Are you looking for an answer to the topic “Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
Taxes are a solution to negative externalities because, applied correctly, they can help internalize the negative social cost of an action. Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities? Private goods have two characteristics: they are excludable and rival in consumption.Remedies for Negative Externalities
One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxes. The goods and services commonly include tobacco, to change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol.A negative externality exists when the production or consumption of a product results in a cost to a third party. Air and noise pollution are commonly cited examples of negative externalities.
- Defining property rights. A strict definition of property rights can limit the influence of economic activities on unrelated parties. …
- Taxes. A government may impose taxes on goods or services that create externalities. …
- Subsidies.

What are negative externalities solutions?
Remedies for Negative Externalities
One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxes. The goods and services commonly include tobacco, to change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol.
What are the solutions to externalities?
- Defining property rights. A strict definition of property rights can limit the influence of economic activities on unrelated parties. …
- Taxes. A government may impose taxes on goods or services that create externalities. …
- Subsidies.
Positive and Negative Externalities Defined Explained in One Minute: Education vs. Pollution?
Images related to the topicPositive and Negative Externalities Defined Explained in One Minute: Education vs. Pollution?

Which of the following is a negative externality?
A negative externality exists when the production or consumption of a product results in a cost to a third party. Air and noise pollution are commonly cited examples of negative externalities.
Which of the following is not a solution to externalities?
Answer and Explanation: The correct answer is D Reward the production of these products through subsidies.
How can government reduce negative externalities?
Government can play a role in reducing negative externalities by taxing goods when their production generates spillover costs. This taxation effectively increases the cost of producing such goods.
Which of the following are solutions that governments use to counter overproduction caused by negative externalities?
Which of the following are solutions that governments use to counter overproduction caused by negative externalities? Solar panels provide a benefit those who buy them by reducing their electricity bill, but they also benefit society as a whole by reducing pollution and resource consumption.
What is positive and negative externalities?
Positive externalities refer to the benefits enjoyed by people outside the marketplace due to a firm’s actions but for which they do not pay any amount. On the other hand, negative externalities are the negative consequences faced by outsiders due a firm’s actions for which it is not charged anything by the market.
See some more details on the topic Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities? here:
Chapter 7 Concept Check Flashcards | Quizlet
Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities? A – taxes. B – price ceilings. C – tax deductions for charitable contributions
Externality – Definition, Categories, Causes and Solutions
An externality is a cost or benefit of an economic activity experienced by an unrelated third party. … Possible solutions include the following: …
Externality Definition & Examples – Investopedia
There are solutions that exist to overcome the negative effects of externalities. These can include those from both the public and private sectors.
Externalities – The Economic Lowdown Podcast Series
These spillover costs and benefits are called externalities. A negative externality occurs when a cost spills over. A positive externality occurs when a …
What are the 4 types of externalities?
There are four main types of externalities: positive production, positive consumption, negative production, and negative consumption.
Which of the following is an example of externalities?
Light pollution is an example of an externality because the consumption of street lighting has an effect on bystanders that is not compensated for by the consumers of the lighting.
What is an example of a negative externality quizlet?
The cost of pollution due to industrial production is an example of a negative externality of production. When people smoke in public places, third parties are victim to second hand smoke. In addition there is an increase in smoking-related diseases which result in higher health care costs that are a burden to society.
Micro 6.3 Negative Externalities: Econ Concepts in 60 Seconds-Externality
Images related to the topicMicro 6.3 Negative Externalities: Econ Concepts in 60 Seconds-Externality
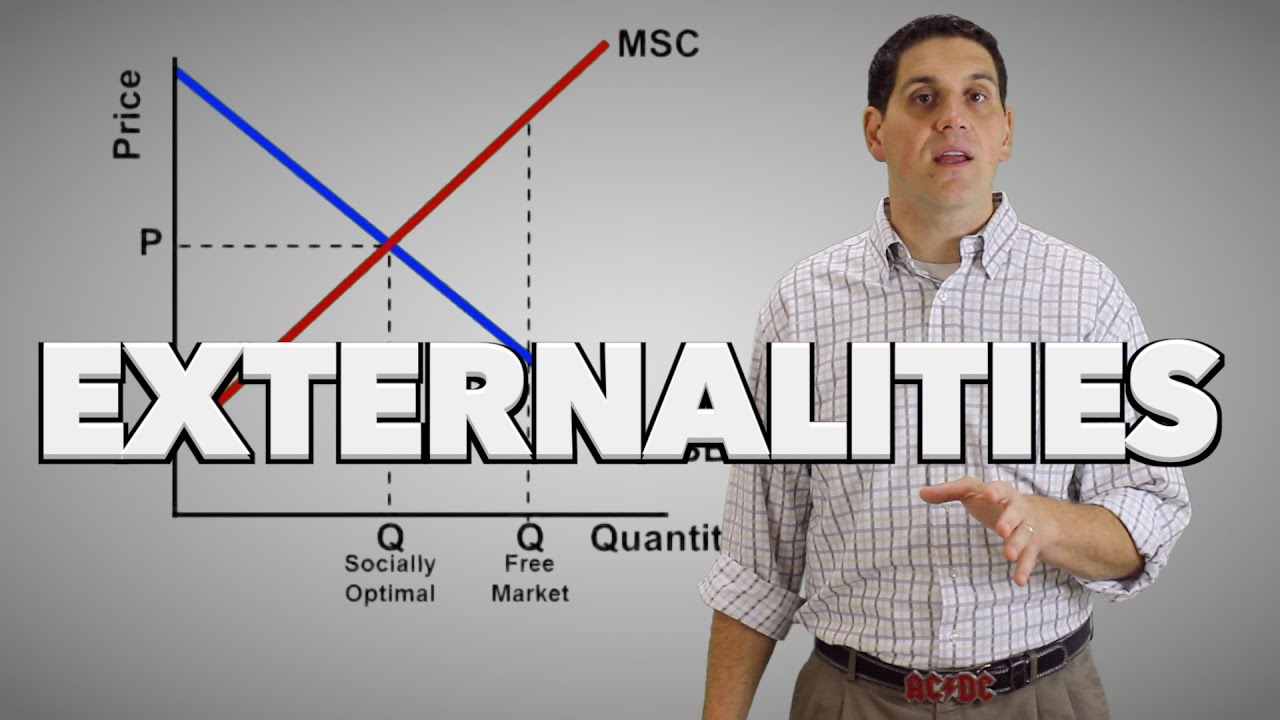
When negative externalities are present in a market what will result?
When negative externalities are present, it means the producer does not bear all costs, which results in excess production. With positive externalities, the buyer does not get all the benefits of the good, resulting in decreased production.
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality additional social cost )?
b. utility. Which of the following is an example of a negative externality (additional social cost)? It is the custom for paper mills located alongside the Layzee River to discharge waste products into the river.
How does Coase Theorem solve negative externalities?
Coase theorem seeks to solve negative externalities by assigning well defined property rights. In turn, two parties can negotiate based on the cost of that externality and the price they are willing to accept in order to reduce such.
Which of the following is a benefit of internalizing a negative externality?
Internalizing a negative externality will cause an industry to increase the quantity it supplies to the market and decrease the price of the good produced.
What are the three main methods to deal with environmental negative externalities?
- Command and Control. This is exactly what it sounds like: governments issue commands in order to control the amount of pollution. …
- Pigouvian taxes. …
- Coasian permit trading.
What causes a negative externality?
Negative externalities occur when the consumption or production of a good causes a harmful effect to a third party.
What two types of policies can the government use to correct negative externalities?
The government can respond to externalities in two ways. The government can use command-and-control policies to regulate behavior directly. Alternatively, it can implement market-based policies such as taxes and subsidies to incentivize private decision makers to change their own behavior.
How can government limit a negative externality How can it spread a positive one?
The government can limit a negative externality by taxing or fining the causer of the externality, and it can spread a positive one by subsidizing the cost of an economic activity that is in the public interest.
Which of the following is true when there are negative externalities associated with the production of a good?
Which of the following is true when there are negative externalities associated with the production of a good? The market will adjust automatically to equate marginal social costs and marginal social benefits.
Negative externalities | Consumer and producer surplus | Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Images related to the topicNegative externalities | Consumer and producer surplus | Microeconomics | Khan Academy

How does the government correct positive externalities?
The government can correct a positive externality by offering buyers per-unit subsidies (or incentives) to increase demand so that the MSB=MSC. Another policy option is to offer sellers per-unit subsidies to encourage more production so the MSB=MSC.
What do you mean by externalities give two examples of positive and negative externalities each?
For example, a factory that pollutes the environment creates a cost to society, but those costs are not priced into the final good it produces. These can come in the form of ‘positive externalities’ that create a benefit to a third party, or, ‘negative externalities’, that create a cost to a third party.
Related searches to Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities?
- negative externalities
- externality la gi
- What is externalities
- Externality examples
- positive and negative externalities
- which of the following activities create positive externalities
- externality examples
- negative externalities examples
- Positive and negative externalities
- which of the following is not a solution to the problem of negative externalities due to pollution
- Externality là gì
- what is externalities
- Negative externalities
- which of the following is a solution to negative externalities
- Negative externalities examples
- which of the following is incentivized by private property rights
- which of the following is not a solution to correct for negative externalities
Information related to the topic Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities?
Here are the search results of the thread Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic Which of the following is a solution to negative externalities?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.