Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which moral theory is defined as a theory based on the idea of a social contract or agreement among individuals for mutual advantage?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Social contract theory, nearly as old as philosophy itself, is the view that persons’ moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract or agreement among them to form the society in which they live.In contemporary moral philosophy, the main impartial moral theory outside the social contract tradition is utilitarianism. Utilitarianism takes persons’ moral status to be grounded on their capacity for well-being and suffering, and takes well-being to be the sole moral value.The U.S. Constitution is often cited as an explicit example of part of America’s social contract. It sets out what the government can and cannot do. People who choose to live in America agree to be governed by the moral and political obligations outlined in the Constitution’s social contract.

Is Utilitarianism a social contract theory?
In contemporary moral philosophy, the main impartial moral theory outside the social contract tradition is utilitarianism. Utilitarianism takes persons’ moral status to be grounded on their capacity for well-being and suffering, and takes well-being to be the sole moral value.
What is a social contract theory example?
The U.S. Constitution is often cited as an explicit example of part of America’s social contract. It sets out what the government can and cannot do. People who choose to live in America agree to be governed by the moral and political obligations outlined in the Constitution’s social contract.
Social Contract Theory | Ethics Defined
Images related to the topicSocial Contract Theory | Ethics Defined

What is Rawls’s social contract theory?
For Rawls a social contract is a hypothetical not an historical contract. Thus Rawls does not claim that people actually agree to a particular set of morally defensible principles of justice. Rather Rawls claims that people would agree to such principles under certain specific conditions.
What is Contractarianism theory?
The moral theory of contractarianism claims that moral norms derive their normative force from the idea of contract or mutual agreement. Contractarians are skeptical of the possibility of grounding morality or political authority in either divine will or some perfectionist ideal of the nature of humanity.
Is social contract theory normative?
III.
The normative dimension of social contract theory is an account of the principles of justice that make the state legitimate.
Is social contract theory deontological?
This distinction is crucial, because it differentiates social contract theory from both deontological and utilitarian ethics. Deontological ethics holds that moral worth of an action is determined by the intrinsic nature of the action itself, and can be discovered through means such as reason, intuition, or emotion.
Who did the social contract theory?
Although similar ideas can be traced to the Greek Sophists, social-contract theories had their greatest currency in the 17th and 18th centuries and are associated with the English philosophers Thomas Hobbes and John Locke and the French philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau.
See some more details on the topic Which moral theory is defined as a theory based on the idea of a social contract or agreement among individuals for mutual advantage? here:
Contractarianism
The moral theory of contractarianism claims that moral norms derive their normative force from the idea of contract or mutual agreement.
How do moral theories stand to each other? | SpringerLink
In a broad sense, contractualism can be construed as the view that moral norms derive their normative force from a contract or mutual agreement.
Social Contract Theory – Ethics Unwrapped
Social contract theory says that people live together in society in accordance with an agreement that establishes moral and political rules of behavior.
social contract | Definition, Examples, Hobbes, Locke …
social contract, in political philosophy, an actual or hypothetical compact, or agreement, between the ruled or between the ruled and their rulers, defining …
What are the advantages of social contract theory?
The social contract is unwritten, and is inherited at birth. It dictates that we will not break laws or certain moral codes and, in exchange, we reap the benefits of our society, namely security, survival, education and other necessities needed to live.
Who created the social contract theory?
The idea of the social contract goes back at least to Protagoras and Epicurus. In its recognizably modern form, however, the idea is revived by Thomas Hobbes and was later developed, in different ways, by John Locke, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and Immanuel Kant.
What utilitarianism means?
Utilitarianism is an effort to provide an answer to the practical question “What ought a person to do?” The answer is that a person ought to act so as to maximize happiness or pleasure and to minimize unhappiness or pain.
What is the social contract theory of the origin of the state?
This theory states that the society or the state came into being by a contract that was made between the individual and the society or the contract that was made amongst the individual people.
Social Contract Theory
Images related to the topicSocial Contract Theory

What is hypothetical social contract theory?
The hypothetical social contract theory, on the present interpre- tation, offers the following candidate justification for this sort of coercion: one may coercively impose an arrangement on individuals, provided that the individuals would be unreasonable to reject the arrangement.
What is virtue ethics theory?
Virtue ethics is a broad term for theories that emphasize the role of character and virtue in moral philosophy rather than either doing one’s duty or acting in order to bring about good consequences.
What is egalitarian theory of justice?
Egalitarianism is the position that equality is central to justice. It is a prominent trend in social and political philosophy and has also become relevant in moral philosophy (moral egalitarianism) since the late twentieth century.
What is the definition of social contract theory quizlet?
What is Social Contract Theory? View that people’s moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract among them to form the society in which they live.
Why does social contract theory have an advantage over divine command theory of natural law theory?
For Social Contract Theorists, the greatest advantage of this approach to morality is that it seems to imply a way in which an objective moral code can be grounded in rational discourse, and how we can thus avoid the difficulties of both Ethical Relativism and Ethical Absolutism (e.g. most Divine Command approaches to …
When was the social contract theory created?
The relation between natural and legal rights is often a topic of social contract theory. The term takes its name from The Social Contract (French: Du contrat social ou Principes du droit politique), a 1762 book by Jean-Jacques Rousseau that discussed this concept.
What according to Locke are the elements of the social contract?
John Locke’s social contract theory includes the idea that life, liberty, and property are given to us by nature and shouldn’t be taken away. Locke’s theory states that people form governments in order to protect these rights, but in order for that to work, people have to follow the laws the government makes.
What is force theory?
Force theory is the process of establishing a new government or country through the use of force. This process involves one group of people entering into an area and making everyone else within that territory submit to the new government and social system.
What is the difference between Hobbes and Locke social contract?
Locke believed that the social contract meant investing some power in the hands of the ruler, whose power would be used to protect his citizens’ human rights. Hobbes believed that humans were to use their reason to leave the state of nature and submit to the absolute authority of the monarch.
Social contract theories
Images related to the topicSocial contract theories
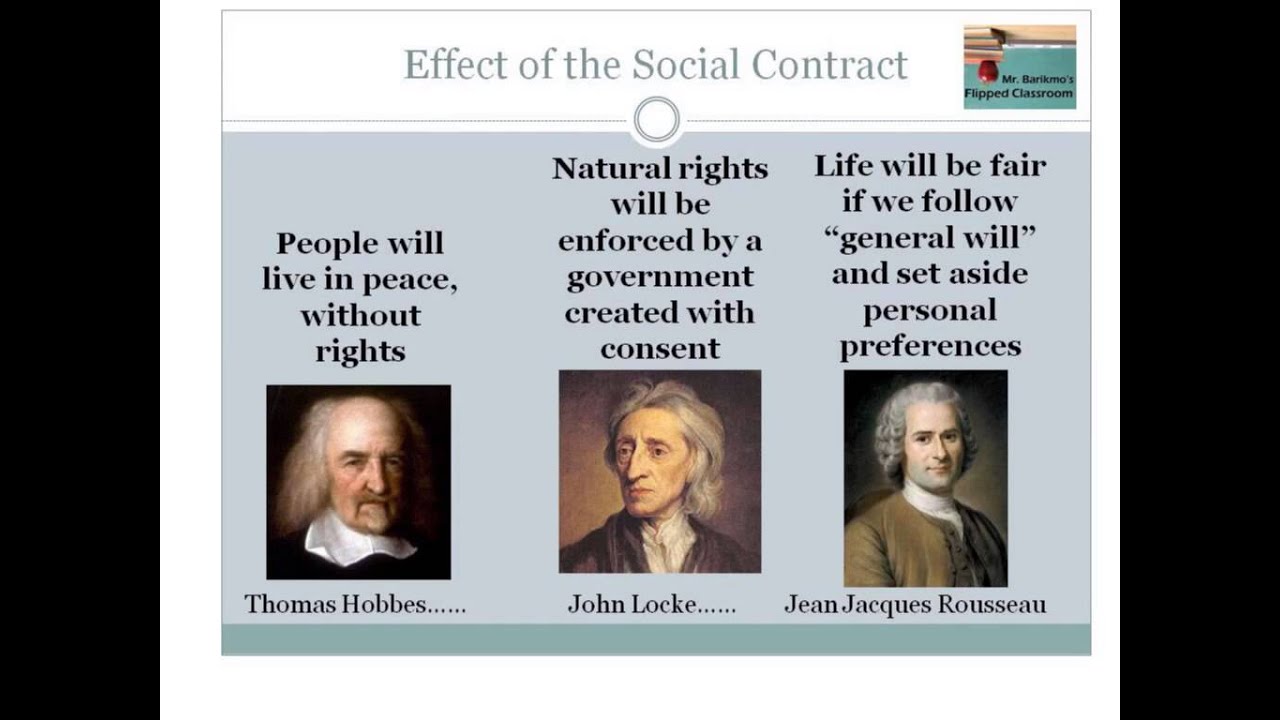
What is The Social Contract according to Hobbes and Locke?
Hobbes and Locke argued that the state had arisen out of a voluntary agreement, or social contract, made by individuals who recognised that only the establishment of sovereign power could safeguard them from the insecurity of the state of nature.
How does social contract theory explain how moral rules are justified?
According to the Social Contract Theory, we are obligated to obey the law because we each participate in a social system that promises more benefits than burdens. The benefits are the benefits of social living: We escape the state of nature and live in a society in which we are secure and enjoy basic rights.
Related searches to Which moral theory is defined as a theory based on the idea of a social contract or agreement among individuals for mutual advantage?
- contractarianism
- contractualism for dummies
- john locke social contract
- what is social contract theory
- social contract theory examples
- social contract theory of origin of state
- contractarianism ethics example situation
- who proposed the social contract theory
Information related to the topic Which moral theory is defined as a theory based on the idea of a social contract or agreement among individuals for mutual advantage?
Here are the search results of the thread Which moral theory is defined as a theory based on the idea of a social contract or agreement among individuals for mutual advantage? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which moral theory is defined as a theory based on the idea of a social contract or agreement among individuals for mutual advantage?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.