Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Depending on the receptor, the same neurotransmitter may have excitatory effects at some synapses while having inhibitory effects at others. For example, acetylcholine excites skeletal muscle cells but inhibits cardiac muscle cells.The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is excitatory at the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle, causing the muscle to contract.Dopamine. Dopamine has effects that are both excitatory and inhibitory. It is associated with reward mechanisms in the brain.
| Type | Excitatory in all cases except in the heart (inhibitory) |
|---|---|
| Functions | Regulates the sleep cycle, essential for muscle functioning |

Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle?
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is excitatory at the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle, causing the muscle to contract.
What neurotransmitter excites cardiac muscle?
| Type | Excitatory in all cases except in the heart (inhibitory) |
|---|---|
| Functions | Regulates the sleep cycle, essential for muscle functioning |
Skeletal Muscle , Cardiac Muscle and Smooth Muscle | Characteristics and Differences
Images related to the topicSkeletal Muscle , Cardiac Muscle and Smooth Muscle | Characteristics and Differences

Is dopamine excitatory or inhibitory?
Dopamine. Dopamine has effects that are both excitatory and inhibitory. It is associated with reward mechanisms in the brain.
What neurotransmitter is excitatory for skeletal muscles quizlet?
Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter that motor neurons use to control skeletal muscle contraction. ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft and binds to protein receptors in fiber membrane, increasing permeability to sodium and potassium ions.
Is GABA inhibitory or excitatory?
GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS and is opposed by the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate.
Is endorphin excitatory or inhibitory?
| Neurotransmitter | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamate | Excitatory | – brain’s main excitatory neurotransmitter – basis of learning and long-term memory |
| Endorphins | Inhibitory | – pain control – stress reduction – positive emotions |
Which neurotransmitter is inhibitory?
Inhibitory. Inhibitory neurotransmitters block or prevent the chemical message from being passed along any farther. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine and serotonin are examples of inhibitory neurotransmitters.
See some more details on the topic Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle? here:
Neurotransmitters and receptors (article) | Khan Academy
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is excitatory at the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle, causing the muscle to contract.
BIO TEST 4 – Chapter 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 Which…
Acetylcholine is also the principal neurotransmitter in all autonomic ganglia. In cardiac tissue, acetylcholine neurotransmission has an inhibitory effect, …
Synaptic Transmission at the Skeletal Neuromuscular …
4.1 Anatomy of the Neuromuscular Junction. The synapse for which most is known is the one formed between a spinal motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell.
Lecture 16 – Columbia University
(Signal to skeletal muscle is always +; a signal (+) means contract; no signal means relax.) … Ex: salivation — S inhibits; PS excites. b. Usually:.
Is glutamate excitatory or inhibitory?
In the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS), glutamate serves as the major excitatory neurotransmitter, whereas GABA and glycine serve as the major inhibitory neurotransmitters.
Is norepinephrine inhibitory or excitatory?
Some of the major excitatory neurotransmitters include epinephrine and norepinephrine. Inhibitory neurotransmitters: These types of neurotransmitters have inhibitory effects on the neuron; they decrease the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential.
Why is serotonin an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
Serotonin is of the inhibitory class of neurotransmitters as it does not stimulate the brain. Instead, it balances out the excessive excitatory neurotransmitter effects. A deficit in serotonin can be linked to depression, sadness, fatigue, suicidal thoughts, and anxiety.
What is the role of GABA?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in your central nervous system. GABA lessens the ability of a nerve cell to receive, create or send chemical messages to other nerve cells. GABA is known for producing a calming effect.
What does dopamine do to the heart?
What Is Dopamine? Dopamine (dopamine hydrochloride) is a catecholamine drug that acts by inotropic effect on the heart muscle (causes more intense contractions) that, in turn, can raise blood pressure.
Types of Muscles 💪 Comparison | Skeletal 💀 vs Cardiac ❤️ vs Smooth 🤮 muscles | Anatomy Physio
Images related to the topicTypes of Muscles 💪 Comparison | Skeletal 💀 vs Cardiac ❤️ vs Smooth 🤮 muscles | Anatomy Physio

Is the excitatory neurotransmitter used at neuromuscular junctions in skeletal muscle?
2.2. Glutamate Is the Neurotransmitter Operating at the Neuromuscular Junction in an Experimental Model of Spinal Cord Injury.
What is the role of acetylcholine in a skeletal muscle contraction?
When a motor nerve cell gets the proper signal from the nervous system, it releases acetylcholine into its synapses with muscle cells. There, acetylcholine opens receptors on the muscle cells, triggering the process of contraction.
What neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction with skeletal muscle?
The arrival of a nerve impulse at the neuromuscular junction causes thousands of tiny vesicles (pouches) filled with a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine to be released from the axon tip into the synapse.
Is NMDA excitatory or inhibitory?
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor is a ligand of glutamate, which is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the human brain.
Is GABA an inhibitor?
GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS) (1). GABA inhibitory neurotransmission is essential in normal brain function, in neuronal activity, information processing and plasticity, and network synchronization, and in disease.
Does GABA inhibit acetylcholine?
We investigated the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on neuromuscular transmission. GABA reduced the non-quantal and evoked quantal release of acetylcholine.
Is oxytocin inhibitory or excitatory?
More recent studies have shown that oxytocin suppresses inhibitory neurons (which reduce neural activity), thereby allowing excitatory cells to respond more strongly and reliably. As a result of improved signal transmission, oxytocin appears to overall enhance the brain’s response to socially relevant stimuli.
Is ACh excitatory or inhibitory?
ACh has excitatory actions at the neuromuscular junction, at autonomic ganglion, at certain glandular tissues and in the CNS. It has inhibitory actions at certain smooth muscles and at cardiac muscle.
Are endorphins inhibitory?
Functions. Endorphins play a major role in the body’s inhibitory response to pain. Research has demonstrated that meditation by trained individuals can be used to trigger endorphin release. Laughter may also stimulate endorphin production and elevate one’s pain threshold.
What are excitatory and inhibitory signals?
A neurotransmitter influences a neuron in one of three ways: excitatory, inhibitory or modulatory. An excitatory transmitter promotes the generation of an electrical signal called an action potential in the receiving neuron, while an inhibitory transmitter prevents it.
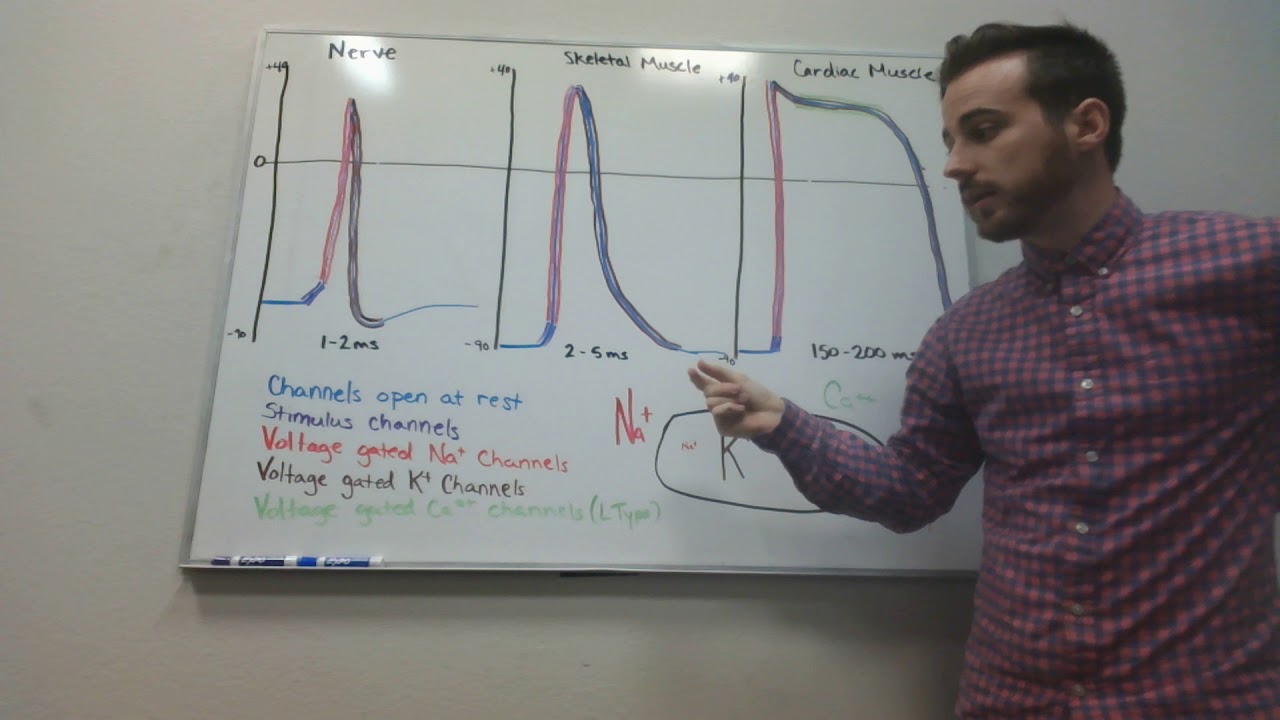
Nerve, Skeletal Muscle and Cardiac Muscle Action Potentials
Images related to the topicNerve, Skeletal Muscle and Cardiac Muscle Action Potentials
Which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain quizlet?
The main inhibitory transmitter in the cerebellum and forebrain is: GABA. In comparison with small molecule transmitters, neuropeptide transmitters: synthesize and transport slower than small molecule transmitters.
What is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
Glycine is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brainstem and spinal cord, where it participates in a variety of motor and sensory functions. Glycine is also present in the forebrain, where it has recently been shown to function as a coagonist at the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) subtype of glutamate receptor.
Related searches to Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle?
- place the following events of synaptic transmission at an adrenergic synapse in order
- what is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain
- what is the opposite of presynaptic inhibition?
- which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle
- which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle quizlet
- which of these does not contribute to the cessation of the signal in a synaptic transmission?
- which of these does not contribute to the cessation of the signal in a synaptic transmission
- what is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
- all of the following are typical characteristics of neurotransmitters except
- what type of neural circuit is best for producing a prolonged output
- an inhibitory local potential causes which of the following
- excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle
- what is the opposite of presynaptic inhibition
Information related to the topic Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle?
Here are the search results of the thread Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which neurotransmitter excites skeletal muscle and inhibits cardiac muscle?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.