Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which kidney process is mostly active and usually requires energy to move solutes?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Keep Reading

Which of the following kidney processes is always active and always requires energy to occur quizlet?
Which of the following kidney processes is always active and always requires energy to occur? proximal tubule.
Is filtration in the kidney active or passive?
Filtrate is produced by the glomerulus when the hydrostatic pressure produced by the heart pushes water and solutes through the filtration membrane. Glomerular filtration is a passive process as cellular energy is not used at the filtration membrane to produce filtrate.
Renal handling of solutes
Images related to the topicRenal handling of solutes

What is the main active transport mechanism in the kidney?
Primary active transport relies on energy from the breakdown of adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) to power a cell membrane protein which ‘pumps’ solutes across a cell membrane.
Do kidneys use passive transport?
…
For help to answer the question:
| A. | passive diffusion |
|---|---|
| C. | active transport |
What is the primary function of the proximal tubule?
The primary function of the proximal tubule is the reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, phosphate and citrate.
Is the primary mode of transport for glucose across the kidney epithelium?
Small plasma primary mode of transport across the kidney epithelium. Sodium primary mode of transport across the kidney epithelium. Substances leaving the plasma must pass through three of the structures listed below before entering the tubule lumen.
Do kidneys use active transport?
Active transport can be seen in the kidneys, at the reabsorption stage in the nephrons. Along the nephron, a large network of capillaries surround the tubules that carry the waste. Substances that the body needs from the waste that can be re-used are reabsorbed into the blood stream.
See some more details on the topic Which kidney process is mostly active and usually requires energy to move solutes? here:
Chapter 19 Flashcards | Quizlet
Which of the following kidney processes is always active and always requires energy to occur? secretion.
Kidney Tubule Absorption – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Most of the reabsorption of solutes necessary for normal body function, such as amino acids, glucose, and salts, takes place in the proximal part of the tubule.
22.2. The Kidneys and Osmoregulatory Organs – BC Open …
All solutes in the glomerular capillaries, except for macromolecules like proteins, pass through by passive diffusion. There is no energy requirement at this …
Processes of the Kidneys
Filtration is the mass movement of water and solutes from plasma to the renal tubule that occurs in the renal corpuscle. About 20% of the plasma volume …
Is reabsorption active or passive?
Reabsorption includes passive diffusion, active transport, and cotransport. Water is mostly reabsorbed by the cotransport of glucose and sodium. Filtrate osmolarity changes drastically throughout the nephron as varying amounts of the components of filtrate are reabsorbed in the different parts of the nephron.
Is glomerular filtration ATP driven?
False, glomerular filtration is not an ATP-driven process. Rather, this is a passive process that does not require any energy input from…
What kind of reabsorption in kidneys are active?
Most of the reabsorption of solutes necessary for normal body function such as amino acids, glucose, and salts takes place in the proximal part of the tubule. This reabsorption may be active, as in the case of glucose, amino acids, and peptides, whereas water, chloride, and other ions are passively reabsorbed.
What is primary and secondary active transport?
In primary active transport, the energy is derived directly from the breakdown of ATP. In the secondary active transport, the energy is derived secondarily from energy that has been stored in the form of ionic concentration differences between the two sides of a membrane.
What is osmosis in kidney?
Osmosis is a phenomenon of paramount significance for the transport of water and solutes through biological membranes. It accounts for fluid transport out of the kidney tubules and the gastrointestinal tract, into capillaries, and across cell membranes.
Nephrology – Physiology Reabsorption and Secretion
Images related to the topicNephrology – Physiology Reabsorption and Secretion
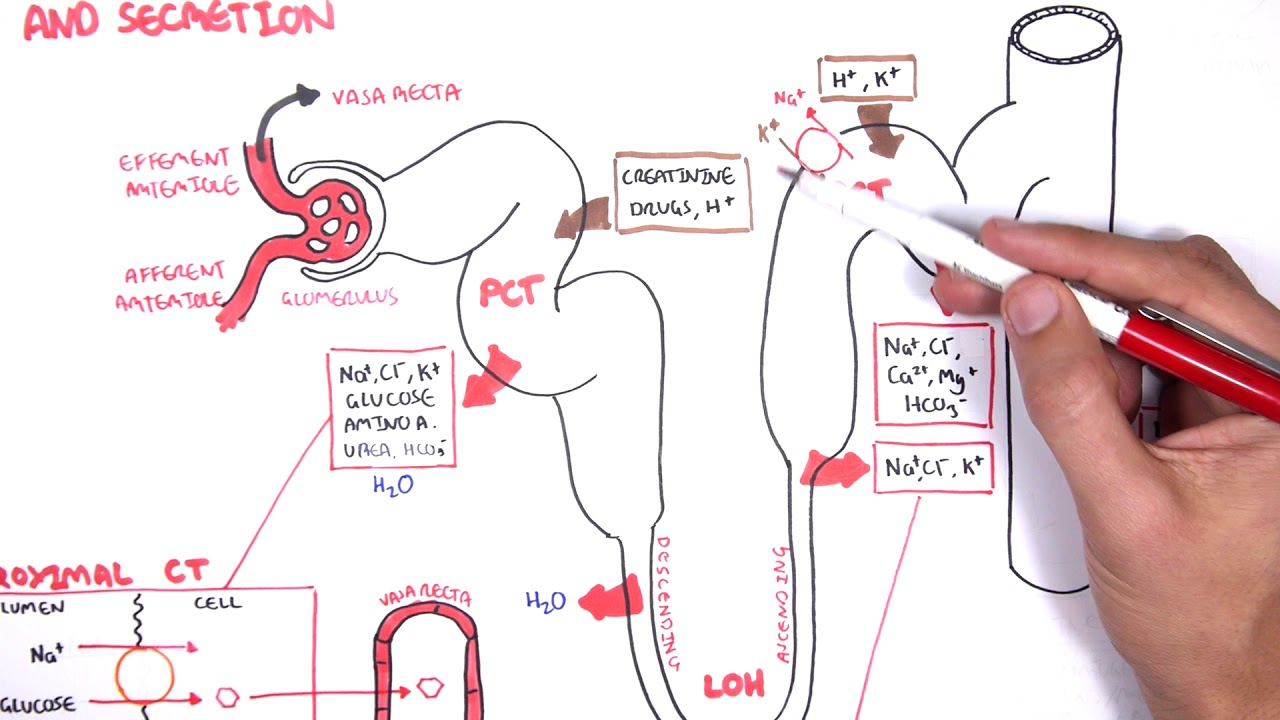
How do kidneys use diffusion?
The tubule of the nephron is surrounded by tiny blood vessels, called capillaries. By a process called diffusion, substances that your body can still use get reabsorbed. The filtrate within the tubule of the nephron contains water, ions, glucose and other useful small molecules at high concentrations.
Is glomerular filtration active or passive transport?
All solutes in the glomerular capillaries, including sodium ions and negatively and positively charged ions, pass through by passive diffusion; the only exception is macromolecules such as proteins. There is no energy requirement at this stage of the filtration process.
What is active and passive transport?
Active transport requires energy for the movement of molecules whereas passive transport does not require energy for the movement of molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient.
What is tubular reabsorption?
Tubular reabsorption is the process that moves solutes and water out of the filtrate and back into your bloodstream. This process is known as reabsorption, because this is the second time they have been absorbed; the first time being when they were absorbed into the bloodstream from the digestive tract after a meal.
What is tubular function?
The function of the proximal tubule is essentially reabsorption of filtrate in accordance with the needs of homeostasis (equilibrium), whereas the distal part of the nephron and collecting duct are mainly concerned with the detailed regulation of water, electrolyte, and hydrogen-ion balance.
What is the main function of the distal tubule?
Abstract. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a short nephron segment, interposed between the macula densa and collecting duct. Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis.
Is glucose movement across the apical membrane active or passive?
Passive transport because glucose moves down its concentration gradient and no additional energy is required.
What is transport epithelium in the kidney?
Introduction. Renal epithelial transport depends on the coordinated function of potassium channels with ion transporters (co-transporters, channels, and exchangers) and ion pumps in apical and basolateral membranes of distinct cell types along the nephron of the mammalian kidney.
What is epithelial transport?
Epithelia define the boundaries of the body and often transfer solutes and water from outside to inside (absorption) or from inside to outside (secretion). Those processes involve dual plasma membranes with different transport components that interact with each other.
Is kidney dialysis similar to active or passive transport?
The cell membranes in the kidneys use a process known as active transport to pump essential materials such as glucose and salts back into the bloodstream. The dialysis membrane cannot carry out active transport like real kidneys do because it is not a living organ.
Notes for IB Biology Chapter 1.4
Images related to the topicNotes for IB Biology Chapter 1.4

What is the difference between active reabsorption and passive reabsorption?
For glucose reabsorption, secondary active transport occurs at the luminal membrane, but passive facilitated diffusion occurs at the basolateral membrane, and passive uptake by bulk flow occurs at the peritubular capillaries. Secondary Active Secretion into the Tubules.
What is an example of secondary active transport?
An example of secondary active transport is the movement of glucose in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Related searches to Which kidney process is mostly active and usually requires energy to move solutes?
- which is not normally be found in the filtrate?
- secretion is similar to
- secretion is similar to ____.
- the process of filtration in the kidney is most accurately described as
- which is not normally be found in the filtrate
- which kidney process is always active and always requires energy to occur
- if blood flow through the afferent arterioles increases quizlet
- which is not a kidney filtration barrier?
- which of the following is the correct classification of vasopressin
- which part of the nephron is responsible for the greatest possible increase in urine concentration
- which kidney process is always active and always requires energy to occur?
- which is not a kidney filtration barrier
- if blood flow through the afferent arterioles increases, quizlet
Information related to the topic Which kidney process is mostly active and usually requires energy to move solutes?
Here are the search results of the thread Which kidney process is mostly active and usually requires energy to move solutes? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which kidney process is mostly active and usually requires energy to move solutes?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.