Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which Lagrange Points Are Stable?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable. The unstable Lagrange points – labeled L1, L2, and L3 – lie along the line connecting the two large masses. The stable Lagrange points – labeled L4 and L5 – form the apex of two equilateral triangles that have the large masses at their vertices.The reason for the stability is a second-order effect: as a body moves away from the exact Lagrange position, Coriolis acceleration (which depends on the velocity of an orbiting object and cannot be modeled as a contour map) curves the trajectory into a path around (rather than away from) the point.About the stability, L2 is unstable in the radial direction: if the probe is a little closer or a little further in the Sun-Earth axis it will be pushed yet further by gravitation.
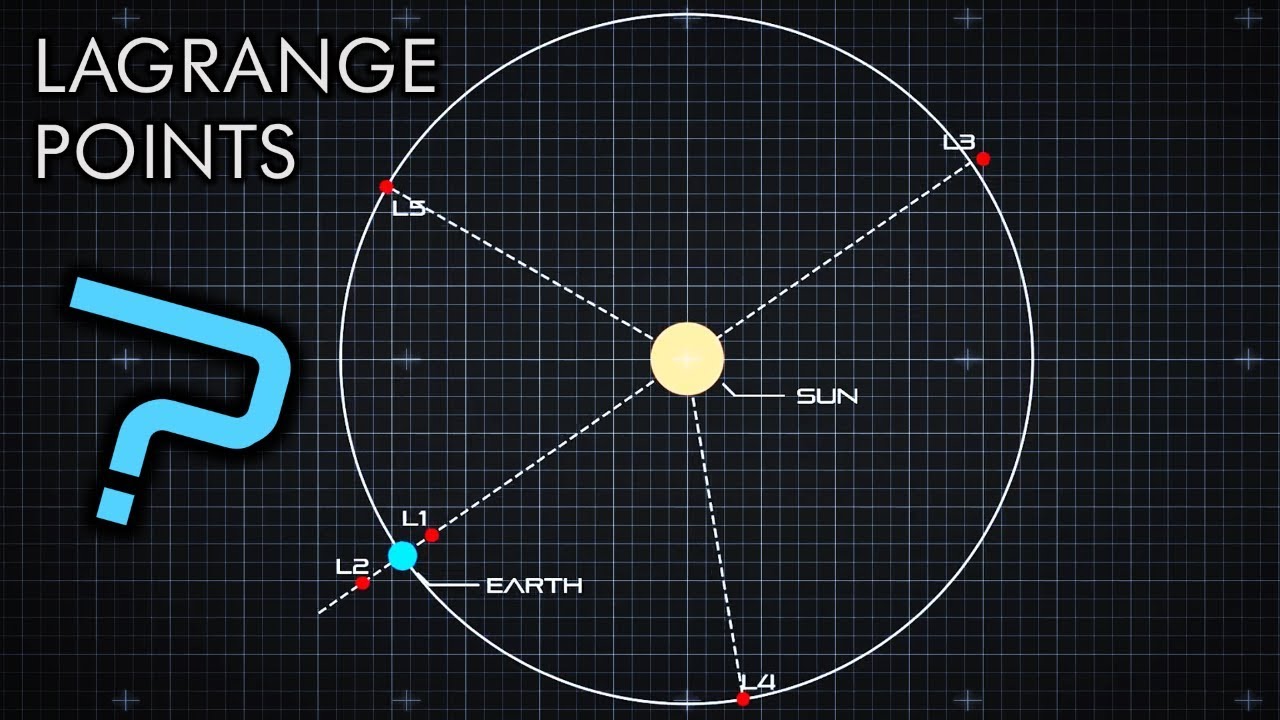
Table of Contents
Why are Lagrange points stable?
The reason for the stability is a second-order effect: as a body moves away from the exact Lagrange position, Coriolis acceleration (which depends on the velocity of an orbiting object and cannot be modeled as a contour map) curves the trajectory into a path around (rather than away from) the point.
Why is Lagrange L2 unstable?
About the stability, L2 is unstable in the radial direction: if the probe is a little closer or a little further in the Sun-Earth axis it will be pushed yet further by gravitation.
What Are Lagrange Points?
Images related to the topicWhat Are Lagrange Points?

Which Lagrange points in the Earth Moon system are stable?
The Lagrange points L4 and L5 constitute stable equilibrium points, so that an object placed there would be in a stable orbit with respect to the Earth and Moon. With small departures from L4 or L5, there would be an effective restoring force to bring a satellite back to the stable point.
Is the L3 Lagrange point Stable?
The L1, L2, and L3 points are always unstable, meaning that an object placed there will eventually leave, but the L4 and L5 points are stable, provided one of the bodies is sufficiently less massive than the other.
How do the L4 and L5 Lagrange points work?
Points L4 and L5, however, are stable, “like a ball in a large bowl,” according to the European Space Agency. These points lie along Earth’s orbit at 60 degrees ahead of and behind Earth, forming the apex of two equilateral triangles that have the large masses (Earth and the sun, for example) as their vertices.
How long will it take Webb to get to L2?
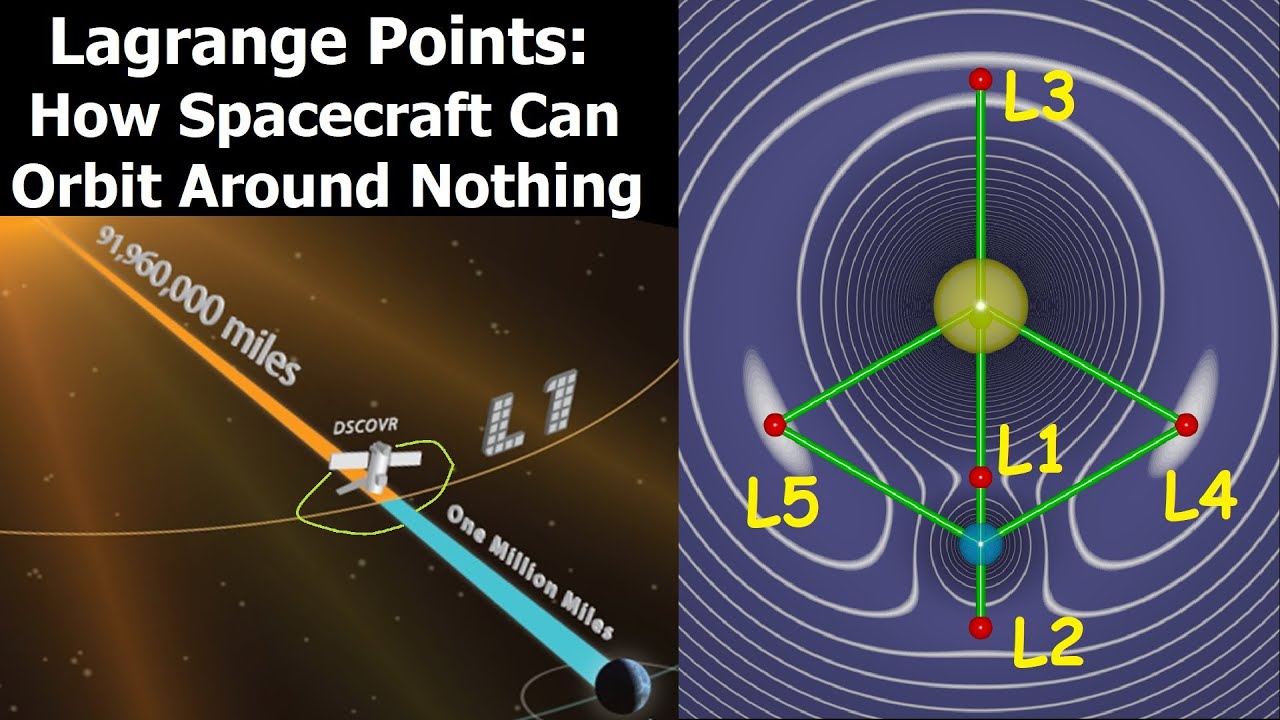
How long will it take Webb to get to L2? It will take roughly 30 days for Webb to reach the start of its orbit at L2, but it will take only 3 days to get as far away as the Moon’s orbit, which is about a quarter of the way there.
Is Lagrange point 2 stable?
Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable. The unstable Lagrange points – labeled L1, L2 and L3 – lie along the line connecting the two large masses.
See some more details on the topic Which Lagrange Points Are Stable? here:
What is a Lagrange Point? | NASA Solar System Exploration
Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable. The unstable Lagrange points – labeled L1, L2 and L3 – lie along the …
Lagrange point – Wikipedia
L4 and L5 are stable, which implies that objects can orbit around them in a rotating coordinate system tied to the two large bodies. When the …
When are Lagrange points L4 and L5 stable? – John D. Cook
The remaining Lagrange points, L4 and L5, are stable. These points are essentially in Earth’s orbit around the Sun, 60° ahead and 60° behind …
ESA – What are Lagrange points? – European Space Agency
A spacecraft at L1, L2, or L3 is ‘meta-stable’, like a ball sitting on top of a hill. A little push or bump and it starts moving away, so a spacecraft must use …
Is L2 point stable?
The satellite at that L2 point will be in a higher orbit and would be expected to fall behind the Earth, as it’s moving more slowly around the Sun. But the gravitational pull of the Earth pulls it forward, helping to keep it in this stable position.
Why is L3 unstable?
If it ahead it will orbit slower. If it is outside L3 it will move further out and if it is inside it will move in towards the sun. So L3 is unstable in the way that a ball on a col, or pass, between mountains is unstable.
What Makes Lagrange Points Special Locations In Space
Images related to the topicWhat Makes Lagrange Points Special Locations In Space
How many Lagrange points does Earth have?
Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable. The unstable Lagrange points – labeled L1, L2, and L3 – lie along the line connecting the two large masses.
What is the 2nd Lagrange point?
L2 is located 1.5 million kilometres directly ‘behind’ the Earth as viewed from the Sun. It is about four times further away from the Earth than the Moon ever gets and orbits the Sun at the same rate as the Earth. It is a great place from which to observe the larger Universe.
Where is the balance point of the Earth Moon system located?
Together they form a single system that orbits the sun. ® The balance point of the Earth-moon system is located within the Earth’s interior, because Earth’s mass is greater than the moon’s mass. ® This balance point is called the barycenter. The barycenter follows a smooth orbit around the sun.
Where will the James Webb Telescope orbit?
Location and orbit
JWST operates in a halo orbit, circling around a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point, approximately 1,500,000 km (930,000 mi) beyond Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Is L2 in the Earth’s shadow?
The Hubble Space Telescope orbits the Earth. The JWST will orbit the Sun. However, it will orbit in a special way so that it will always be in position with the Earth between it and the Sun (but not in the Earth’s shadow). This location is called the L2 Lagrange point.
How far is L2 from Mars?
And the new observatory, which is scheduled to launch on Dec. 25, will be going much farther afield as well — all the way out to the Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 2 (L2), about 930,000 miles (1.5 million kilometers) from our planet in the Marsward (not sunward) direction.
How long will it take for the James Webb telescope to unfold?
NASA’s James Webb telescope completes final unfolding in space Considered the most powerful telescope in space, the James Webb telescope has completed its deployment process. It will still be five months before it will start picking up images.
What Are The Lagrange Points? Finding Stable Points in Space
Images related to the topicWhat Are The Lagrange Points? Finding Stable Points in Space

What is the current status of the James Webb telescope?
Webb is currently at its observing spot, Lagrange point 2 (L2), nearly 1 million miles (1.6 million km). It is the largest and most powerful space telescope ever launched.
How long will the Webb mission last?
James Webb Could Last As Long As 20 Years
On December 29, 2021, NASA confirmed that the overwhelmingly successful launch from JWST’s Ariane 5 rocket had saved much of the telescope’s onboard fuel (as had the telescope’s precise course correction burns).
Related searches to Which Lagrange Points Are Stable?
- lagrange points animation
- how to find quadratic equation from maximum point
- how big are lagrange points
- how to find equidistant points on y axis
- why are l4 and l5 stable
- how to find critical points using lagrange multipliers
- why are some lagrange points unstable
- How to calculate lagrange points
- which lagrange points are stable
- how to calculate lagrange points
- what are lagrangian points
- stable lagrange points definition
- where is the lagrange point
- why is the lagrange point gravitationally stable
- where are earth’s lagrangian points
- coriolis force lagrange points
Information related to the topic Which Lagrange Points Are Stable?
Here are the search results of the thread Which Lagrange Points Are Stable? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which Lagrange Points Are Stable?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
