Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
LDL is responsible for carrying cholesterol to cells that need it.HDL (high-density lipoprotein), or “good” cholesterol, absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver. The liver then flushes it from the body. High levels of HDL cholesterol can lower your risk for heart disease and stroke.LDL (low-density lipoprotein): carries cholesterol (much of it synthesized in the liver) to body cells.
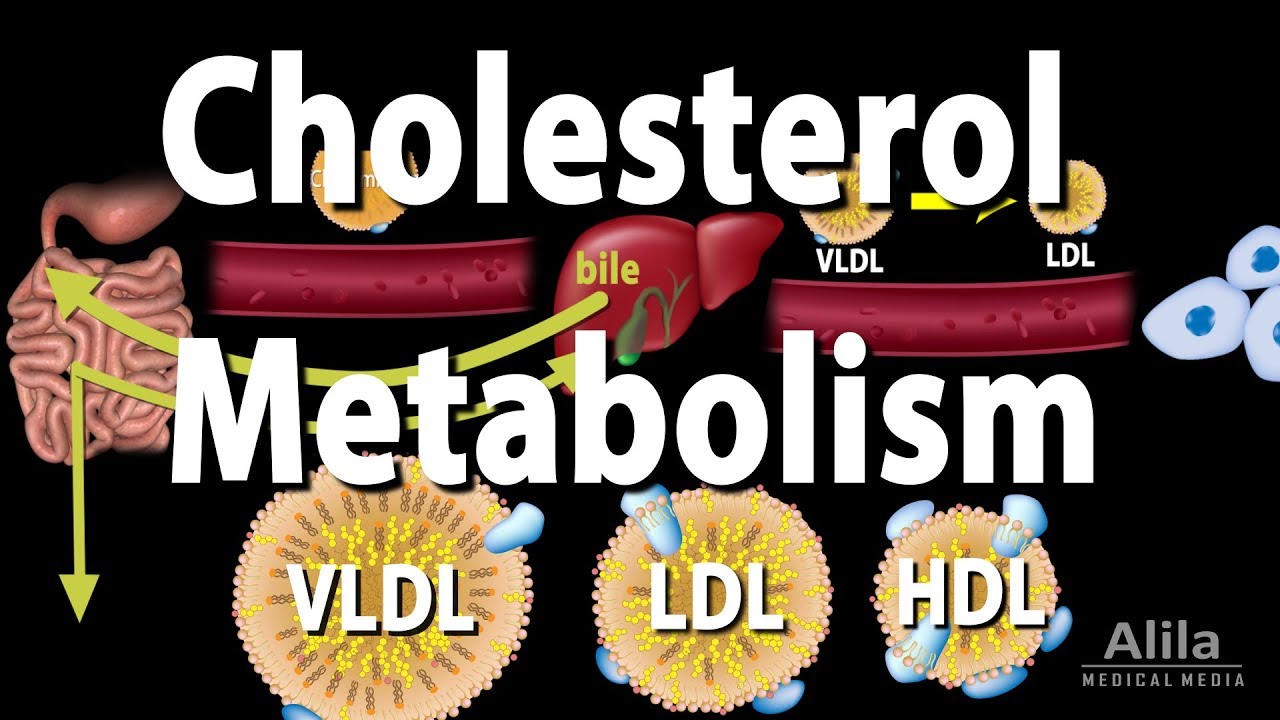
Which lipoprotein picks up cholesterol from your arteries?
HDL (high-density lipoprotein), or “good” cholesterol, absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver. The liver then flushes it from the body. High levels of HDL cholesterol can lower your risk for heart disease and stroke.
Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body?
LDL (low-density lipoprotein): carries cholesterol (much of it synthesized in the liver) to body cells.
Cholesterol Metabolism, LDL, HDL and other Lipoproteins, Animation
Images related to the topicCholesterol Metabolism, LDL, HDL and other Lipoproteins, Animation

Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body quizlet?
High Density Lipoproteins (HDL): Transports cholesterol to the liver for excretion.
Which lipoprotein picks up cholesterol from your arteries and other places in the body and returns it back to the liver for further metabolism quizlet?
HDL: picks up cholesterol from other lipoproteins and body cells and returns them to the liver to reuse or eliminate.
What is VLDL vs LDL?
The main difference between VLDL and LDL is that they have different percentages of the cholesterol, protein, and triglycerides that make up each lipoprotein. VLDL contains more triglycerides. LDL contains more cholesterol. VLDL and LDL are both considered types of “bad” cholesterol.
What is VLDL cholesterol?
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol is produced in the liver and released into the bloodstream to supply body tissues with a type of fat (triglycerides). There are several types of cholesterol, each made up of lipoproteins and fats.
Where do you get LDL cholesterol from?
Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, salts, and cholesterol (as found in fatty meats, some processed foods, dairy, and cured meats) and low in healthy proteins (fish, nuts, avocados, and others) and fiber (such as leafy vegetables, and apples) can lead to high LDL.
See some more details on the topic Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries? here:
Cholesterol | MedlinePlus
HDL stands for high-density lipoprotein. It is sometimes called “good” cholesterol because it carries cholesterol from other parts of your body …
What is cholesterol and how does arteriosclerosis develop?
“LDL” cholesterol: “LDL” stands for “low-density lipoprotein.” This type of parcel transports cholesterol from the liver to the rest of the body …
Solved 1.Which lipoprotein transports dietary fat to the – Chegg
chylomicrons d.LDLs (low-density lipoproteins) e.phospholipids 2.Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body, but can get stuck in arteries …
Blood Fats Explained – Heart UK
cholesterol in our body from the liver to the cells … lipoprotein particle made in the liver. … an artery can become so narrow it cannot deliver.
Where are HDL made?
HDL is mainly secreted by the liver and small intestines. The liver, which secretes ~70–80% of the total HDL in plasma, is the main source of HDL in the circulation.
How do LDL and HDL differ structurally and functionally?
The main structural difference between LDL and HDL is their compositions. Approximately 50 percent of the weight of an LDL particle is cholesterol and only 25 percent is protein. High-density lipoprotein particles, on the other hand, consist of 20 percent cholesterol by weight and 50 percent protein.
Which lipoprotein scavenges cholesterol from tissues or artery walls and transports it back to the liver for removal or repackaging?
LDL carries cholesterol to the peripheral tissues, while HDL carries out “reverse transport,” bringing cholesterol from the peripheral tissues back to the liver. Although each LP is composed of one predominant type of lipid, other lipids are usually present, too.
What do chylomicrons transport?
Chylomicrons. Chylomicrons (Fig. 20-14) are formed in the intestinal epithelium to transport long-chain triglycerides to the tissues. Medium- and short-chain fats are transported directly to the liver through the portal circulation without packaging into lipoprotein particles.
Which lipoproteins transport dietary fat to the cells in your body?
The intestine secretes dietary fat in chylomicrons, lipoproteins that transport triglyceride to tissues for storage. Dietary cholesterol is transported to the liver by chylomicron remnants which are formed from chylomicrons.
HDL ( Reverse cholesterol transport)
Images related to the topicHDL ( Reverse cholesterol transport)
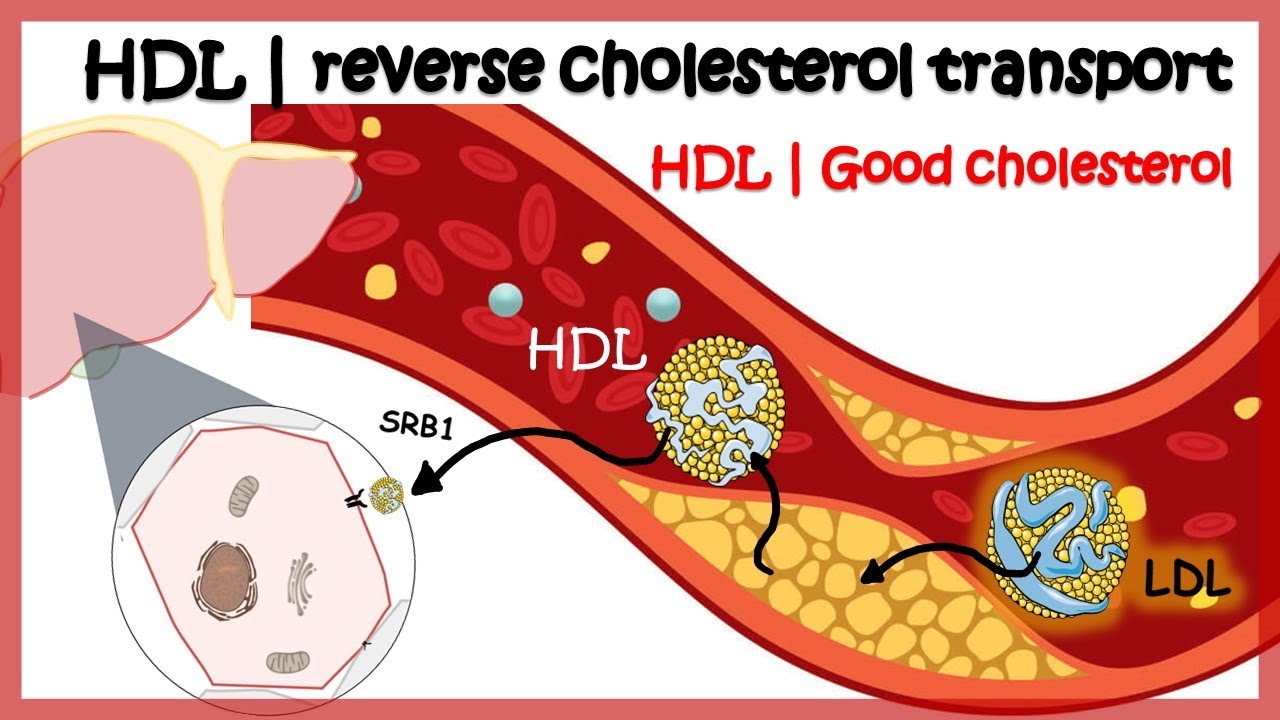
Which lipoprotein delivers triglycerides and cholesterol from the liver to the body’s tissue?
LDL, a class of lipoprotein, delivers triglycerides and cholesterol from the liver to the body’s tissues. True or false? Where can vitamin K be made or obtained? A cardiovascular disease characterized by artery walls hardening with plaque.
Which lipoprotein transports cholesterol to the liver?
The HDL then transports the cholesterol to the liver either directly by interacting with hepatic SR-B1 or indirectly by transferring the cholesterol to VLDL or LDL, a process facilitated by CETP. Cholesterol efflux from macrophages to HDL plays an important role in protecting from the development of atherosclerosis.
What are triglycerides?
Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) found in your blood. When you eat, your body converts any calories it doesn’t need to use right away into triglycerides. The triglycerides are stored in your fat cells. Later, hormones release triglycerides for energy between meals.
Does VLDL carry cholesterol?
Your liver makes VLDL and releases it into your bloodstream. The VLDL particles mainly carry triglycerides, another type of fat, to your tissues. VLDL is similar to LDL cholesterol, but LDL mainly carries cholesterol to your tissues instead of triglycerides.
Does LDL transport cholesterol?
LDLs are the primary plasma carriers of cholesterol for delivery to all tissues. LDL can be absorbed by the liver and other tissues via receptor mediated endocytosis.
What is difference between LDL and HDL?
There are two types: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). As a general rule, HDL is considered “good” cholesterol, while LDL is considered “bad.” This is because HDL carries cholesterol to your liver, where it can be removed from your bloodstream before it builds up in your arteries.
What is the function of LDL?
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) transport cholesterol from its site of synthesis in the liver to the various tissues and body cells, where it is separated from the lipoprotein and is used by the cell.
Where do chylomicrons go?
Nearly all dietary lipid is transported in chylomicrons from the gut to the blood through the lymphatic system by entering specialized lymphatic vessels, referred to as lacteals, in the villi of the intestine (Fig.
What is the HDL cholesterol range?
| At risk | Desirable | |
|---|---|---|
| Men | Less than 40 mg/dL (1.0 mmol/L) | 60 mg/dL (1.6 mmol/L) or above |
| Women | Less than 50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) | 60 mg/dL (1.6 mmol/L) or above |
Are there 2 types of LDL?
In most of the studies using these methods, LDL particles are classified into 3 or 4 subclasses, including large (LDL I), intermediate (LDL II), small (LDL III), and, in some studies, very small (LDL IV) LDLs [3, 18]. LDL III and LDL IV (when discerned) are referred to as sdLDL.
Metabolism | Lipoprotein Metabolism | Chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL
Images related to the topicMetabolism | Lipoprotein Metabolism | Chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL

What causes high HDL cholesterol?
Your diet.
Foods that are high in unsaturated fats, such as fish, nuts, and green leafy vegetables raise HDL in a good way. Other foods increase HDL cholesterol too much. They are some of the same foods that also raise unhealthy LDL cholesterol, like: Red meat.
What creates cholesterol in the body?
The cholesterol in your blood comes from two sources: the foods you eat and your liver. Your liver makes all the cholesterol your body needs. Cholesterol and other fats are carried in your bloodstream as spherical particles called lipoproteins.
Related searches to Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries?
- cholesterol structure
- how to reduce cholesterol
- which lipoprotein transports dietary fat to the cells in your body?
- which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the tissues
- why does cholesterol build up in arteries
- which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries
- which lipoprotein transports dietary fat to the cells in your body quizlet
- hdl cholesterol
- which lipoprotein transports dietary fat to the cells in your body
- ldl cholesterol
Information related to the topic Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries?
Here are the search results of the thread Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which lipoprotein carries cholesterol to the cells in your body but can get stuck in arteries?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.