Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Abstract. GABA, the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult brain, has a parallel inhibitory role in the immune system.Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) acts as the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS).Some of the major inhibitory neurotransmitters include serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Modulatory neurotransmitters: These neurotransmitters, often referred to as neuromodulators, are capable of affecting a larger number of neurons at the same time.

Table of Contents
What is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) acts as the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS).
Which neurotransmitter has inhibitory?
Some of the major inhibitory neurotransmitters include serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Modulatory neurotransmitters: These neurotransmitters, often referred to as neuromodulators, are capable of affecting a larger number of neurons at the same time.
THE NEUROTRANSMITTER SONG
Images related to the topicTHE NEUROTRANSMITTER SONG

Is GABA an excitatory or inhibitory?
GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult brain. Early in development, however, GABAergic synaptic transmission is excitatory and can exert widespread trophic effects. During the postnatal period, GABAergic responses undergo a switch from being excitatory to inhibitory.
Are GABA receptors inhibitory?
Because of this property of the GABA channel receptor, GABA is classified as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, as opposed to excitatory neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, which augment the nerve impulses in the neuron. GABA is the natural “key” to the GABA channel receptor’s “lock”.
Is GABA the main inhibitory neurotransmitter?
GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS) (1).
What makes GABA an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means it decreases the neuron’s action potential. When the action potential drops below a certain level, known as the threshold potential, the neuron will not generate action potentials and thus not excite nearby neurons.
Which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain quizlet?
The main inhibitory transmitter in the cerebellum and forebrain is: GABA. In comparison with small molecule transmitters, neuropeptide transmitters: synthesize and transport slower than small molecule transmitters.
See some more details on the topic Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter? here:
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) – Cleveland Clinic
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in your brain, meaning it slows your brain’s functions.
What are neurotransmitters? – Queensland Brain Institute
A neurotransmitter influences a neuron in one of three ways: excitatory, inhibitory or modulatory. An excitatory transmitter promotes the …
The Role of Neurotransmitters – Verywell Mind
Some of the major inhibitory neurotransmitters include serotonin and … This powerful hormone acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain.
Chemical Neurotransmitters – Hyperphysics
One mechanism for inhibition of the firing of the post-synaptic neuron is to … In the brain, acetylcholine functions as both a neurotransmitter and a …
Is acetylcholine inhibitory or excitatory?
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is excitatory at the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle, causing the muscle to contract. In contrast, it is inhibitory in the heart, where it slows heart rate.
Why is serotonin an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
Serotonin is of the inhibitory class of neurotransmitters as it does not stimulate the brain. Instead, it balances out the excessive excitatory neurotransmitter effects. A deficit in serotonin can be linked to depression, sadness, fatigue, suicidal thoughts, and anxiety.
Is Dopamine an excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitter?
Dopamine has effects that are both excitatory and inhibitory. It is associated with reward mechanisms in the brain.
Is glutamate an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
In the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS), glutamate serves as the major excitatory neurotransmitter, whereas GABA and glycine serve as the major inhibitory neurotransmitters.
Excitatory vs. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters (BIOS 041)
Images related to the topicExcitatory vs. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters (BIOS 041)

What are excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters?
An excitatory transmitter promotes the generation of an electrical signal called an action potential in the receiving neuron, while an inhibitory transmitter prevents it. Whether a neurotransmitter is excitatory or inhibitory depends on the receptor it binds to.
What is GABA and glutamate?
Glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) are the major neurotransmitters in the mammalian brain. Inhibitory GABA and excitatory glutamate work together to control many processes, including the brain’s overall level of excitation.
Is endorphins inhibitory or excitatory?
| Neurotransmitter | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamate | Excitatory | – brain’s main excitatory neurotransmitter – basis of learning and long-term memory |
| Endorphins | Inhibitory | – pain control – stress reduction – positive emotions |
What is the role of GABA in the brain?
GABA’s main job is to work as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means it blocks messages sent between the nerve cells and the brain or spinal cord. Specifically, GABA blocks certain nerve signals in the brain to reduce fear, anxiety, and stress.
What does GABA stand for?
Introduction. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid that serves as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain and a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord.
What is the role of glutamate?
Glutamate is an important neurotransmitter present in over 90% of all brain synapses and is a naturally occurring molecule that nerve cells use to send signals to other cells in the central nervous system. Glutamate plays an essential role in normal brain functioning and its levels must be tightly regulated.
How does GABA inhibit dopamine?
A separate study showed that GABA-AR activation inhibits dopamine release in the absence of nicotinic receptor activation which led to the proposal that GABA-A receptors may be present on the terminals of dopaminergic neurons (Lopes et al., 2019).
Does GABA inhibit acetylcholine?
We investigated the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on neuromuscular transmission. GABA reduced the non-quantal and evoked quantal release of acetylcholine.
Which of the following is an inhibitory neurotransmitter quizlet?
GABA is another common neurotransmitter, and it is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter. It is involved in anxiety, arousal, and sleep.
Excitatory vs. inhibitory effects of Neurotransmitters – VCE Psychology
Images related to the topicExcitatory vs. inhibitory effects of Neurotransmitters – VCE Psychology
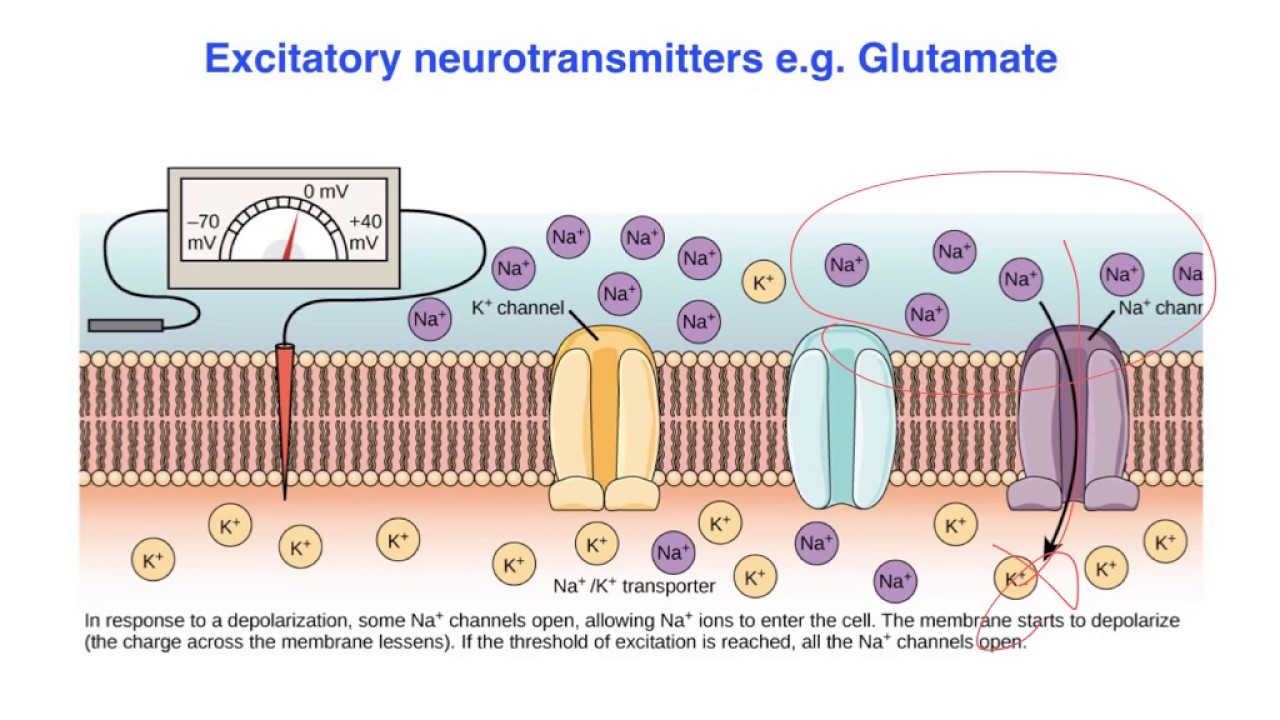
Which is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter quizlet?
- GABA. The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain is.
- Glutamate. The most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain is.
- Acetylcholine. The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is.
- Glutamate and Adenosine. …
- Glutamate. …
- GABA. …
- Dopamine. …
- Norepinephrine.
What does an inhibitory local potential cause?
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a kind of synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential.
Related searches to Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter?
- epilepsy and gaba
- What is GABA
- glutamate
- gaba b
- what is gaba
- Epilepsy and gaba
- Alcohol GABA
- GABA synthesis
- gaba synthesis
- alcohol gaba
- GABA receptor
- Neurotransmitters classification
- neurotransmitters classification
- gaba receptor
Information related to the topic Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter?
Here are the search results of the thread Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.
