Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market? The externality causes a difference between the private benefit from consumption and the social benefit.When negative externalities are present, it means the producer does not bear all costs, which results in excess production. With positive externalities, the buyer does not get all the benefits of the good, resulting in decreased production.Definition of Positive Externality: This occurs when the consumption or production of a good causes a benefit to a third party. For example: When you consume education you get a private benefit.

How a positive externality affects a competitive market?
When negative externalities are present, it means the producer does not bear all costs, which results in excess production. With positive externalities, the buyer does not get all the benefits of the good, resulting in decreased production.
Which of the following is an example of positive externality?
Definition of Positive Externality: This occurs when the consumption or production of a good causes a benefit to a third party. For example: When you consume education you get a private benefit.
Positive and Negative Externalities Defined Explained in One Minute: Education vs. Pollution?
Images related to the topicPositive and Negative Externalities Defined Explained in One Minute: Education vs. Pollution?

What happens when positive externalities are present in a market?
When a positive externality is present, the market produces less than the socially optimal quantity of the good or service, since there is a benefit to society that is not captured by the individual.
When positive externalities are present in a market quizlet?
When a positive externality is present in a market, the quantity consumed: is less than the socially optimal quantity. When private benefits equal social benefits, it means that: positive externalities are not present in the market.
What impact do positive externalities have on production quizlet?
This occurs when the production of a good causes a third party benefit. As a result there is a eternal benefit where the production of a good or service positively impacts a third party.
What is positive externality?
A positive externality exists when a benefit spills over to a third-party. Government can discourage negative externalities by taxing goods and services that generate spillover costs. Government can encourage positive externalities by subsidizing goods and services that generate spillover benefits.
What impact do positive externalities have on production?
Due to the positive externalities, the social marginal cost of production is less than the private marginal cost. It leads to the under-production of the good or service as the external benefit accruing to society is not taken into account by the market-driven processes of price determination.
See some more details on the topic Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market? here:
ECON 202 Module 8 Flashcards | Quizlet
Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market? The externality causes a difference between the private benefit from …
Deadweight losses – ECON 150: Microeconomics
A deadweight loss also exists when there is a positive externality because at the market quantity, the marginal social benefit is greater than the marginal …
Externalities, Equilibrium, and Market Failure – Investopedia
As implied by their names, positive externalities generally have a positive effect, while negative ones have the opposite impact. But how do these economic …
5.1 Externalities – Principles of Microeconomics – BCcampus …
Which of the following statements about external costs is TRUE? a) Economics uses the term “external cost” to describe a spillover effect from market activity …
What is an example of a positive externality quizlet?
benefit or cost experienced by someone who is not a producer or consumer of a good or service. Which of the following is an example of a positive externality? Mandatory motorcycle helmet laws are designed to reduce the severity of injuries resulting from motorcycle involvement in traffic accidents.
What is a positive externality Brainly?
A positive externality is a benefit that is enjoyed by a third-party as a result of an economic transaction. Third-parties include any individual, organisation, property owner, or resource that is indirectly affected.
Positive externalities | Consumer and producer surplus | Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Images related to the topicPositive externalities | Consumer and producer surplus | Microeconomics | Khan Academy

How do positive externalities affect demand curves?
A positive externality increases the social benefits of economic activity, so an adjusted demand/benefit curve would lie farther left on the diagram, reflecting a lower social price at each quantity.
What are externalities give an example of a positive externality and its impact on welfare of the people?
Externalities are the good and bad impact of an activity without paying the price or penalty for that. Example of a positive externality is when a beautiful garden maintained by Mr. X raises welfare of Mr.
How do you find the positive externality?
- The market surplus at Q1 is equal to total private benefits – total private costs, in this case b. (b+c) – (c)].
- The social surplus at Q1 is equal to total social benefits – total social costs, in this case a+b. …
- The market surplus at Q2 is equal to b-f. …
- The social surplus at Q2 is equal to a+b+d.
When a positive externality is present in a market the imposition of a government subsidy will?
The effect of a government subsidy in a market where a positive externality is present is: to increase surplus.
When a negative externality exists in a market for a good?
A negative externality exists when the production or consumption of a product results in a cost to a third party. Air and noise pollution are commonly cited examples of negative externalities.
When there is a negative externality the competitive output?
When there is a negative externality, the competitive output is greater than the economically efficient output level. is too low and equilibrium quantity is too high. the marginal social cost of producing a good or service exceeds the private cost.
What are positive externalities quizlet?
Positive Externality. a production or consumption activity that creates an external benefit. Marginal Private Cost. the cost of producing an additional unit of a good or service that is borne by the producer of that good or service. Marginal External Cost.
What is the difference between a positive and negative externality quizlet?
An externality is benefit or cost that affects someone who is not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service; Examples of a negative externality include pollution, while something such as a technology spillover is an example of a positive externality.
Positive Externalities of Production as a Market Failure
Images related to the topicPositive Externalities of Production as a Market Failure
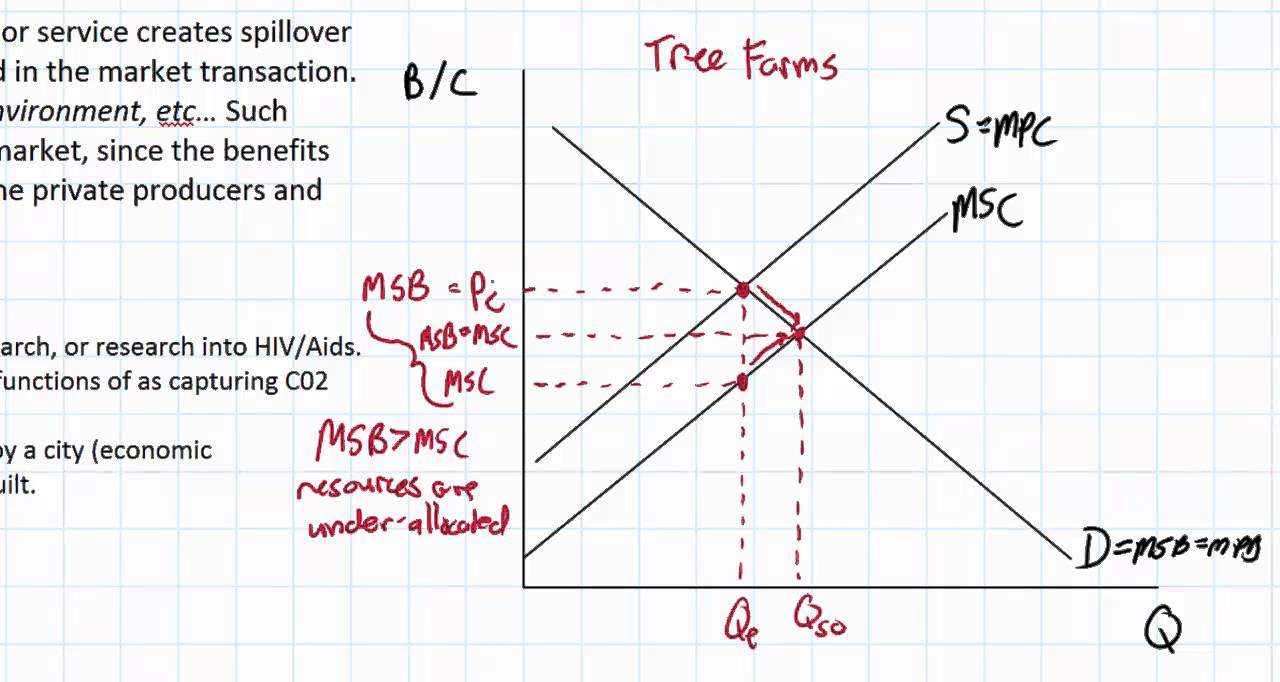
What makes an externality positive rather than negative?
Externalities are negative when the social costs outweigh the private costs. Some externalities are positive. Positive externalities occur when there is a positive gain on both the private level and social level. Research and development (R&D) conducted by a company can be a positive externality.
What is an externality and provide one example of a positive externality and one example of a negative externality?
For example, education is a positive externality of school because people learn and develop skills for careers and their lives. In comparison, negative externalities are a cost of production or consumption. For example, pollution is a negative externality that results from both producing and consuming certain products.
Related searches to Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market?
- if the social cost of producing a good or service exceeds the private cost
- when negative externalities are present in a market quizlet
- which of the following displays these two characteristics: rivalry and nonexcludability
- for a good with a positive externality the marginal social benefit curve will always be
- if the social cost of producing a good or service exceeds the private cost, ______.
- a negative externality occurs when
- when the social cost of producing a good is higher than the private cost, then
- in the case of a positive externality the entire demand curve lies
- which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market
- when the social benefit of producing a good is higher than the private benefit then
- which of the following displays these two characteristics rivalry and nonexcludability
- for a good with a positive externality, the marginal social benefit curve will always be
- when the social cost of producing a good is higher than the private cost then
Information related to the topic Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market?
Here are the search results of the thread Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.