath it. The third rule comes from the study of faults. A fault is a break in Earth’s crust.
Which layer of rock is the youngest?
The law of superposition states that rock strata (layers) farthest from the ground surface are the oldest (formed first) and rock strata (layers) closest to the ground surface are the youngest (formed most recently).
Which layer is older fault E or intrusion D?
The principle of cross-cutting relationships states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts. The fault labeled ‘E’ cuts through all three sedimentary rock layers (A, B, and C) and also cuts through the intrusion (D). So the fault must be the youngest formation that is seen.
Why is the age of a fault younger than the rock in which it is found?
Why is a fault younger than the rocks that it breaks? A fault is always younger than the rock it cuts through. The surface where new rock layers meet a much older rock surface beneath them is called an unconformity. An unconformity is a gap in the geologic record.
What is the correct sequence of rock stratification?
Answer. Sedimentary rocks are the product of 1) weathering of preexisting rocks, 2) transport of the weathering products, 3) deposition of the material, followed by 4) compaction, and 5) cementation of the sediment to form a rock.
See some more details on the topic Which is younger the fault or the intrusion? here:
Determining Relative Ages | CK-12 Foundation
The principle of cross-cutting relationships states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts through.
Relative Ages of Rocks | Earth Science
The principle of cross-cutting relationships states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts through. The fault labeled ‘E’ cuts …
15.6: Determining Relative Ages – K12 LibreTexts
The principle of cross-cutting relationships states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts through.
Explain Why The Age Of A Fault Is Younger – Micro B Life
The principle of cross-cutting relationships states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts through.
Where was the youngest layer of rock found?
Superposition. Sedimentary rocks are deposited one on top of another. Therefore, the youngest layers are found at the top, and the oldest layers are found at the bottom of the sequence.
Which layer is the oldest which layer is the youngest How can you tell?
The many horizontal layers of sedimentary rock illustrate the principle of original horizontality (Figure below). The youngest rock layers are at the top and the oldest are at the bottom, which is described by the law of superposition.
What is a fault in rock layers?
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake – or may occur slowly, in the form of creep. Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers.
What is an intrusion in rock layers?
An intrusion is a body of igneous (created under intense heat) rock that has crystallized from molten magma. Gravity influences the placement of igneous rocks because it acts on the density differences between the magma and the surrounding wall rocks (country or local rocks).
What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks?
The two main categories of igneous rocks are extrusive and intrusive. Extrusive rocks are formed on the surface of the Earth from lava, which is magma that has emerged from underground. Intrusive rocks are formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of the planet.
Laws of Relative Rock Dating
Images related to the topicLaws of Relative Rock Dating
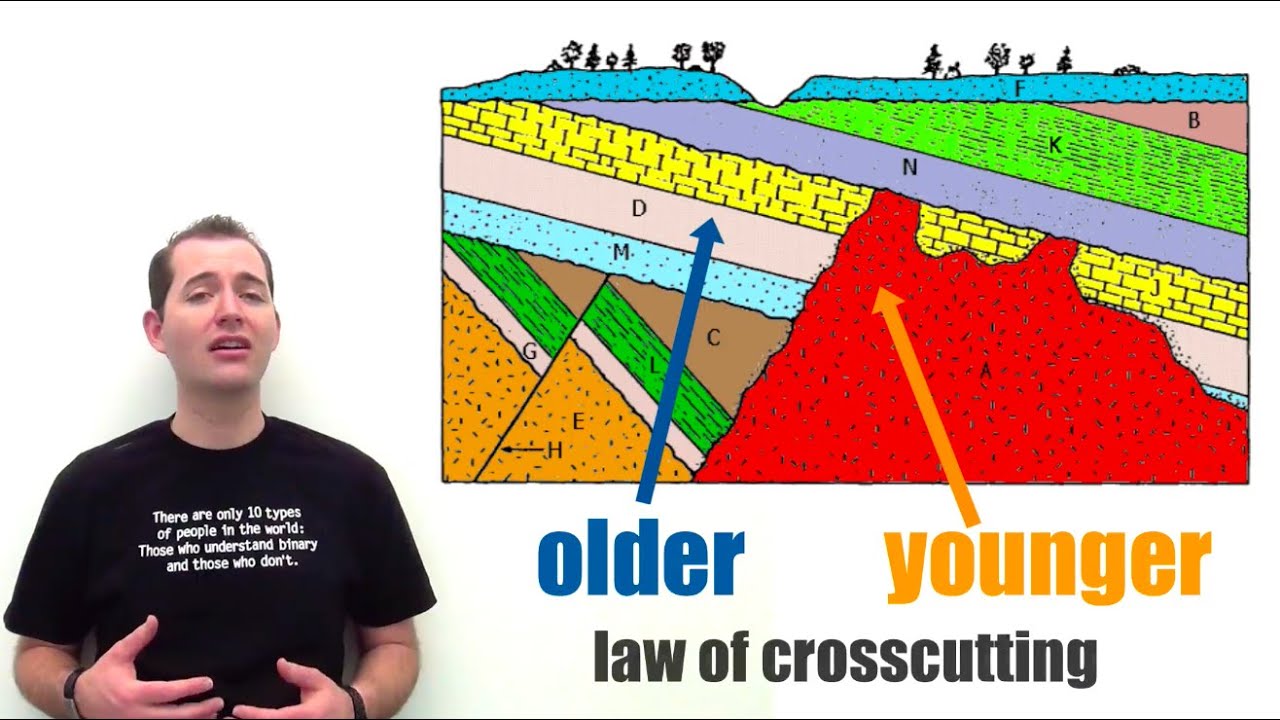
Which rock is the oldest?
The oldest intact rock found on Earth to date is from the Acasta Gneiss Complex of northwest Canada. U/Pb dates of zircon from the gneiss reach into the Hadean Eon at 4.02 Ga.
How can you tell the age of rock layers?
The age of rocks is determined by radiometric dating, which looks at the proportion of two different isotopes in a sample. Radioactive isotopes break down in a predictable amount of time, enabling geologists to determine the age of a sample using equipment like this thermal ionization mass spectrometer.
What layer is the second layer of the rock?
Crust: It is the outermost layer of the Earth. It’s made of solid rocks, mainly granite and basalt, and minerals. It is 40 km deep and it is divided into oceanic crust and continental crust. Mantle: It is the second layer of the Earth.
How can you determine which fossil is the oldest and youngest?
The principle of superposition states that in an undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks, each layer of rock is older than the one above it and younger than the one below it (Figures 1 and 2). Accordingly, the oldest rocks in a sequence are at the bottom and the youngest rocks are at the top.
What is the relative age of the igneous intrusion?
What is the relative age of the igneous intrusion? The igneous intrusion is the same age as layer 3.
How do you determine the age of a fault?
A fault is always younger than the rocks it cuts across. To determine the relative age of a fault one must know something about the relative age of the youngest rock the fault cross cuts. Sometimes it is possible to place a rock or a rock formation into a relative time scale based on inclusions.
Why is an igneous intrusion younger?
The rock layers below an extrusion are always older than the extrusion. Beneath the surface, magma may push into bodies of rock. There, the magma cools and hardens into a mass of igneous rock called an intrusion. An intrusion is always younger than the rock layers around and beneath it.
What is the difference between intrusion and extrusion?
Intrusion stay inside of the rock layers and never make it to the surface, which makes it just magma, while extrusions are only on the surface and are lava.
What states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed?
The law of superposition is the principle that states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed.
When placing rocks and events in sequence the notion that the oldest rocks are located at the bottom is referred to as?
law of superposition, a major principle of stratigraphy stating that within a sequence of layers of sedimentary rock, the oldest layer is at the base and that the layers are progressively younger with ascending order in the sequence.
Relative Age of Rock Layers
Images related to the topicRelative Age of Rock Layers

What is the sedimentary sequence?
Sedimentary sequences are layers of rock which are derived from weathered rocks, biogenic (= of living organisms) activity, or precipitation from solution. The Perth Basin contains very thick Mesozoic and older Permian sedimentary sequences which are the targets for drilling in the area.
What is a geological sequence?
In geology, a sequence is a stratigraphic unit which is bounded by an unconformity at the top and at the bottom.
Related searches to Which is younger the fault or the intrusion?
- what is fault creep quizlet
- explain why the age of a fault is younger than the rocks in which it is found
- which among this is the most severe fault
- what is absolute age
- which layer is the oldest?
- which rock layer is the youngest
- which among these is the most severe fault
- what is the correct sequence in the relative age of rock from youngest to oldest
- is an intrusion always younger than a fault
- which is younger the fault or the intrusion
- which layer is the oldest
- which of the following is most accurate concerning fault creep
- is the intrusion the youngest rock in the section how do you know
- which principle explains that the fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks affected
- is a fault older than an intrusion
- rock layers oldest to youngest answers
- is the intrusion the youngest rock in the section? how do you know?
- which among these is most severe fault
Information related to the topic Which is younger the fault or the intrusion?
Here are the search results of the thread Which is younger the fault or the intrusion? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which is younger the fault or the intrusion?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.