Are you looking for an answer to the topic “What is genomic imprinting give an example?“? We answer all your questions at the website Ecurrencythailand.com in category: +15 Marketing Blog Post Ideas And Topics For You. You will find the answer right below.
(For example, the maternal genes that control insulin production will be imprinted in a male but will be expressed in any of the male’s offspring that inherit these genes.) The nature of imprinting must therefore be epigenetic rather than DNA sequence dependent.These include Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes (the first examples of genomic imprinting in humans), Silver-Russell syndrome, Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome, Albright hereditary osteodystrophy and uniparental disomy 14 [1, 2].Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that results in monoallelic gene expression according to parental origin. It has long been established that imprinted genes have major effects on development and placental biology before birth.
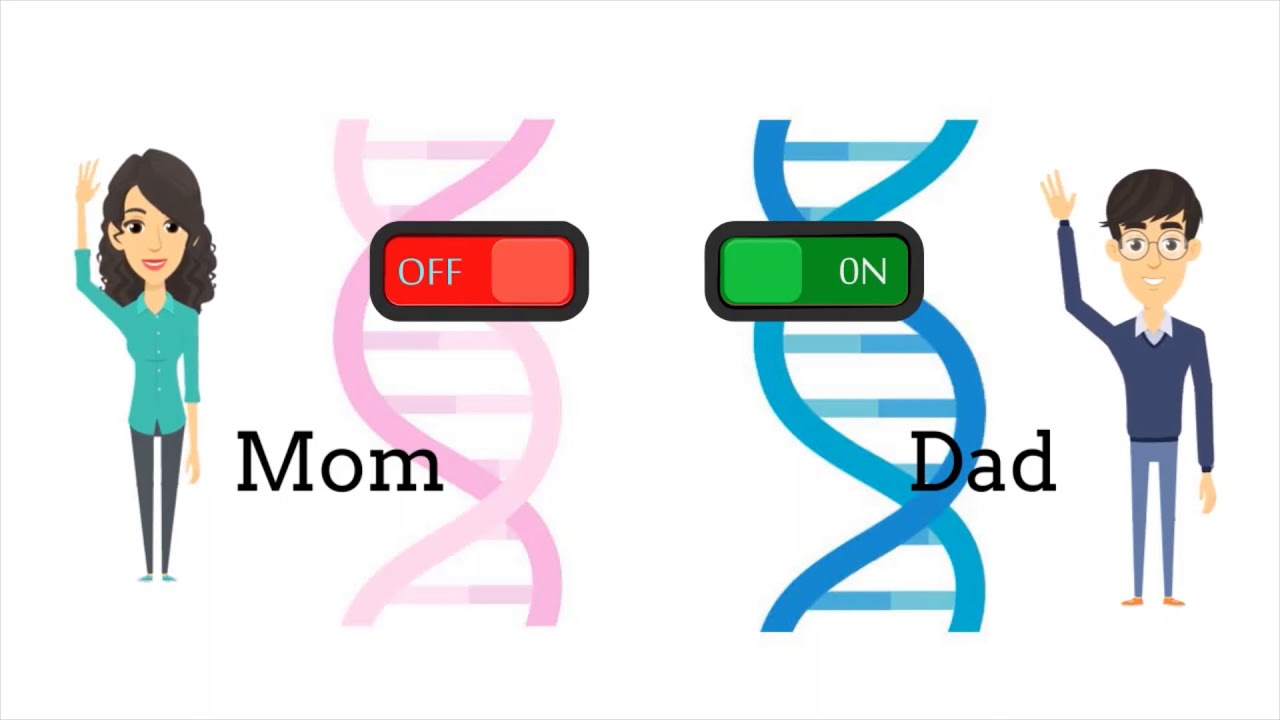
What is genomic imprinting example?
These include Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes (the first examples of genomic imprinting in humans), Silver-Russell syndrome, Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome, Albright hereditary osteodystrophy and uniparental disomy 14 [1, 2].
What is genomic imprinting in biology?
Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that results in monoallelic gene expression according to parental origin. It has long been established that imprinted genes have major effects on development and placental biology before birth.
Genomic Imprinting
Images related to the topicGenomic Imprinting

What is genomic imprinting and what is its significance?
Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic gene-marking phenomenon that occurs in the germline, whereby genes are expressed from only one of the two parental copies in embryos and adults. Imprinting is essential for normal mammalian development and its disruption can cause various developmental defects and diseases.
How does genomic imprinting occur?
Genomic imprinting occurs when two alleles at a locus are not functionally equivalent and is considered the primary epigenetic phenomenon that can lead to the manifestation of parent-of-origin effects [4].
Which two disease are an example of genomic imprinting?
Appropriate imprinting of certain genes is important for normal development. Human diseases involving genomic imprinting include Angelman syndrome, Prader–Willi syndrome and male infertility.
What is an example of imprinting in humans?
For example, if someone decided to hatch eggs and then return them to their mother after a few days, they will have imprinted on the person and not the mother. Filial imprinting usually happens just after an animal is born when they see their parent.
What is genomic imprinting quizlet?
genomic imprinting. a phenomenon in which expression of an allele in offspring depends on whether the allele is inherited from the male or female parent.
See some more details on the topic What is genomic imprinting give an example? here:
Genetic Imprinting – National Human Genome Research Institute
Genomic imprinting is the process by which only one copy of a gene in an individual (either from their mother or their father) is expressed, while the other …
What are genomic imprinting and uniparental disomy?
In genes that undergo genomic imprinting, the parent of origin is often marked, or “stamped,” on the gene during the formation of egg and sperm …
Genomic Imprinting and Patterns of Disease Inheritance – Nature
Some examples of genetic diseases related to errors in the imprinting of specific genes and chromosomal regions include Prader-Willi syndrome, Angelman syndrome …
Genomic imprinting disorders in humans: a mini-review – NCBI
These include Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes (the first examples of genomic imprinting in humans), …
How do you test for genomic imprinting?
Genomic imprinting is manifested as differential allelic expression (DAE) depending on the parent-of-origin. The most direct way to identify imprinted genes is to directly score the DAE in a context where one can identify which parent transmitted each allele.
Which genes are imprinted?
Two major clusters of imprinted genes have been identified in humans, one on the short (p) arm of chromosome 11 (at position 11p15) and another on the long (q) arm of chromosome 15 (in the region 15q11 to 15q13).
What is the significance of imprinting?
Imprinting is potentially a mechanism to balance parental resource allocation and it plays an important role in growth. The placenta, as the interface between mother and fetus, is central to prenatal growth control.
What does imprinting mean in science terms?
imprinting, in psychobiology, a form of learning in which a very young animal fixes its attention on the first object with which it has visual, auditory, or tactile experience and thereafter follows that object.
Genomic Imprinting
Images related to the topicGenomic Imprinting
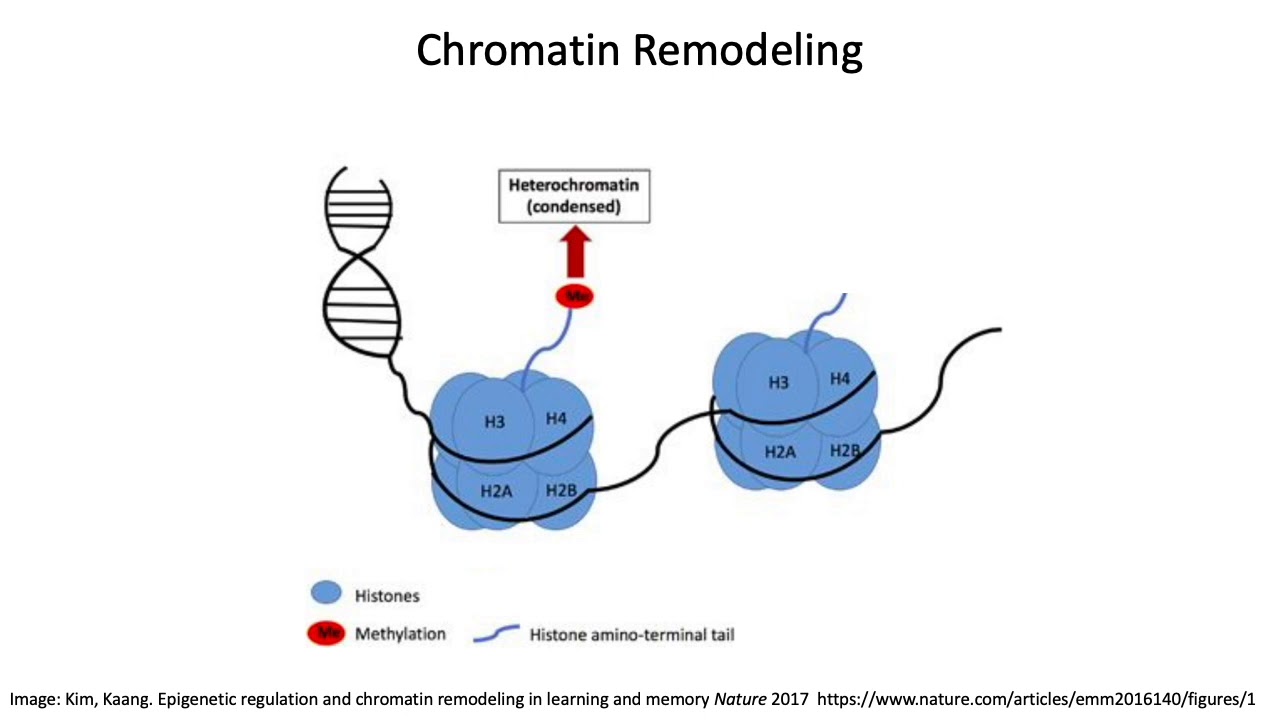
What is the role of imprinting in human genetic disorders?
Imprinted genes are intricately involved in fetal and behavioral development. Consequently, abnormal expression of these genes results in numerous human genetic disorders including carcinogenesis.
When was genomic imprinting discovered?
This process was first described in 1984, when two laboratories discovered a mark, or “imprint,” that differentiates between certain genes on the maternal and paternal chromosomes and results in the expression of only one copy of those genes in the offspring.
What genomic means?
Listen to pronunciation. (jeh-NOH-mix) The study of the complete set of DNA (including all of its genes) in a person or other organism. Almost every cell in a person’s body contains a complete copy of the genome.
Which disease is associated with imprinting?
Over the years, a number of diseases and disorders have been linked to this sort of genetic imprinting, including Angelman syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.
How is Angelman syndrome an example of epigenetics?
One of the epigenetic research models in Angelman syndrome (AS). This neurologic disorder associated with improper central nervous system development and function, together with Prader-Willi syndrome are caused by the defects of epigenetic regulation.
Which gene is imprinted in Prader-Willi?
The Imprinted in Prader-Willi Syndrome (IPW) gene is a lncRNA known to modulate another evolutionarily distinct imprinted gene cluster at the human chromosomal region 14q32 expressed only from maternally inherited alleles (137).
Which of the following is an example of imprinting quizlet?
Piaget’s cognitive development theory. Which of the following is an example of imprinting? A duckling demonstrates attachment to a bouncing ball. an early and secure attachment to her own parents.
What is imprinting state the importance of imprinting with suitable examples?
Imprinting is a form of learning in which an animal gains its sense of species identification. Birds do not automatically know what they are when they hatch – they visually imprint on their parents during a critical period of development. After imprinting, they will identify with that species for life.
Do dogs imprint?
Dogs, like humans, are not born knowing everything; they have to be taught. This process of learning is called imprinting, and many animals do it.
How does methylation relate to genomic imprinting quizlet?
How does methylation relate to genomic imprinting? Methylation patterns maintained chemically in organic specialized tissues allow for permanent regulation of either maternal or paternal allele expression of certain genes at the start of development in mammals.
Genomic Imprinting
Images related to the topicGenomic Imprinting

What is epigenetics quizlet?
Epigenetics is the study of changes in individuals, and individual cells, caused by changes in gene expression that are unrelated to changes in the genetic code itself.
How many autosomal chromosomes are present in human cells?
In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differ between males and females.
Related searches to What is genomic imprinting give an example?
- genomic imprinting khan academy
- what is genomic imprinting quizlet
- what is genomic imprinting and how is it maintained
- genomic imprinting mechanism
- what is the process of genomic imprinting
- genomic imprinting pdf
- is genomic imprinting normal
- explain genomic imprinting
- genomic imprinting examples
- paternal imprinting example
- genomic imprinting ppt
- what is genomic imprinting and how is it maintained give an example
- genomic imprinting definition
- what causes genomic imprinting
- maternal imprinting
- what is an example of genomic imprinting
Information related to the topic What is genomic imprinting give an example?
Here are the search results of the thread What is genomic imprinting give an example? from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic What is genomic imprinting give an example?. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.