Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which law of Mendel is shown in F2 generation?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Mendel did the same experiment for all seven characteristics. In each case, one value of the characteristic disappeared in the F1 plants and then showed up again in the F2 plants. And in each case, 75 percent of F2 plants had one value of the characteristic and 25 percent had the other value.To test this prediction, Mendel allowed the F1 generation plants to self-pollinate. He was surprised by the results. Some of the F2 generation plants had white flowers. He studied hundreds of F2 generation plants, and for every three purple-flowered plants, there was an average of one white-flowered plant.Therefore, a dihybrid organism is one that is heterozygous at two different genetic loci. In 1865, Gregor Mendel performed dihybrid crosses on pea plants and discovered a fundamental law of genetics called the Law of Independent Assortment.
What did Mendel see in the F2 generation?
To test this prediction, Mendel allowed the F1 generation plants to self-pollinate. He was surprised by the results. Some of the F2 generation plants had white flowers. He studied hundreds of F2 generation plants, and for every three purple-flowered plants, there was an average of one white-flowered plant.
Which of Mendel’s laws is shown in the F2 generation of cross 2?
Therefore, a dihybrid organism is one that is heterozygous at two different genetic loci. In 1865, Gregor Mendel performed dihybrid crosses on pea plants and discovered a fundamental law of genetics called the Law of Independent Assortment.
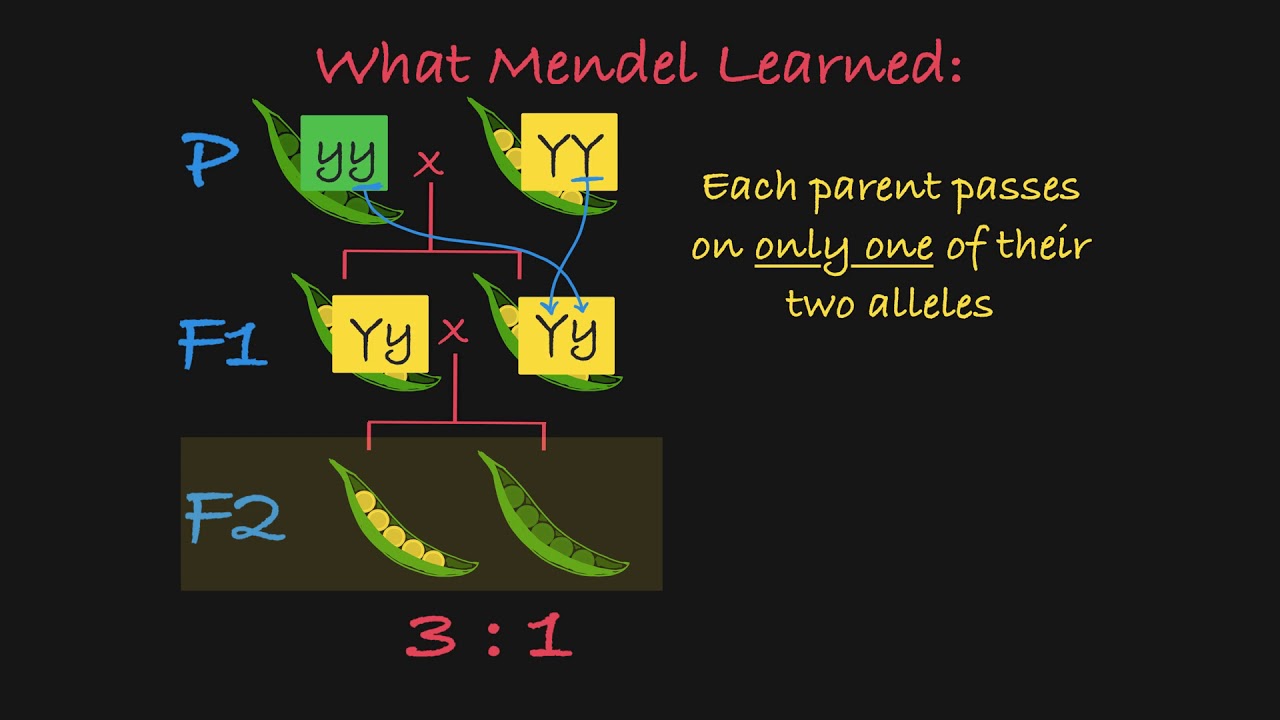
Mendel’s P, F1, and F2 Generations Explained
Images related to the topicMendel’s P, F1, and F2 Generations Explained

Which law of Mendel was formulated on the basis of the analysis of F2 generation of a monohybrid cross?
Law of dominance explains that in a monohybrid cross between a pair of contrasting traits, only one parental character will be expressed in the F1 generation and both parental characters will be expressed in the F2 generation in the ratio 3:1.
Which law of Mendel is shown in F1 generation?
Law of Dominance
This law states that in a heterozygous condition, the allele whose characters are expressed over the other allele is called the dominant allele and the characters of this dominant allele are called dominant characters. The characters that appear in the F1 generation are called as dominant characters.
What is the F2 generation?
Medical Definition of F2 generation
: the generation produced by interbreeding individuals of an F1 generation and consisting of individuals that exhibit the result of recombination and segregation of genes controlling traits for which stocks of the P1 generation differ. — called also second filial generation.
Why did Mendel continue some of his experiments to the F2 or F3 generation?
Why did Mendel continue some of his experiments to the F2 or F3 generation? To observe whether or not a recessive trait would appear.
What is Mendel Second law of Independent Assortment?
Mendel’s Second Law – the law of independent assortment; during gamete formation the segregation of the alleles of one allelic pair is independent of the segregation of the alleles of another allelic pair.
See some more details on the topic Which law of Mendel is shown in F2 generation? here:
12.3D: Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment – Biology …
The law of independent assortment states that a gamete into which an r allele sorted would be equally likely to contain either a Y allele or a y allele.
An Overview On Law Of Segregation And Law Of Dominance
In a monohybrid cross, both the alleles are expressed in the F2 generation without any blending. Thus, the law of segregation is based on the fact that each …
Mendel’s First Law of Genetics (Law of Segregation)
Mendel’s First Law of Genetics (Law of Segregation) · Allele – one alternative form of a given allelic pair; tall and dwarf are the alleles for the height of a …
Laws of Inheritance – Mt Hood Community College Biology 102
Observing that true-breeding pea plants with contrasting traits gave rise to F1 generations that all expressed the dominant trait and F2 generations that …
What is the independent law of assortment?
The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. Independent assortment of genes and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 during his studies of genetics in pea plants.
What is F1 generation and F2 generation?
F1 generation is the first filial generation, whereas F2 generation is the second filial generation obtained by crossing the F1 generation.
What is the appropriate ratio obtained in F2 generation under which law of Mendel Do you find this ratio?
| Question | 9:6:1 `F_(2)` generation ratio is obtained in case of |
|---|---|
| Chapter Name | Genetic Basis Of Inheritance |
| Subject | Biology (more Questions) |
| Class | 12th |
| Type of Answer | Video & Image |
What is the approximate ratio obtained in F2 generation under which law of Mendel Do you find this ratio?
In the F2 generation of Mendel’s dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1 but here 9 and 1 represent the parental types i.e., they show the parental phenotype but 3 and 3 represent the recombinants i.e., showing one character of one parent and the other character of another parent.
Laws of Genetics – Lesson 5 | Don’t Memorise
Images related to the topicLaws of Genetics – Lesson 5 | Don’t Memorise

Which law is applicable to dihybrid cross?
The Law of Independent Assortment states that during a dihybrid cross (crossing of two pairs of traits), an assortment of each pair of traits is independent of the other. In other words, during gamete formation, one pair of trait segregates from another pair of traits independently.
What is Mendel’s 3rd law?
MENDEL’s third law is also called the principle of independent assortment. It says that every trait is inherited independently of the others and it thus covers the case that new combinations of genes can arise, which were not existing before.
What is the F2 ratio?
So, the observed ratio in the F2 generation is 9:7.
What were his findings with respect to inheritance of traits in F1 and F2 generation?
Explanation: Mendel found that paired pea traits were either dominant or recessive. … Dominant traits, like round peas, appeared in the first-generation hybrids (F1), whereas recessive traits, like wrinkled peas, were masked. However, recessive traits reappeared in the second generation (F2).
What is the genotype of F2 generation?
The F2 generation would have genotypes of (GG, Gg, and gg) and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1. One-fourth of the F2 generation would be homozygous dominant (GG), one-half would be heterozygous (Gg), and one-fourth would be homozygous recessive (gg).
What is the genotypic ratio of F2 generation?
F2 generation in a Mendelian cross showed that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are the same as 1 : 2 : 1.
How do we obtain F2 generation?
F2 generation can be obtained by allowing flowers on the plants of F1 generation to be self-pollinated.
Why did Mendel grow two offspring generations?
Mendel was interested in the offspring of two different parent plants, so he had to prevent self-pollination.
What is the law of Independence?
Mendel’s law of independent assortment states that the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene.
Which of the following is the best statement of the use of the addition rule of probability?
Which of the following is the best statement of the use of the addition rule of probability? The probability that either one of two independent events will occur.
P, F1, F2 Generation, Law of Segregation, Law of Dominance – Genetics (Most Important)
Images related to the topicP, F1, F2 Generation, Law of Segregation, Law of Dominance – Genetics (Most Important)

What is Mendel’s 1st and 2nd law?
Conclusion. Mendel’s first law describes the segregation of the two copies of alleles of a particular gene into the gametes. Mendel’s second law describes the independent assortment of alleles of different genes from each other during the formation of gametes.
Which is an example of Mendel’s law of Independent Assortment?
For instance, one baby could receive the bbgg genotype, giving it white fur and red eyes. Alternatively, a baby rabbit could also receive the genotype Bbgg, giving it black fur and red eyes. This is the law of independent assortment.
Related searches to Which law of Mendel is shown in F2 generation?
- law of dominance example
- mendels first law
- which law of mendel is shown in f2 generation shown
- which law of mendel is shown in f2 generation below
- which law of mendel is shown in f2 generation 1
- mendel’s law of dominance
- law of independent assortment
- which law of mendel is shown in f2 generation 2
- mendels law of dominance
- which law of mendel is shown in f2 generation punnett square
- law of inheritance
- which law of mendel is shown in f2 generation definition
- law of dominance
- mendel’s first law
- law of independent assortment example
- what is the law of segregation
Information related to the topic Which law of Mendel is shown in F2 generation?
Here are the search results of the thread Which law of Mendel is shown in F2 generation? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which law of Mendel is shown in F2 generation?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.